
Mosasaurs comprise a group of extinct, large marine reptiles from the Late Cretaceous.Their first fossil remains were discovered in a limestone quarry at Maastricht on the Meuse in 1764. They belong to the order Squamata, which includes lizards and snakes.

Mosasaurus is the type genus of the mosasaurs, an extinct group of aquatic squamate reptiles. It lived from about 82 to 66 million years ago during the Campanian and Maastrichtian stages of the Late Cretaceous. The earliest fossils of Mosasaurus known to science were found as skulls in a chalk quarry near the Dutch city of Maastricht in the late 18th century, which were initially thought to have been the bones of crocodiles or whales. One particular skull discovered around 1780, and which was seized by France during the French Revolutionary Wars for its scientific value, was famously nicknamed the "great animal of Maastricht". In 1808, naturalist Georges Cuvier concluded it belonged to a giant marine lizard with similarities to monitor lizards but otherwise unlike any known living animal. This concept was revolutionary at the time and helped support the then-developing ideas of extinction. However, Cuvier did not designate a scientific name for the new animal; this was done by William Daniel Conybeare in 1822 when he named it Mosasaurus in reference to its origin in fossil deposits near the Meuse River. The exact affinities of Mosasaurus as a squamate remain controversial, and scientists continue to debate whether its closest living relatives are monitor lizards or snakes.
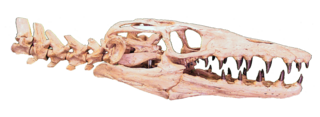
Selmasaurus is an extinct genus of marine lizard belonging to the mosasaur family. It is classified as part of the Plioplatecarpinae subfamily alongside genera like Angolasaurus and Platecarpus. Two species are known, S. russelli and S. johnsoni, both are exclusively known from Santonian deposits in the United States.

The Mosasaurinae are a subfamily of mosasaurs, a diverse group of Late Cretaceous marine squamates. Members of the subfamily are informally and collectively known as "mosasaurines" and their fossils have been recovered from every continent except for South America.
Plioplatecarpinae is a subfamily of mosasaurs, a diverse group of Late Cretaceous marine squamates. Members of the subfamily are informally and collectively known as "plioplatecarpines" and have been recovered from all continents, though the occurrences in Australia remain questionable. The subfamily includes the genera Latoplatecarpus, Platecarpus, Plioplatecarpus and Plesioplatecarpus.

The Halisaurinae are a subfamily of mosasaurs, a group of Late Cretaceous marine lizards. They were small to medium-sized, ranging from just under 3 meters in Eonatator sternbergi to as much as 8 or 9 meters in Pluridens serpentis. They tended to have relatively slender jaws and small, numerous teeth, suggesting a diet of small fish and other prey. Although the skeleton is primitive compared to other Mosasauridae in many respects, halisaurines had the distinctive hypocercal tail of other mosasaurids suggesting good swimming ability, and they persisted alongside other mosasaurs until the end of the Cretaceous. The earliest known remains of halisaurines occur in rocks of Santonian age and the subfamily persists until the latest Maastrichtian. Halisaurines are known from North and South America, Europe, Asia and Africa, indicating a more or less global distribution in the Late Cretaceous. Four genera are currently recognized: Eonatator, Halisaurus, Phosphorosaurus and Pluridens.

Eonatator is an extinct genus of marine lizard belonging to the mosasaur family. It is a close relative of Halisaurus, and part of the same subfamily, the Halisaurinae. It is known from the Late Cretaceous of North America, Colombia and Sweden. Originally, this taxon was included within Halisaurus, but was placed in its own genus, which also led to the subfamily Halisaurinae being created for the two genera.
Platecarpus is an extinct genus of aquatic lizards belonging to the mosasaur family, living around 84–81 million years ago during the middle Santonian to early Campanian, of the Late Cretaceous period. Fossils have been found in the United States and possible specimens in Belgium and Africa. A well-preserved specimen of Platecarpus shows that it fed on moderate-sized fish, and it has been hypothesized to have fed on squid, and ammonites as well. Like other mosasaurs, it was initially thought to have swum in an eel-like fashion, although another study suggests that it swam more like modern sharks. An exceptionally well-preserved specimen of P. tympaniticus known as LACM 128319 shows skin impressions, pigments around the nostrils, bronchial tubes, and the presence of a high-profile tail fluke, showing that it and other mosasaurs did not necessarily have an eel-like swimming method, but were more powerful, fast swimmers. It is held in the Natural History Museum of Los Angeles County.

