
Ground sloths are a diverse group of extinct sloths in the mammalian superorder Xenarthra. They varied widely in size with the largest, belonging to genera Lestodon, Eremotherium and Megatherium, being around the size of elephants. Ground sloths represent a paraphyletic group, as living tree sloths are thought to have evolved from ground sloth ancestors.

Mylodontidae is a family of extinct South American and North American ground sloths within the suborder Folivora of order Pilosa, living from around 23 million years ago (Mya) to 11,000 years ago. This family is most closely related to another family of extinct ground sloths, Scelidotheriidae, as well as to the extant arboreal two-toed sloths, family Choloepodidae; together these make up the superfamily Mylodontoidea. Phylogenetic analyses based on morphology uncovered the relationship between Mylodontidae and Scelidotheriidae; in fact, the latter was for a time considered a subfamily of mylodontids. However, molecular sequence comparisons were needed for the correct placement of Choloepodidae. These studies have been carried out using mitochondrial DNA sequences as well as with collagen amino acid sequences. The latter results indicate that Choloepodidae is closer to Mylodontidae than Scelidotheriidae is. The only other living sloth family, Bradypodidae, belongs to a different sloth radiation, Megatherioidea.

Scelidotheriidae is a family of extinct ground sloths within the order Pilosa, suborder Folivora and superfamily Mylodontoidea, related to the other extinct mylodontoid family, Mylodontidae, as well as to the living two-toed sloth family Choloepodidae. The only other extant family of the suborder Folivora is the distantly related Bradypodidae. Erected as the family Scelidotheriidae by Ameghino in 1889, the taxon was demoted to a subfamily of Mylodontidae by Gaudin in 1995. However, recent collagen sequence data indicates the group is less closely related to Mylodon and Lestodon than Choloepus is, and thus it has been elevated back to full family status by Presslee et al. (2019).

The Great American Biotic Interchange, also known as the Great American Interchange and the Great American Faunal Interchange, was an important late Cenozoic paleozoogeographic biotic interchange event in which land and freshwater fauna migrated from North America to South America via Central America and vice versa, as the volcanic Isthmus of Panama rose up from the sea floor, forming a land bridge between the previously separated continents. Although earlier dispersals had occurred, probably over water, the migration accelerated dramatically about 2.7 million years (Ma) ago during the Piacenzian age. It resulted in the joining of the Neotropic and Nearctic biogeographic realms definitively to form the Americas. The interchange is visible from observation of both biostratigraphy and nature (neontology). Its most dramatic effect is on the zoogeography of mammals, but it also gave an opportunity for reptiles, amphibians, arthropods, weak-flying or flightless birds, and even freshwater fish to migrate. Coastal and marine biota were affected in the opposite manner; the formation of the Central American Isthmus caused what has been termed the Great American Schism, with significant diversification and extinction occurring as a result of the isolation of the Caribbean from the Pacific.

Megalonyx is an extinct genus of ground sloths of the family Megalonychidae, native to North America. It evolved during the Pliocene Epoch and became extinct during at the end of the Late Pleistocene, living from ~5 million to ~13,000 years ago. The type species, M. jeffersonii, the youngest and largest known species, measured about 3 meters (9.8 ft) in length and weighed up to 1,000 kilograms (2,200 lb).

Scelidotherium is an extinct genus of ground sloth of the family Scelidotheriidae, endemic to South America during the Late Pleistocene epoch. It lived from 780,000 to 11,000 years ago, existing for approximately 0.67 million years.

Choloepus is a genus of xenarthran mammals from Central and South America within the monotypic family Choloepodidae, consisting of two-toed sloths, sometimes also called two-fingered sloths. The two species of Choloepus, Linnaeus's two-toed sloth and Hoffmann's two-toed sloth, were formerly believed on the basis of morphological studies to be the only surviving members of the sloth family Megalonychidae, but have now been shown by molecular results to be closest to extinct ground sloths of the family Mylodontidae.

Megalonychidae is an extinct family of sloths including the extinct Megalonyx. Megalonychids first appeared in the early Oligocene, about 35 million years (Ma) ago, in southern Argentina (Patagonia). There is, however, one possible find dating to the Eocene, about 40 Ma ago, on Seymour Island in Antarctica. They first reached North America by island-hopping across the Central American Seaway, about 9 million years ago, prior to formation of the Isthmus of Panama about 2.7 million years ago. Some megalonychid lineages increased in size as time passed. The first species of these were small and may have been partly tree-dwelling, whereas the Pliocene species were already approximately half the size of the huge Late Pleistocene Megalonyx jeffersonii from the last ice age.

