Amphibians are ectothermic, anamniotic, four-limbed vertebrate animals that constitute the class Amphibia. In its broadest sense it is a paraphyletic group encompassing all tetrapods, excluding the amniotes. All extant (living) amphibians belong to the monophyletic subclass Lissamphibia, with three living orders: Anura (frogs), Urodela (salamanders), and Gymnophiona (caecilians). Evolved to be mostly semiaquatic, amphibians have adapted to inhabit a wide variety of habitats, with most species living in freshwater, wetland or terrestrial ecosystems. Their life cycle typically starts out as aquatic larvae with gills known as tadpoles, but some species have developed behavioural adaptations to bypass this.

Salamanders are a group of amphibians typically characterized by their lizard-like appearance, with slender bodies, blunt snouts, short limbs projecting at right angles to the body, and the presence of a tail in both larvae and adults. All ten extant salamander families are grouped together under the order Urodela from the group Caudata. Salamander diversity is highest in eastern North America, especially in the Appalachian Mountains; most species are found in the Holarctic realm, with some species present in the Neotropical realm.

The Baw Baw National Park is a national park located on the boundary between the Victorian Alps and Gippsland regions of Victoria, Australia. The 13,530-hectare (33,400-acre) national park is situated approximately 120 kilometres (75 mi) east of Melbourne and 50 kilometres (31 mi) north of the Latrobe Valley. The park contains the forest covered Baw-Baw Plateau and surrounds the Mount Baw Baw Alpine Resort.

The Blanding's turtle is a semi-aquatic turtle of the family Emydidae. This species is native to central and eastern parts of Canada and the United States. It is considered to be an endangered species throughout much of its range. The Blanding's turtle is of interest in longevity research, as it shows few or no common signs of aging and is physically active and capable of reproduction into eight or nine decades of life.

The Mexican burrowing toad is the single living representative of the family Rhinophrynidae. It is a unique species in its taxonomy and morphology, with special adaptations to assist them in digging burrows where they spend most of their time. These adaptations include a small pointed snout and face, keratinized structures and a lack of webbing on front limbs, and specialized tongue morphology to assist in feeding on ants and termites underground. The body is nearly equal in width and length. It is a dark brown to black color with a red-orange stripe on its back along with splotches of color on its body. The generic name Rhinophrynus means 'nose-toad', from rhino- (ῥῑνο-), the combining form of the Ancient Greek rhis and phrunē.

The Scaphiopodidae are a family of American spadefoot toads, which are native to North America. The family is small, comprising only seven different species.

The Baw Baw frog is a critically endangered species of Australian frog as categorised on the IUCN Red List and listed under the Flora and Fauna Guarantee Act (1988), endemic to Baw Baw National Park. It has suffered a decline in population, mostly due to infection caused by chytrid fungus. Zoos Victoria has undertaken a breeding program to ensure survival of the species which commenced in 2010, and in October 2018 successfully collected the first eggs laid in captivity.

The mountain yellow-legged frog, also known as the southern mountain yellow-legged frog, is a species of true frog endemic to California in the United States. It occurs in the San Jacinto Mountains, San Bernardino Mountains, and San Gabriel Mountains in Southern California and the Southern Sierra Nevada. It is a federally listed endangered species, separated into two distinct population segments (DPS): a northern DPS, listed endangered in 2014, and a southern DPS that was listed endangered in 2002.

The foothill yellow-legged frog is a small-sized frog from the genus Rana in the family Ranidae. This species was historically found in the Coast Ranges from northern Oregon, through California, and into Baja California, Mexico as well as in the foothills of the Sierra Nevada and southern Cascade Range in California. The foothill yellow-legged frog is a Federal Species of Concern and California State Endangered. A federal rule to list four out of six extant distinct population segments (DPS) under the Endangered Species Act was proposed in December 2021.

Rheobatrachus, whose members are known as the gastric-brooding frogs or platypus frogs, is a genus of extinct ground-dwelling frogs native to Queensland in eastern Australia. The genus consisted of only two species, the southern and northern gastric-brooding frogs, both of which became extinct in the mid-1980s. The genus is unique because it contains the only two known frog species that incubated the prejuvenile stages of their offspring in the stomach of the mother.
Nectophrynoides wendyae, also known as the Uzungwe Scarp tree toad or Wendy's forest toad, is a terrestrial toad in the family Bufonidae. It is endemic to Tanzania and is only known from a single valley in the Udzungwa Mountains. The specific name wendyae honours Wendy Clarke, the describer's wife.

