
Ground sloths are a diverse group of extinct sloths in the mammalian superorder Xenarthra. They varied widely in size with the largest, belonging to genera Lestodon, Eremotherium and Megatherium, being around the size of elephants. Ground sloths represent a paraphyletic group, as living tree sloths are thought to have evolved from ground sloth ancestors.

Megalonychidae is an extinct family of sloths including the extinct Megalonyx. Megalonychids first appeared in the early Oligocene, about 35 million years (Ma) ago, in southern Argentina (Patagonia). There is, however, one possible find dating to the Eocene, about 40 Ma ago, on Seymour Island in Antarctica. They first reached North America by island-hopping across the Central American Seaway, about 9 million years ago, prior to formation of the Isthmus of Panama about 2.7 million years ago. Some megalonychid lineages increased in size as time passed. The first species of these were small and may have been partly tree-dwelling, whereas the Pliocene species were already approximately half the size of the huge Late Pleistocene Megalonyx jeffersonii from the last ice age.

Hapalops is an extinct genus of ground sloth from the Early to Late Miocene of Brazil, Bolivia, Colombia, and Argentina in South America.

The giant Cuban owl or giant cursorial owl (Ornimegalonyx) is an extinct genus of giant owl that measured 1.1 metres in height. It is closely related to the many species of living owls of the genus Strix. It was a flightless or nearly flightless bird and it is believed to be the largest owl that ever existed. It lived on the island of Cuba.

Megalocnus is a genus of extinct ground sloths that were native to Cuba during the Pleistocene and Holocene epochs. They were among the largest of the Caribbean sloths (Megalocnidae), with individuals estimated to have weighed up to 270 kg to 200 kg, around the size of a black bear when alive. Its relatives include other megalocnid sloths, such as Acratocnus, Mesocnus, Miocnus, Neocnus andParocnus. The former species M. zile from Hispaniola is currently thought to be a junior synonym of Parocnus serus.

Thalassocnus is an extinct genus of semiaquatic ground sloths from the Miocene and Pliocene of the Pacific South American coast. It is monotypic within the subfamily Thalassocninae. The five species—T. antiquus, T. natans, T. littoralis, T. carolomartini, and T. yuacensis—represent a chronospecies, a population gradually adapting to marine life in one direct lineage. They are the only known aquatic sloths, but they may have also been adapted to a terrestrial lifestyle. They have been found in the Pisco Formation of Peru, the Tafna Formation of Argentina, and the Bahía Inglesa, Coquimbo, and Horcón formations of Chile. Thalassocninae has been placed in both the families Megatheriidae and Nothrotheriidae.

Lestodon is an extinct genus of giant ground sloth native to South America during the Pleistocene epoch. Its fossil remains have been primarily been found in the Pampas and adjacent regions. The largest member of the family Mylodontidae, It is estimated to have weighed 4,100 kilograms. It was a herbivore and primarily fed on the grasses and low-growing plants.
The mammalian order Pilosa, which includes the sloths and anteaters, includes various species from the Caribbean region. Many species of sloths are known from the Greater Antilles, all of which became extinct over the last millennia, but some sloths and anteaters survive on islands closer to the mainland.

Nematherium is an extinct genus of ground sloth belonging to Mylodontoidea, it is either considered to be a member of Mylodontidae or Scelidotheriidae. It lived during the Middle Miocene epoch (Santacrucian). Fossils have been found in the Cura-Mallín Formation of Chile and the Santa Cruz and Sarmiento Formations of Argentina.

Pelecyodon is an extinct genus of ground sloths from the Early Miocene (Santacrucian) of South America. Fossils have been found in the Santa Cruz Formation in Argentina.

Eionaletherium is an extinct genus of ground sloth from the Late Miocene coasts of Venezuela containing one species: E. tanycnemius.

Diabolotherium is an extinct genus of megatheriine ground sloth, known from the Late Pleistocene of Peru. Unlike most other extinct mainland sloths, it seems to have been a climber, similar to extinct sloths from the Caribbean. Fossils of the genus were found at the coastal Piedra Escrita site and the Andean Casa del Diablo cave.