Sloths are a Neotropical group of xenarthran mammals constituting the suborder Folivora, including the extant arboreal tree sloths and extinct terrestrial ground sloths. Noted for their slowness of movement, tree sloths spend most of their lives hanging upside down in the trees of the tropical rainforests of South America and Central America. Sloths are considered to be most closely related to anteaters, together making up the xenarthran order Pilosa.

Acratocnus is an extinct genus of Caribbean sloths that were found on Cuba, Hispaniola, and Puerto Rico during the Late Pleistocene and early-mid Holocene.

Catonyx is an extinct genus of ground sloth of the family Scelidotheriidae, endemic to South America during the Pliocene and Pleistocene epochs. It lived from 2.5 Ma to about 10,000 years ago, existing for approximately 2.49 million years. The most recent date obtained is about 9600 B.P.

Thinobadistes is an extinct genus of ground sloth of the family Mylodontidae endemic to North America during the Miocene-Pliocene epochs (Hemphillian). It lived from 10.3 to 4.9 mya, existing for approximately 5.4 million years.
Miocnus is an extinct genus of ground sloths of the family Megalocnidae endemic to Cuba during the Pleistocene and very early Holocene epochs, living from 1.8 Mya—11,000 years ago, existing for approximately 1.789 million years.
The mammalian order Pilosa, which includes the sloths and anteaters, includes various species from the Caribbean region. Many species of sloths are known from the Greater Antilles, all of which became extinct over the last millennia, but some sloths and anteaters survive on islands closer to the mainland.
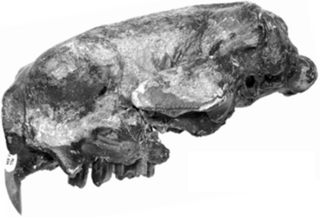
Ahytherium is an extinct genus of megalonychid sloth that lived during the Pleistocene of what is now Brazil. It contains a single species, A. aureum.
The Alachua Formation is a Miocene geologic formation in Florida. The claystones, sandstones and phosphorites of the formation preserve many fossils of mammals, birds, reptiles and fish, among others megalodon.
Surameryx is an extinct genus of herbivorous artiodactyls originally described as belonging to the extinct family Palaeomerycidae. A single species, S. acrensis, was described from the Late Miocene of the Madre de Dios Formation, South America. It was originally interpreted as one of the few northern mammals that entered South America before the Pliocene. However, both its identification as a member of the family Palaeomerycidae and claims about its Miocene age were subsequently challenged.

Megalocnidae is an extinct family of sloths, native to the islands of the Greater Antilles from the Early Oligocene to the Mid-Holocene. They are known from Cuba, Hispaniola and Puerto Rico, but are absent from Jamaica. While they were formerly placed in the Megalonychidae alongside two-toed sloths and ground sloths like Megalonyx, recent mitochondrial DNA and collagen sequencing studies place them as the earliest diverging group basal to all other sloths. or as an outgroup to Megatherioidea. They displayed significant diversity in body size and lifestyle, with Megalocnus being terrestrial and probably weighing several hundred kilograms, while Neocnus was likely arboreal and similar in weight to extant tree sloths, at less than 10 kilograms.
Neonematherium is an extinct genus of scelidotheriid ground sloths that lived in Argentina, Chile, and Colombia during the Early to Late Miocene. Fossils have been found in the Honda Group of Colombia, and the Río Frías Formation of Chile.

Ortotherium is a genus of megalonychid ground sloth from the Late Miocene Ituzaingó Formation of Entre Rios Province, Argentina. Although many species were described, the only valid species of the genus is Ortotherium laticurvatum, with many species being junior synonyms. Ortotherium is known from very fragmentary material, all of which is material from the mandible and teeth. The holotype of O. laticurvatum consists of an incomplete left dentary that had been unearthed from a series of sediments known as ‘Conglomerado osifero’ in Paraná, Argentina. Argentina paleontologist Florentino Ameghino named the species in 1885, though he would go on to name four more, invalid, species of the genus. One species however, O. brevirostrum, has been reclassified as Mesopotamocnus.















