
The River Welland is a lowland river in the east of England, some 65 miles (105 km) long. It drains part of the Midlands eastwards to The Wash. The river rises in the Hothorpe Hills, at Sibbertoft in Northamptonshire, then flows generally northeast to Market Harborough, Stamford and Spalding, to reach The Wash near Fosdyke. It is a major waterway across the part of the Fens called South Holland, and is one of the Fenland rivers that were laid out with washlands. There are two channels between widely spaced embankments with the intention that flood waters would have space in which to spread while the tide in the estuary prevented free egress. However, after the floods of 1947, new works such as the Coronation Channel were constructed to control flooding in Spalding, and the washlands are no longer used solely as pasture, but may be used for arable farming.

The River Glen is a river in Lincolnshire, England with a short stretch passing through Rutland near Essendine.

Spalding is a market town on the River Welland in the South Holland district of Lincolnshire, England. The town had a population of 34,113 at the 2017 census. The town is the administrative centre of the South Holland District. The town is located between the cities of Peterborough and Lincoln, as well as the towns of Bourne, Market Deeping, March, Boston, Wisbech, Holbeach and Sleaford.

Twenty is a village in the South Kesteven district of Lincolnshire, England. It is situated approximately 3 miles (5 km) east of Bourne, and 5 miles (8 km) west of Spalding.

Stretham Old Engine is a steam-powered engine just south of Stretham in Cambridgeshire, England, that was used to pump water from flood-affected areas of The Fens back into the River Great Ouse. It is one of only three surviving drainage engines in East Anglia, and is a Grade II* listed building.

The South Forty-Foot Drain, also known as the Black Sluice Navigation, is the main channel for the land-drainage of the Black Sluice Level in the Lincolnshire Fens. It lies in eastern England between Guthram Gowt and the Black Sluice pumping station on The Haven, at Boston. The Drain has its origins in the 1630s, when the first scheme to make the Fen land available for agriculture was carried out by the Earl of Lindsey, and has been steadily improved since then. Water drained from the land entered The Haven by gravity at certain states of the tide until 1946, when the Black Sluice pumping station was commissioned.

Bourne Eau is a short river which rises from an artesian spring in the town of Bourne in Lincolnshire, England, and flows in an easterly direction to join the River Glen at Tongue End. Within the town, it once powered three water mills, one of which is now a heritage centre. At Eastgate, it becomes much wider as it was navigable in the 18th and 19th centuries, and this was the location of the terminal basin. Below the town it is an embanked river, as its normal level is higher than that of the surrounding Fens. Navigation ceased in the 1860s and the river now forms an important part of the drainage system that enables the surrounding fen land to be used for agriculture.
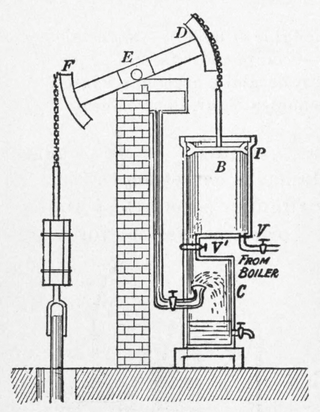
A beam engine is a type of steam engine where a pivoted overhead beam is used to apply the force from a vertical piston to a vertical connecting rod. This configuration, with the engine directly driving a pump, was first used by Thomas Newcomen around 1705 to remove water from mines in Cornwall. The efficiency of the engines was improved by engineers including James Watt, who added a separate condenser; Jonathan Hornblower and Arthur Woolf, who compounded the cylinders; and William McNaught, who devised a method of compounding an existing engine. Beam engines were first used to pump water out of mines or into canals but could be used to pump water to supplement the flow for a waterwheel powering a mill.

