Related Research Articles

Pilbara Iron is a wholly owned subsidiary of the multinational Rio Tinto Group, that manages assets for Hamersley Iron Pty Ltd, a wholly owned subsidiary of Rio Tinto, and Robe River Iron Associates, an unincorporated joint venture between Rio and three Japanese steel companies Mitsui Iron Ore Development P/L (33%), Nippon Steel Australia P/L (10.5%) and Sumitomo Metal Australia P/L (3.5%).

Karijini National Park is an Australian national park centred in the Hamersley Ranges of the Pilbara region in the northwestern section of Western Australia. The park is located north of the Tropic of Capricorn, 1,055 kilometres (656 mi) from the state's capital city, Perth. Formerly known as Hamersley Range National Park, the park was officially renamed in 1991.
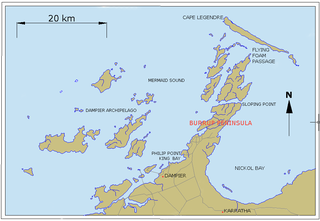
Dampier is a major industrial port in the Pilbara region in the northwest of Western Australia. It is located near the city of Karratha and Port Walcott.
The Pilbara is a large, dry, thinly populated region in the north of Western Australia. It is known for its Aboriginal peoples; its ancient landscapes; the red earth; and its vast mineral deposits, in particular iron ore. It is also a global biodiversity hotspot for subterranean fauna.

GWR 4073 "Castle" Class No. 4079 Pendennis Castle is a 4-6-0 steam locomotive built in 1924 for the Great Western Railway (GWR) at Swindon Works to a design of Charles Collett. It was employed on long-distance express passenger trains on the GWR and its successor, British Railways' Western Region.

Tom Price is a mining town in the Pilbara region of Western Australia. It is located inland, at the edge of the Hamersley Range. Tom Price is the highest town above sea level in Western Australia, and is consequently dubbed "Top Town in WA".

Newman, originally named Mount Newman until 1981, is a town in the Pilbara region of Western Australia. It is located about 1,186 kilometres (737 mi) north of Perth, and 9 kilometres (5.6 mi) north of the Tropic of Capricorn. It can be reached by the Great Northern Highway. Newman is a modern mining town, with homes contrasting with the surrounding reddish desert. As of the 2021 census, Newman had a population of 6,456. The Hickman Crater, a meteorite impact crater discovered in 2007, is 35 kilometres (22 mi) north of Newman.
Karratha is a city in the Pilbara region of Western Australia, adjoining the port of Dampier. It is located in the traditional lands and waters of the Ngarluma people, for whom it has been Ngurra (home/Country) for tens of thousands of years. It was established in 1968 to accommodate the processing and exportation workforce of the Hamersley Iron mining company and, in the 1980s, the petroleum and liquefied natural gas operations of the Woodside-operated North West Shelf Venture located on Murujuga. As of the 2021 census, Karratha had an urban population of 17,013. The city's name comes from the cattle station of the same name, which derives from a word in a local Aboriginal language meaning "good country" or "soft earth". More recently, Ngarluma people have indicated the name may actually relate to an early interpretation of "Gardarra", stemming from the sacred site for the whale, located in the Karratha area, called "Gardarrabuga". The city is the seat of government of the City of Karratha, a local government area covering the surrounding region.

The Hamersley Range is a mountainous region of the Pilbara region of Western Australia. The range was named on 12 June 1861 by explorer Francis Thomas Gregory after Edward Hamersley, a prominent promoter of his exploration expedition to the northwest.

Railways in Western Australia were developed in the 19th century both by the Government of Western Australia and a number of private companies. Today passenger rail services are controlled by the Public Transport Authority through Transperth, which operates public transport in Perth, and Transwa, which operates country passenger services. Journey Beyond operates the Indian Pacific.
Karratha Airport is an airport in Karratha, in the Pilbara region of Western Australia. The airport is 14 km (8.7 mi) from Karratha and 5 nautical miles south of Dampier.
Pilbara newspapers is a selection of newspapers published in the Pilbara region of Western Australia.

The Hamersley & Robe River railway, majority-owned by Rio Tinto, and operated by its subsidiary Pilbara Iron, is a private rail network in the Pilbara region of Western Australia for the purpose of carrying iron ore. The network is larger than any other Australian heavy freight rail network in private ownership. The total length of its track is about 1,700 km (1,056 mi).

The Mount Newman railway, owned and operated by BHP, is a private rail network in the Pilbara region of Western Australia built to carry iron ore. It is one of two railway lines BHP operates in the Pilbara, the other being the Goldsworthy railway.

The Brockman 2 mine is an iron ore mine located in the Pilbara region of Western Australia, 60 kilometres north-west of Tom Price.
The Yandicoogina mine, often shortened to Yandi, is an iron ore mine located in the Pilbara region of Western Australia, 95 kilometres north-west of Newman. it should not be confused with BHP Billiton's Yandi mine, which is located nearby.

Iron ore mining in Western Australia, in the 2018–19 financial year, accounted for 54 percent of the total value of the state's resource production, with a value of A$78.2 billion. The overall value of the minerals and petroleum industry in Western Australia was A$145 billion in 2018–19, a 26 percent increase on the previous financial year.
The heavy-haul railways in the Pilbara are a series of company-owned railways in the Pilbara region in the north-west of the state of Western Australia. Their routes total 2782 kilometres.

Hamersley News was a fortnightly English language newspaper published in Perth, Western Australia by Hamersley Iron Pty Ltd. It was distributed to mining communities in Dampier, Karratha, Tom Price and Paraburdoo.
The Yindjibarndi are an Aboriginal Australian people of the Pilbara region of Western Australia. They form the majority of Aboriginal people around Roebourne. Their traditional lands lie around the Fortescue River.
References
- ↑ "Cossack". Hamersley News . Vol. XI, no. 3. Western Australia. 9 February 1978. p. 12. Retrieved 23 September 2023– via National Library of Australia.
- ↑ "Marble Bar heatwave, 1923–1924". Australian Climate Extremes. Bureau of Meteorology. Archived from the original on 17 March 2009. Retrieved 21 September 2008.
- ↑ "Excess force used to quell detainees". The Age. 25 August 2015. Retrieved 2 November 2024.
- ↑ Piesse, Emily (7 November 2018). "BHP runaway iron ore train left a twisted wreck after derailment stopped it reaching WA town". ABC News. Retrieved 17 October 2024.