Prognathodon is an extinct genus of marine lizard belonging to the mosasaur family. It is classified as part of the Mosasaurinae subfamily, alongside genera like Mosasaurus and Clidastes. Prognathodon has been recovered from deposits ranging in age from the Campanian to the Maastrichtian in the Middle East, Europe, New Zealand, and North America.

Halisaurus is an extinct genus of marine reptile belonging to the mosasaur family. The holotype, consisting of an angular and a basicranium fragment discovered near Hornerstown, New Jersey, already revealed a relatively unique combination of features and prompted a new genus to be described. It was named by Othniel Charles Marsh in 1869 and means "ocean lizard". It was renamed by Marsh to Baptosaurus in 1870, since he believed the name to already be preoccupied by the fish Halosaurus. According to modern rules, a difference of a letter is enough and the substitute name is unneeded, making "Baptosaurus" a junior synonym.

The Bearpaw Formation, also called the Bearpaw Shale, is a geologic formation of Late Cretaceous (Campanian) age. It outcrops in the U.S. state of Montana, as well as the Canadian provinces of Alberta and Saskatchewan, and was named for the Bear Paw Mountains in Montana. It includes a wide range of marine fossils, as well as the remains of a few dinosaurs. It is known for its fossil ammonites, some of which are mined in Alberta to produce the organic gemstone ammolite.

Ectenosaurus is an extinct genus of marine lizard belonging to the mosasaur family. It is classified as part of the Plioplatecarpinae subfamily alongside genera like Angolasaurus and Platecarpus. Ectenosaurus is known from the Santonian and Campanian of Kansas, Alabama, and Texas.

Angolasaurus is an extinct genus of mosasaur. Definite remains from this genus have been recovered from the Turonian of Angola, and possibly the Turonian of the United States and Brazil, and the Maastrichtian of Niger. While at one point considered a species of Platecarpus, recent phylogenetic analyses have placed it between the (then) plioplatecarpines Ectenosaurus and Selmasaurus, maintaining a basal position within the plioplatecarpinae.

Phosphorosaurus is an extinct genus of marine lizard belonging to the mosasaur family. Phosphorosaurus is classified within the Halisaurinae subfamily alongside the genera Pluridens, Eonatator and Halisaurus.

Latoplatecarpus is an extinct genus of plioplatecarpine mosasaur known from the Late Cretaceous of the northern Gulf of Mexico and the Western Interior Basin of North America.

The Oulad Abdoun Basin is a phosphate sedimentary basin located in Morocco, near the city of Khouribga. It is the largest in Morocco, comprising 44% of Morocco's phosphate reserves, and at least 26.8 billion tons of phosphate. It is also known as an important site for vertebrate fossils, with deposits ranging from the Late Cretaceous (Cenomanian-Turonian) to the Eocene epoch (Ypresian), a period of about 25 million years.

This timeline of mosasaur research is a chronologically ordered list of important fossil discoveries, controversies of interpretation, and taxonomic revisions of mosasaurs, a group of giant marine lizards that lived during the Late Cretaceous Epoch. Although mosasaurs went extinct millions of years before humans evolved, humans have coexisted with mosasaur fossils for millennia. Before the development of paleontology as a formal science, these remains would have been interpreted through a mythological lens. Myths about warfare between serpentine water monsters and aerial thunderbirds told by the Native Americans of the modern western United States may have been influenced by observations of mosasaur fossils and their co-occurrence with creatures like Pteranodon and Hesperornis.
Gavialimimus is an extinct genus of plioplatecarpine mosasaur from the Maastrichtian of Morocco. The holotype MHNM.KHG.1231, an articulated skull and associated fragmentary postcrania, was found in the Ouled Abdoun Basin.

