Amphibians of Australia are limited to members of the order Anura, commonly known as frogs. All Australian frogs are in the suborder Neobatrachia, also known as the modern frogs, which make up the largest proportion of extant frog species. About 230 of the 5,280 species of frog are native to Australia with 93% of them endemic. Compared with other continents, species diversity is low, and may be related to the climate of most of the Australian continent. There are two known invasive amphibians, the cane toad and the smooth newt.

Wallace's flying frog, also known as the gliding frog or the Abah River flying frog, is a moss frog found at least from the Malay Peninsula into western Indonesia, and is present in Borneo and Sumatra. It is named for the biologist, Alfred R. Wallace, who collected the first known specimen.

The Betic midwife toad or Sapo Partero Bético is a species of frog in the family Alytidae. It is endemic to mountainous in south eastern Spain. Its natural habitats are temperate forests, freshwater marshes, intermittent freshwater marshes, pastureland, ponds, and aquaculture ponds. It is threatened by habitat loss.
The Bale Mountains tree frog is a species of frogs in the family Brevicipitidae. It is the only species in the monotypic genus Balebreviceps and endemic to the Bale Mountains of Ethiopia. Its natural habitats are tree heath woodland near the timberline as well as partly cleared mixed forest further down. Despite its entire range being within the Bale Mountains National Park, it is threatened by habitat loss and deterioration (deforestation) caused by cattle grazing, firewood collection, fencing, and settlement development.

Bilbo's rain frog is an amphibian species in the family Brevicipitidae, endemic to South Africa. The frog was named after Bilbo Baggins, the main character from The Hobbit by J.R.R Tolkien. The frog was named as such because the scientist who discovered it used to read the novel to his children. Its natural habitats are temperate grasslands and edges of wood plantations, wherein it spends most of its time in its burrow. The species is threatened by construction, maintenance of roads, silviculture, general habitat degradation/habitat loss, and by road traffic. As a result, it is listed as Near Threatened in the IUCN Red List of Threatened Species.

The cape rain frog or giant rain frog is a species of frog in the family Brevicipitidae. Adults grow up to 45 mm in length. It was the first African frog species to be scientifically described by Carl Linnaeus in 1758, under the name Rana gibbosa. It is the most common and largest of rain frogs. The name "rain frog" that is applied to the genus refers to a belief that these frogs bring rain.

Ericabatrachus is a genus of frogs in the family Petropedetidae endemic to the Bale Mountains in Ethiopia. It is monotypic, being represented by the single species Ericabatrachus baleensis, commonly known as the Bale Mountains frog.

Odorrana graminea, the large odorous frog, inhabits fast-flowing streams in elevated mountainous regions of Southern China and Northern Indochina. It is one of 56 species in the genus Odorrana. Male O. graminea are noted for their ultrasonic call characteristics and are one of three frog species able to detect ultrasonic frequencies, likely evolved to facilitate communication amidst noisy streams and waterfalls. Studies on O. graminea courtship vocalizations suggest female preference for increased proportion of nonlinear vocal phenomena (NLP).
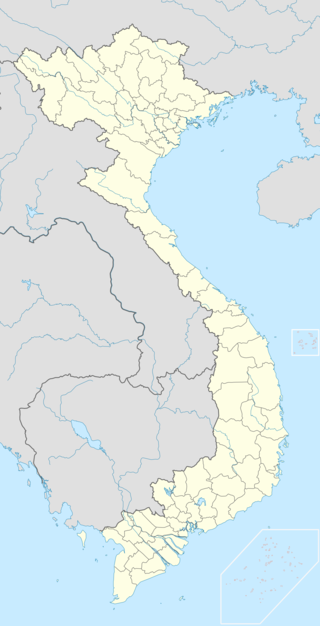
Vampyrius vampyrus is a medium-sized species of flying frogs endemic to Vietnam. It is found in southern Vietnam, and is not known to be found in other places globally. It Is in the kingdom Animalia, phylum Chordata, and class Amphibia. Along with this, it is in the order Anura, family Rhacophoridae, and it is the only member of the genus Vampyrus. It is also known as the vampire tree frog or the vampire flying frog because of the presence of a pair of fang-like hooks in the mouth of the tadpoles.