Yaguarasaurine per Palci et al. (2013)  | |||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Basal plioplatecarpine per Rivera-Sylva et al. (2023)  | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| Yaguarasaurus Temporal range: Turonian, | |
|---|---|
 | |
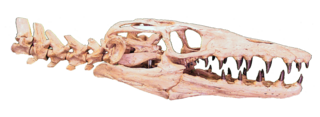
| Skull and first cervical vertebrae of Y. columbianus. Geological Museum José Royo y Gómez, Bogotá | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Reptilia |
| Order: | Squamata |
| Clade: | † Mosasauria |
| Family: | † Mosasauridae |
| Clade: | † Russellosaurina |
| Subfamily: | † Yaguarasaurinae |
| Genus: | † Yaguarasaurus Páramo 1994 |
| Type species | |
| †Yaguarasaurus columbianus Páramo 1994 | |
| Other species [1] | |
| |
Yaguarasaurus is an extinct genus of mosasauroid from the Late Cretaceous (Turonian) period of Colombia, South America. The remains discovered (an articulated skull, some vertebrae and ribs) were defined as a new genus and species of mosasaurid, Yaguarasaurus columbianus, by the Colombian paleontologist María Páramo, former director of the Museo de Geología José Royo y Gómez of INGEOMINAS in Bogotá. The first fossils remains of this animal suggested a cranial length of 47 centimetres (19 in) and a total length of 5 metres (16 ft); an additional skull that measures 87 centimetres (34 in) long implies a larger size. [2]
This reptile is a member of the family of marine lizards Mosasauridae characteristic of Middle and Upper Cretaceous, with global distribution, but in South America known only through isolated remains (Price, 1957, Pierce and Welles, 1959 ; Bonaparte, 1978; [3] Ameghino, 1918). This mosasaur discovered in Yaguará, was at the moment of discovery the most complete material known in South America. [4]

The remains were found in a limestone bed (Upper Turonian) of the La Frontera Formation, member of the Villeta Group, near Yaguará, Huila, in a site called Cueva Rica. [5] Its name means "Yaguará lizard of Colombia".

The following cladograms illustrate the phylogenetic analyses of two competing hypotheses on the classification of Yaguarasaurus. Topology A represents the traditional view of the genus belonging to the subfamily Yaguarasaurinae following Palci et al. (2013). [6] Topology B follows Rivera-Sylva et al. (2023) and depicts a new hypothesis holding Yaguarasaurus as a basal member of the Plioplatecarpinae, [1] which was first proposed by Polcyn et al. (2023) based on the discovery of symapomorphies in the braincase. [7]
In the second scenario, the two species of Yaguarasaurus are paraphyletic with respect to more derived plioplatecarpines, with Y. regiomontanus lying further up the tree.
Yaguarasaurine per Palci et al. (2013)  | |||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Basal plioplatecarpine per Rivera-Sylva et al. (2023)  | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|

Mosasaurs are an extinct group of large aquatic reptiles within the family Mosasauridae that lived during the Late Cretaceous. Their first fossil remains were discovered in a limestone quarry at Maastricht on the Meuse in 1764. They belong to the order Squamata, which includes lizards and snakes.
Selmasaurus is an extinct genus of marine lizard belonging to the mosasaur family. It is classified as part of the Plioplatecarpinae subfamily alongside genera like Angolasaurus and Platecarpus. Two species are known, S. russelli and S. johnsoni; both are exclusively known from Santonian deposits in the United States.
Plioplatecarpinae is a subfamily of mosasaurs, a diverse group of Late Cretaceous marine squamates. Members of the subfamily are informally and collectively known as "plioplatecarpines" and have been recovered from all continents, though the occurrences in Australia remain questionable. The subfamily includes the genera Latoplatecarpus, Platecarpus, Plioplatecarpus and Plesioplatecarpus.

The Halisaurinae are a subfamily of mosasaurs, a group of Late Cretaceous marine lizards. They were small to medium-sized, ranging from just under 3 meters in Eonatator sternbergi to as much as 8 or 9 meters in Pluridens serpentis. They tended to have relatively slender jaws and small, numerous teeth, suggesting a diet of small fish and other prey. Although the skeleton is primitive compared to other Mosasauridae in many respects, halisaurines had the distinctive hypocercal tail of other mosasaurids suggesting good swimming ability, and they persisted alongside other mosasaurs until the end of the Cretaceous. The earliest known remains of halisaurines occur in rocks of Santonian age and the subfamily persists until the latest Maastrichtian. Halisaurines are known from North and South America, Europe, Asia and Africa, indicating a more or less global distribution in the Late Cretaceous. Four genera are currently recognized: Eonatator, Halisaurus, Phosphorosaurus and Pluridens.

