
The giant anteater is an insectivorous mammal native to Central and South America. It is one of four living species of anteaters, of which it is the largest member. The only extant member of the genus Myrmecophaga, it is classified with sloths in the order Pilosa. This species is mostly terrestrial, in contrast to other living anteaters and sloths, which are arboreal or semiarboreal. The giant anteater is 182 to 217 cm in length, with weights of 33 to 50 kg for males and 27 to 47 kg for females. It is recognizable by its elongated snout, bushy tail, long fore claws, and distinctively colored pelage.

The silky anteater, also known as the pygmy anteater, has traditionally been considered a single species of anteater, Cyclopes didactylus, in the genus Cyclopes, the only living genus in the family Cyclopedidae. Found in southern Mexico, and Central and South America, it is the smallest of all known anteaters. It has nocturnal habits and appears to be completely arboreal; its hind feet are highly modified for climbing.

The southern tamandua, also called the collared anteater or lesser anteater, is a species of anteater from South America and the island of Trinidad in the Caribbean. It is a solitary animal found in many habitats, from mature to highly disturbed secondary forests and arid savannas. It feeds on ants, termites, and bees. Its very strong foreclaws can be used to break insect nests or to defend itself.

The Myrmecophagidae are a family of anteaters, the name being derived from the Ancient Greek words for 'ant' and 'eat'. Two genera and three species are in the family, consisting of the giant anteater, and the tamanduas. The fossil Eurotamandua from the Messel Pit in Germany may be an early anteater, but its status is currently debated.
La Venta is a fossil locality located in the modern departments of Tolima and Huila in Colombia. This site is one of the richest Neogene fossil assemblages in South America and represents the best-known Cenozoic fossil site outside of Argentina. It provides a glimpse of what life in the region was like before the main wave of the Great American Interchange.
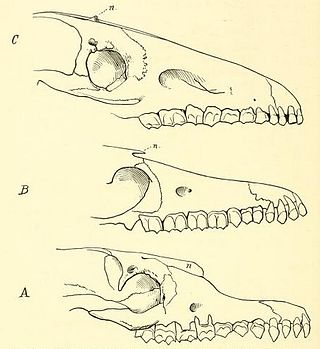
Scalabrinitherium is an extinct genus of mammals of the family Macraucheniidae. Fossils of this animal were found among the fossils of prehistoric xenarthrans in the Ituzaingó Formation of Argentina.

Metaxytherium is an extinct genus of dugong that lived from the Oligocene until the end of the Pliocene. Fossil remains have been found in Africa, Europe, North America and South America. Generally marine seagrass specialists, they inhabited the warm and shallow waters of the Paratethys, Mediterranean, Caribbean Sea and Pacific coastline. American species of Metaxytherium are considered to be ancestral to the North Pacific family Hydrodamalinae, which includes the giant Steller's sea cow.

Anteaters are the four extant mammal species in the suborder Vermilingua, commonly known for eating ants and termites. The individual species have other names in English and other languages. Together with sloths, they are within the order Pilosa. The name "anteater" is also commonly applied to the aardvark, numbat, echidnas, and pangolins, although they are not closely related to them.
The South American land mammal ages (SALMA) establish a geologic timescale for prehistoric South American fauna beginning 64.5 Ma during the Paleocene and continuing through to the Late Pleistocene. These periods are referred to as ages, stages, or intervals and were established using geographic place names where fossil materials where obtained.
The Colloncuran age is a period of geologic time within the Middle Miocene epoch of the Neogene, used more specifically within the SALMA classification in South America. It follows the Friasian and precedes the Laventan age.
Palaeomyrmidon is an extinct genus of anteater. Its closest living relative is the silky anteater. Although the silky anteater is arboreal, Palaeomyrmidon lived on the ground. Palaeomyrmidon is known from a fossil skull that was found in the Andalhualá Formation of Argentina.

Protamandua is an extinct genus of anteaters. Its closest living relatives are the giant anteater and tamanduas. Fossils of Protamandua are restricted to the Santa Cruz Formation of Argentina. It may have been a common ancestor of Myrmecophaga and Tamandua.

Neotamandua borealis is an extinct species of anteater. Fossils were found in the Honda Group at the Konzentrat-Lagerstätte of La Venta, Colombia. It was suggested to be an ancestor of the giant anteater, and is also related to the tamanduas. The species was described by Hirschfeld in 1976.
This paleomammalogy list records new fossil mammal taxa that were described during the year 2013, as well as notes other significant paleomammalogy discoveries and events which occurred during that year.

The Pisco Formation is a geologic formation located in Peru, on the southern coastal desert of Ica and Arequipa. The approximately 640 metres (2,100 ft) thick formation was deposited in the Pisco Basin, spanning an age from the Late Miocene up to the Early Pliocene, roughly from 9.6 to 4.5 Ma. The tuffaceous sandstones, diatomaceous siltstones, conglomerates and dolomites were deposited in a lagoonal to near-shore environment, in bays similar to other Pacific South American formations as the Bahía Inglesa and Coquimbo Formations of Chile.

Boreostemma is an extinct genus of glyptodonts from northern South America. Fossils assigned to the genus were first described as belonging to Asterostemma from southern South America, but have been placed in the new genus Boreostemma by Carlini et al. in 2008. The type species is B. pliocena. Fossils of Boreostemma have been found in the Honda Group of Colombia, in Peru and Venezuela.
Promacrauchenia is an extinct genus of macraucheniids that lived during the Late Miocene to Late Pliocene epochs of what is now Argentina and Bolivia. It belongs to the subfamily Macraucheniinae, which also includes Huayqueriana, Macrauchenia, and Xenorhinotherium. Fossils of this genus have been found in the Ituzaingó, Andalhuala, and Cerro Azul Formations of Argentina.

Magdalenabradys is an extinct genus of mylodontid ground sloths that lived during the Middle Miocene and Early Pliocene of what is now Colombia and Venezuela. Fossils have been found in the Villavieja Formation of the Honda Group in Colombia, and the Codore and Urumaco Formations of Venezuela.
The Camacho Formation is a Huayquerian geologic formation in Uruguay.
