Megalocnidae is an extinct family of sloths, native to the islands of the Greater Antilles from the Early Oligocene to the Mid-Holocene. They are known from Cuba, Hispaniola and Puerto Rico, but are absent from Jamaica. While they were formerly placed in the Megalonychidae alongside two-toed sloths and ground sloths like Megalonyx, recent mitochondrial DNA and collagen sequencing studies place them as the earliest diverging group basal to all other sloths. or as an outgroup to Megatherioidea. They displayed significant diversity in body size and lifestyle, with Megalocnus being terrestrial and probably weighing several hundred kilograms, while Neocnus was likely arboreal and similar in weight to extant tree sloths, at less than 10 kilograms.
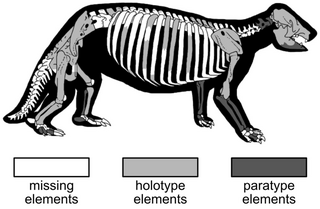
Parocnus is an extinct genus of sloth native to Cuba and Hispaniola, belonging to the family Megalocnidae. It was a terrestrial ground sloth, being the second largest Caribbean sloth after Megalocnus, with the body mass of the various species of the genus estimated at around 32–79 kilograms (71–174 lb), comparable to a pig.

Proeremotherium is an extinct genus of megatheriine ground sloths in the family Megatheriidae. It lived during the Late Miocene and Early Pliocene of what is now Venezuela. So far, two largely complete skulls have been recovered in the Falcón Basin in Venezuela. The finds identify the animals as medium-sized representatives of the Megatheriidae. In the cranial anatomy, Proeremotherium resembles the later and giant Eremotherium. It is therefore assumed that the two ground sloths are directly related to each other.
Baraguatherium is an extinct genus of ground sloths of the family Mylodontidae that lived during the Early Miocene of what is now Venezuela. It dates to the Early Miocene, around 20.44 to 15.97 million years ago and represents the oldest representative of its family in the northern part of South America to date. The structure of the teeth suggests that the genus represents a rather basal form within the Mylodontidae. Unlike other mylodonts, which tended to prefer open grasslands, Baraguatherium lived in a riverine, coastal tropical rainforest.
Lakukullus is an extinct genus of nothrotheriid ground sloths that lived during the Middle Miocene around 13.8 to 11.8 million years ago of what is now Bolivia.
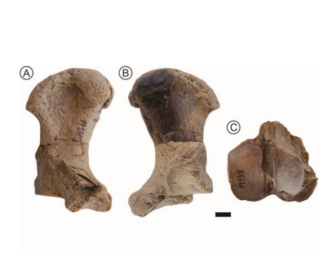
Prepoplanops is an extinct genus of ground sloth of the family Megatheriidae. It lived in the Miocene around 18 to 16 million years ago of what is now Argentina. The only known species is Prepoplanops boleadorensis.
Huilabradys is an extinct genus of ground sloths of the family Nothrotheriidae that lived in what is now Colombia. Huilabradys was discovered in the strata of the La Tatacoa desert in the Huila department, in the Villavieja Formation, and is part of the so-called La Venta fauna, a fossiliferous location from the mid-Miocene period that has provided a notable paleontological contribution on the Miocene faunas of northern South America. The remains discovered are basically fragments of the jaws and teeth, allowed the identification of this species, whose only species is Huilabradys magdaleniensis, and was classified as a member of the nothrotheriid subfamily Nothrotheriinae, which comprises small to medium-sized species of ground sloths.

Ortotherium is a genus of megalonychid ground sloth from the Late Miocene Ituzaingó Formation of Entre Rios Province, Argentina. Although many species were described, the only valid species of the genus is Ortotherium laticurvatum, with many species being junior synonyms. Ortotherium is known from very fragmentary material, all of which is material from the mandible and teeth. The holotype of O. laticurvatum consists of an incomplete left dentary that had been unearthed from a series of sediments known as ‘Conglomerado osifero’ in Paraná, Argentina. Argentina paleontologist Florentino Ameghino named the species in 1885, though he would go on to name four more, invalid, species of the genus. One species however, O. brevirostrum, has been reclassified as Mesopotamocnus.

















