
Apiaceae or Umbelliferae is a family of mostly aromatic flowering plants named after the type genus Apium and commonly known as the celery, carrot or parsley family, or simply as umbellifers. It is the 16th-largest family of flowering plants, with more than 3,800 species in about 446 genera, including such well-known and economically important plants as ajwain, angelica, anise, asafoetida, caraway, carrot, celery, chervil, coriander, cumin, dill, fennel, lovage, cow parsley, parsley, parsnip and sea holly, as well as silphium, a plant whose identity is unclear and which may be extinct.

Caraway, also known as meridian fennel and Persian cumin, is a biennial plant in the family Apiaceae, native to western Asia, Europe, and North Africa.

Persicaria maculosa is an annual plant in the buckwheat family, Polygonaceae. Common names include lady's thumb, spotted lady's thumb, Jesusplant, and redshank. It is widespread across Eurasia from Iceland south to Portugal and east to Japan. It is also present as an introduced and invasive species in North America, where it was first noted in the Great Lakes region in 1843 and has now spread through most of the continent.

Smyrnium olusatrum, common name alexanders is an edible flowering plant of the family Apiaceae (Umbelliferae), which grows on waste ground and in hedges around the Mediterranean and Atlantic coastal regions of Europe. It was formerly widely grown as a pot herb, but is now appreciated mostly by foragers.

Scandix pecten-veneris is a species of edible plant belonging to the family Apiaceae. It is native to Eurasia, but is known to occur elsewhere. It is named for its long fruit, which has a thickened body up to 1.5 centimeters long and a beak which can measure up to 7 centimeters long and is lined with comblike bristles.

Chaerophyllum temulum, the rough chervil, is a species of flowering plant in the family Apiaceae.

Peucedanum is a genus of flowering plant in the carrot family, Apiaceae.

Epilobium palustre is a species of willowherb known by the common name marsh willowherb. This plant has a circumboreal distribution, and can be found farther south in mountainous areas.

Selinum carvifolia is a flowering plant of the genus Selinum in the family Apiaceae. The specific name carvifolia signifies 'having leaves resembling those of Caraway'. It is a plant of fens and damp meadows, growing in most of Europe, with the exception of much of the Mediterranean region, eastwards to Central Asia. Its common name in English is Cambridge milk parsley, because it is confined, in the UK, to the county of Cambridgeshire and closely resembles milk parsley, an umbellifer of another genus, but found in similar habitats. The two plants are not only similar in appearance, but also grow in similar moist habitats, although they may be told apart in the following manner: P. palustre has hollow, often purplish stems, pinnatifid leaf lobes and deflexed bracteoles; while S. carvifolia has solid, greenish stems, entire or sometimes lobed leaf-lobes and erecto-patent bracteoles. Also, when the two plants are in fruit, another difference becomes apparent: the three dorsal ridges on the fruit of S. carvifolia are winged, while those on the fruit of P. palustre are not. Yet a further difference lies in the respective leaflets of the plants : those of Peucedanum palustre are blunt and pale at the tip, while those of Selinum carvifolia are sharply pointed and of a darker green. S. carvifolia used also to occur in the English counties of Nottinghamshire and Lincolnshire but is now extinct in both. Growing in only three small Cambridgeshire fens, it is one of England's rarest umbellifers. It is naturalized in the United States, where it is known by the common name little-leaf angelica.

Oenanthe pimpinelloides is a species of flowering plant in the family Apiaceae known by the common name corky-fruited water-dropwort. It is a plant of damp or dry grassland and more ruderal tall herb communities.

Bartsia alpina is a species of perennial flowering plant, known by the common name alpine bartsia or velvetbells. It is found in the mountainous regions of Europe and also occurs in Iceland, Greenland and north‐eastern Canada.

Peucedanum verticillare, common name giant hog fennel or milk parsley, is a herbaceous plant in the genus Peucedanum of the family Apiaceae.

Peucedanum officinale is a herbaceous perennial plant in the family Apiaceae found mainly in Central Europe and Southern Europe. It is also native to the UK, where it has the common names hog's fennel and sulphurweed, but it is a rare plant there, occurring only in certain localities in the counties of Essex and Kent. It was formerly also found near the town of Shoreham-by-Sea in the county of West Sussex, but has long been extinct there.
Selinum is a Eurasiatic genus of flowering plants in the parsley family Apiaceae.
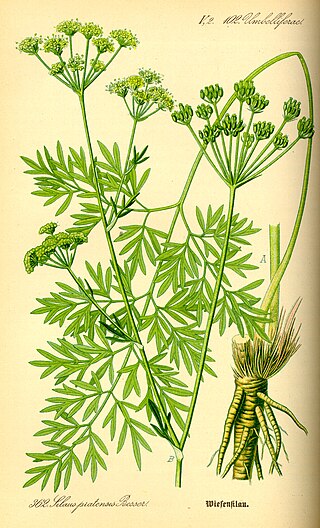
Silaum silaus, commonly known as pepper-saxifrage, is a perennial plant in the family Apiaceae (Umbelliferae) found across south-eastern, central, and western Europe, including the British Isles. It grows in damp grasslands on neutral soils.
Milk parsley is a common name for several plants and may refer to:

Alchemilla arvensis, known as parsley-piert, is a sprawling, downy plant common all over the British Isles where It grows on arable fields and bare wastelands, particularly in dry sites. The short-stalked leaves have three segments each lobed at the tip. Flowers April–September. The tiny green flower has four sepals and no petals, the fruit is oval pointed. Stipules form a leaf-like cup, enclosing the flower. The name of parsley piert has nothing to do with parsley. It is a corruption of the French perce-pierre, meaning 'stone-piercer' and was given to the plant because of its habit of growing in shallow, stony soil and emerging between stones. As in the case of saxifrage it was wrongly assumed that the plant could pierce stones; and it was thought that a medicine made of parsley piert would break up stones in the bladder and kidneys. Old folk-names for the plant include 'colicwort' and 'bowel-hive-grass', showing that it was also used for intestinal ailments.

Peucedanum japonicum, also known as coastal hog fennel, is a species of Peucedanum, a genus rich in medicinal species belonging to the parsley family, Apiaceae.
Fennel is a species of plant, Foeniculum vulgare

Oenanthe lachenalii, parsley water-dropwort, is a flowering plant in the carrot family, which is native to Europe and parts of North Africa. It is a declining plant of coastal wetlands.
















