
Miracinonyx is an extinct genus of felids belonging to the subfamily Felinae that was endemic to North America from the Pleistocene epoch and morphologically similar to the modern cheetah, although its apparent similar ecological niches have been considered questionable due to anatomical morphologies of the former that would have limited the ability to act as a specialized pursuit predator. The genus was originally known from fragments of skeletons, but nearly complete skeletons have been recovered from Natural Trap Cave in northern Wyoming.

Megalonyx is an extinct genus of ground sloths of the family Megalonychidae, native to North America. It evolved during the Pliocene Epoch and became extinct during at the end of the Late Pleistocene, living from ~5 million to ~13,000 years ago. The type species, M. jeffersonii, the youngest and largest known species, measured about 3 meters (9.8 ft) in length and weighed up to 1,000 kilograms (2,200 lb).

Megalonychidae is an extinct family of sloths including the extinct Megalonyx. Megalonychids first appeared in the early Oligocene, about 35 million years (Ma) ago, in southern Argentina (Patagonia). There is, however, one possible find dating to the Eocene, about 40 Ma ago, on Seymour Island in Antarctica. They first reached North America by island-hopping across the Central American Seaway, about 9 million years ago, prior to formation of the Isthmus of Panama about 2.7 million years ago. Some megalonychid lineages increased in size as time passed. The first species of these were small and may have been partly tree-dwelling, whereas the Pliocene species were already approximately half the size of the huge Late Pleistocene Megalonyx jeffersonii from the last ice age.

Pseudhipparion is an extinct genus of three-toed horse endemic to North America during the Miocene. They were herding animals whose diet consisted of C3 plants. Fossils found in Georgia and Florida indicate that it was a lightweight horse, weighing up to 90 pounds. In 2005, fossils were unearthed in Oklahoma. Seven species of Pseudhipparion are known from the fossil record which were very small, following the trend of Bergmann's rule.

Tremarctos floridanus is an extinct species of bear in the family Ursidae, subfamily Tremarctinae. T. floridanus became extinct at the end of the last ice age, 11,000 years ago. It's fossils have been found throughout the Southeastern United States, in northeastern Mexico, and in Belize from the Rancholabrean epoch, and from earlier epochs at some sites in western North America.

Eremotherium is an extinct genus of giant ground sloth in the family Megatheriidae. Eremotherium lived in southern North America, Central America, and northern South America from the Pliocene, around 5.3 million years ago, to the end of the Late Pleistocene, around 10,000 years ago. Eremotherium was one of the largest ground sloths, with a body size comparable to elephants, weighing around 4–6.5 tonnes and measuring about 6 metres (20 ft) long, slightly larger than its close relative Megatherium.

Paramylodon is an extinct genus of ground sloth of the family Mylodontidae endemic to North America during the Pliocene through Pleistocene epochs, living from around ~4.9 Mya–12,000 years ago.

Mount Blanco is a small white hill — an erosional remnant — located on the eastern border of the Llano Estacado within Blanco Canyon in Crosby County, Texas. With Blanco Canyon, it is the type locality of the early Pleistocene Blanco Formation of Texas and Kansas, as well as the Blancan fauna, which occurs throughout North America. Mount Blanco is a Late Blancan age site, and is associated with other Late Blancan sites from Texas such as Red Light and Hudspeth local faunas from Hudspeth County, and the Cita Canyon fauna from Randall County.
Pliometanastes is an extinct genus of ground sloths of the family Megalonychidae endemic to North America during the Late Miocene epoch through very early Pliocene epoch. Its fossils have been found in Costa Rica and across the southern United States from California to Florida.
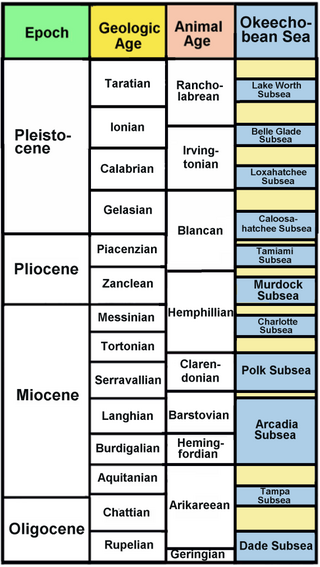
The Okeechobean Sea was a Cenozoic eutropical subsea, which along with the Choctaw Sea, occupied the eastern Gulf of Mexico basin system bounding Florida.

Hypolagus is an extinct genus of lagomorph, first recorded in the Hemingfordian of North America. It entered Asia during the early Turolian and spread to Europe not much later, where it survived until the Middle Pleistocene. Though unknown in the Iberian Peninsula, fossils of this genus have been found in the Balearic Islands, suggesting an eastern migration during the dry period in the Mediterranean region known as the Messinian Salinity Crisis.
Lestobradys is an extinct genus of ground sloth, which existed in Uruguay during the Late Miocene period; Huayquerian in the South American land mammal age (SALMA). The type species is L. sprechmanni, found in the Camacho Formation of Uruguay.

Paleontology in Florida refers to paleontological research occurring within or conducted by people from the U.S. state of Florida. Florida has a very rich fossil record spanning from the Eocene to recent times. Florida fossils are often very well preserved.
The Alachua Formation is a Miocene geologic formation in Florida. The claystones, sandstones and phosphorites of the formation preserve many fossils of mammals, birds, reptiles and fish, among others megalodon.

The Bone Valley Formation is a geologic formation in Florida. It is sometimes classified as the upper member of the Peace River Formation of the Hawthorn Group. It contains economically important phosphorite deposits that are mined in west-central Florida, as well as rich assemblages of vertebrate fossils.
The Goliad Formation (Tg) is a geologic formation in Texas. It preserves fossils dating back to the Serravallian to earliest Pliocene stages of the Neogene period, including the gomphothere Blancotherium among many other fossil mammals, reptiles, birds and fish.
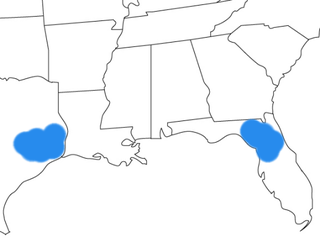
Floridachoerus olseni is an extinct peccary that lived during the Hemingfordian age of the Early Miocene, and was endemic to North America. F. olseni was in existence for approximately 4.46 million years. Remains of this extinct mammal were located at the fossil rich Thomas Farm site in Gilchrist County, Florida and Toledo Bend site, Newton County, Texas. Floridachoerus olseni was named after Stanley. J. Olsen of the Florida Geological Survey in 1962. Olsen previously worked at the site for Harvard University.
Surameryx is an extinct genus of herbivorous artiodactyls originally described as belonging to the extinct family Palaeomerycidae. A single species, S. acrensis, was described from the Late Miocene of the Madre de Dios Formation, South America. It was originally interpreted as one of the few northern mammals that entered South America before the Pliocene. However, both its identification as a member of the family Palaeomerycidae and claims about its Miocene age were subsequently challenged.

Hydrochoerus hesperotiganites is an extinct species of capybara that lived in San Diego County, California, during the Rancholabrean stage of the Pleistocene. It is currently the only known capybara of the genus Hydrochoerus found in North America. It was closely related to the modern Greater and Lesser Capybara.

Magdalenabradys is an extinct genus of mylodontid ground sloths that lived during the Middle Miocene and Early Pliocene of what is now Colombia and Venezuela. Fossils have been found in the Villavieja Formation of the Honda Group in Colombia, and the Codore and Urumaco Formations of Venezuela.

