Russellosaurus is an extinct genus of tethysaurine mosasauroid from the Late Cretaceous of North America. The genus was described from a skull discovered in an exposure of the Arcadia Park Shale at Cedar Hill, Dallas County in the south-central part of the DFW Metroplex in Texas, United States. The skull was found in 1992 by a member of the Dallas Paleontological Society, who then donated to the museum. Other fragmentary specimens of Russelosaurus have been recovered from the slightly older Kamp Ranch Limestone at two other localities in the Dallas area.

Yaguará is a town and municipality in the Huila Department, Colombia. The urban centre is located at an elevation of 650 metres (2,130 ft) in the Magdalena River Valley and the Eastern Ranges of the Colombian Andes. The municipality borders Teruel and Palermo in the north, Gigante, Hobo and Tesalia in the south, Campoalegre and Hobo in the east and Tesalia and Iquira in the west. The departmental capital Neiva is 49 kilometres (30 mi) to the northeast. The Betania Reservoir is situated within the boundaries of Yaguará.

Tethysaurus is an extinct genus of tethysaurine mosasauroid from the Early Turonian period. The only species is Tethysaurus nopcsai.

Angolasaurus is an extinct genus of mosasaur. Definite remains from this genus have been recovered from the Turonian and Coniacian of Angola, and possibly the Coniacian of the United States, the Turonian of Brazil, and the Maastrichtian of Niger. While at one point considered a species of Platecarpus, recent phylogenetic analyses have placed it between the (then) plioplatecarpines Ectenosaurus and Selmasaurus, maintaining a basal position within the plioplatecarpinae.

The Yaguarasaurinae are a subfamily of mosasaurs, a diverse group of Late Cretaceous marine squamates. Members of the subfamily are informally and collectively known as "yaguarasaurines" and have been recovered from North and South America and Europe. Three genera, Yaguarasaurus, Russellosaurus and Romeosaurus are known. Yaguarasaurus and Russellosaurus were previously considered part of the Tethysaurinae until they were grouped with Romeosaurus as yaguarasaurines.

This timeline of mosasaur research is a chronologically ordered list of important fossil discoveries, controversies of interpretation, and taxonomic revisions of mosasaurs, a group of giant marine lizards that lived during the Late Cretaceous Epoch. Although mosasaurs went extinct millions of years before humans evolved, humans have coexisted with mosasaur fossils for millennia. Before the development of paleontology as a formal science, these remains would have been interpreted through a mythological lens. Myths about warfare between serpentine water monsters and aerial thunderbirds told by the Native Americans of the modern western United States may have been influenced by observations of mosasaur fossils and their co-occurrence with creatures like Pteranodon and Hesperornis.
The La Frontera Formation (Spanish: Formación La Frontera, K2F, Ksf) is a geological formation, part of the Villeta Group, of the Altiplano Cundiboyacense and neighbouring areas of the Eastern Ranges of the Colombian Andes. The sequence of limestones and lydites dates to the Late Cretaceous period; Turonian epoch and has a maximum thickness of 206 metres (676 ft).
María Euridice Páramo Fonseca is a Colombian paleontologist and geologist. She has contributed to paleontology in Colombia in the fields of describing various Cretaceous reptiles, most notably the mosasaurs Eonatator and Yaguarasaurus, the ichthyosaur Kyhytysuka, and the plesiosaurs Leivanectes and Stenorhynchosaurus.

Goulmimichthys is an extinct genus of ray-finned fishes in the family Pachyrhizodontidae. The genus, first described by Cavin in 1995, is known from various Turonian age formations. The type species G. arambourgi from the Akrabou Formation in the El Rachidia Province of Morocco, and other fossils described are G. gasparini of the La Frontera Formation, Colombia, and G. roberti from the Agua Nueva Formation of Mexico.

The Hondita Formation is a fossiliferous geological formation of the Upper Magdalena Valley (VSM) and surrounding Central and Eastern Ranges of the Colombian Andes, extending from Cundinamarca in the north to Huila and easternmost Tolima in the south. The lowermost unit of the Güagüaquí Group, a sequence of sandy limestones and shales, dates to the Late Cretaceous period; Turonian epoch, and has a maximum thickness of 90 metres (300 ft).

Bachea is an extinct genus of ray-finned fish that lived during the Late Cretaceous in what is now central Colombia, South America. The type species is Bachea huilensis, described in 1997 by María Páramo from the Turonian of Huila, Colombia.

Gavialimimus is an extinct genus of plioplatecarpine mosasaur from the Maastrichtian of Morocco. The holotype MHNM.KHG.1231, an articulated skull and associated fragmentary postcrania, was found in the Ouled Abdoun Basin.
Sarabosaurus is a monospecific genus of plioplatecarpine mosasaurid from the lower Turonian Tropic Shale of Utah, United States. The type and only species, S. dahli, was named in honor of Steve Dahl, a volunteer at the Grand Staircase-Escalante National Monument in Kanab, Utah.