The Crossness Pumping Station is a former sewage pumping station designed by the Metropolitan Board of Works's chief engineer Sir Joseph Bazalgette and architect Charles Henry Driver. It is located at Crossness Sewage Treatment Works, at the eastern end of the Southern Outfall Sewer and the Ridgeway path in the London Borough of Bexley. Constructed between 1859 and 1865 by William Webster, as part of Bazalgette's redevelopment of the London sewerage system, it features spectacular ornamental cast ironwork, that Nikolaus Pevsner described as "a masterpiece of engineering – a Victorian cathedral of ironwork".

The Westonzoyland Pumping Station Museum of Steam Power and Land Drainage is a small industrial heritage museum dedicated to steam powered machinery at Westonzoyland in the English county of Somerset. It is a Grade II* listed building.

Pinchbeck is a village and civil parish in the South Holland district of Lincolnshire, England. The civil parish population was 5,153 at the 2001 census, 5,455 at the 2011 census and 6,011 at the 2021 census. It is situated 2 miles (3.2 km) north from the centre of Spalding.

A scoop wheel or scoopwheel is a pump, usually used for land drainage.

The Witham Navigable Drains are located in Lincolnshire, England, and are part of a much larger drainage system managed by the Witham Fourth District Internal Drainage Board. The Witham Fourth District comprises the East Fen and West Fen, to the north of Boston, which together cover an area of 97 square miles (250 km2). In total there are over 438 miles (705 km) of drainage ditches, of which under 60 miles (97 km) are navigable. Navigation is normally only possible in the summer months, as the drains are maintained at a lower level in winter, and are subject to sudden changes in level as a result of their primary drainage function, which can leave boats stranded. Access to the drains is from the River Witham at Anton's Gowt Lock.

Pode Hole is a village in South Holland, Lincolnshire, England. It is 2 miles (3.2 km) from Spalding and 10 miles from Bourne. The village lies at the confluence of several drainage channels, where two pumping stations discharge water into Vernatt's Drain from land in Deeping Fen to the South and West. Water from Pinchbeck South Fen to the North is also lifted into Vernatt's Drain. The village arose to service the pumping stations.

Guthram Gowt is a small settlement in the South Holland district of Lincolnshire, England. It is situated 5 miles (8 km) both east from Bourne and west from Spalding, and at a bend in the River Glen.

The Dogdyke Engine is a drainage engine near Tattershall, Lincolnshire, in England. The drainage of 2,500 acres (1,012 ha) of land around Tattershall was authorised in 1796, and came under the control of the Witham Third District commissioners in 1844

Deeping Fen is a low-lying area in the South Holland district of Lincolnshire, England, which covers approximately 47 square miles (120 km2). It is bounded by the River Welland and the River Glen, and is extensively drained, but the efficient drainage of the land exercised the minds of several of the great civil engineers of the 17th and 18th centuries.

Witham First District IDB is an English internal drainage board which was set up under the terms of the Land Drainage Act 1930. The Board inherited the responsibilities of the Witham General Drainage Commissioners, who were first constituted by an Act of Parliament of 1762. They manage the land drainage of an area to the west of the River Witham, between Lincoln and Dogdyke, which includes the valley of the River Slea to above Sleaford.

South Holland IDB is an English internal drainage board set up under the terms of the Land Drainage Act 1930. It has responsibility for the land drainage of 148.43 square miles (384.4 km2) of low-lying land in South Lincolnshire. It is unusual as its catchment area is the same as the area of the drainage district, and so it does not have to deal with water flowing into the area from surrounding higher ground. No major rivers flow through the area, although the district is bounded by the River Welland to the west and the River Nene to the east.

Witham Third District IDB is an English internal drainage board set up under the terms of the Land Drainage Act 1930. The Board inherited the responsibilities of the Witham General Drainage Commissioners, who were first constituted by an Act of Parliament of 1762. They manage the land drainage of an area to the north and east of the River Witham, between Lincoln and Dogdyke, which includes the valley of the River Bain to above Hemingby, and the valleys of Barlings Eau and most of its tributaries, to the north east of Lincoln.





















