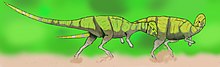
Marginocephalia is a clade of ornithischian dinosaurs that is characterized by a bony shelf or margin at the back of the skull. These fringes were likely used for display. This clade was officially defined in the PhyloCode by Daniel Madzia and colleagues in 2021 as "the smallest clade containing Ceratops montanus, Pachycephalosaurus wyomingensis, and Triceratops horridus". There are two clades included in Marginocephalia: the thick-skulled Pachycephalosauria and the horned Ceratopsia. All members of Marginocephalia were primarily herbivores. They basally used gastroliths to aid in digestion of tough plant matter until they convergently evolved tooth batteries in Neoceratopsia and Pachycephalosauria. Marginocephalia first evolved in the Jurassic Period and became more common in the Cretaceous. They are basally small facultative quadrupeds while derived members of the group are large obligate quadrupeds. Primitive marginocephalians are found in Asia, but the group migrated upwards into North America.

Pachycephalosauria is a clade of ornithischian dinosaurs. Along with Ceratopsia, it makes up the clade Marginocephalia. With the exception of two species, most pachycephalosaurs lived during the Late Cretaceous Period, dating between about 85.8 and 66 million years ago. They are exclusive to the Northern Hemisphere, all of them being found in North America and Asia. They were all bipedal, herbivorous/omnivorous animals with thick skulls. Skulls can be domed, flat, or wedge-shaped depending on the species, and are all heavily ossified. The domes were often surrounded by nodes and/or spikes. Partial skeletons have been found of several pachycephalosaur species, but to date no complete skeletons have been discovered. Often isolated skull fragments are the only bones that are found.

Pachycephalosaurus is a genus of pachycephalosaurid ornithischian dinosaur. The type species, P. wyomingensis, is the only known species, but some researchers argue that Stygimoloch might be a second species, P. spinifer, or a juvenile specimen of P. wyomingensis. It lived during the Maastrichtian age of the Late Cretaceous period in what is now western North America. Remains have been excavated in Montana, South Dakota, Wyoming, and Alberta. Measuring 4.5 m (15 ft) and weighing 450 kg (990 lb), the species is known mainly from a single skull, plus a few extremely thick skull roofs. More complete fossils would come to be found in the following years.

Stegoceras is a genus of pachycephalosaurid (dome-headed) dinosaur that lived in what is now North America during the Late Cretaceous period, about 77.5 to 74 million years ago (mya). The first specimens from Alberta, Canada, were described in 1902, and the type species Stegoceras validum was based on these remains. The generic name means "horn roof", and the specific name means "strong". Several other species have been placed in the genus over the years, but these have since been moved to other genera or deemed junior synonyms. Currently only S. validum and S. novomexicanum, named in 2011 from fossils found in New Mexico, remain. The validity of the latter species has also been debated, and it may not even belong to the genus Stegoceras.

Homalocephale is a genus of pachycephalosaurid dinosaur that lived during the Late Cretaceous period of what is now the Nemegt Formation, Mongolia, about 70 million years ago. The genus was described in 1974 by Halszka Osmólska and Teresa Maryańska, and consists of a single species, H. calathocercos. Though Homalocephale has been regarded as a synonym of Prenocephale, juvenile specimens of the latter indicate that they were distinct. Homalocephale was 1.8 m (5.9 ft) long and possibly an omnivore.

Yaverlandia is a genus of maniraptoran dinosaur. Known from a partial fossil skull found in Lower Cretaceous strata of the Wessex Formation on the Isle of Wight. it was described as the earliest known member of the pachycephalosaurid family, but research by Darren Naish shows it to have actually been a theropod, seemingly a maniraptoran. The type species is Y. bitholus.

Tylocephale is a genus of pachycephalosaurid dinosaur, a group of dome-headed, herbivorous ornithischians, that lived during the Late Campanian stage of the Late Cretaceous in what is now Mongolia. It is known from a partial skull and associated mandible that were unearthed in 1971 by a Polish-Mongolian Expedition to the Barun Goyot Formation of the Gobi Desert. The specimen was described in 1974 by Polish paleontologists Teresa Maryańska and Halszka Osmólska as a new genus and species.

Goyocephale is an extinct genus of pachycephalosaurian ornithischian that lived in Mongolia during the Late Cretaceous about 76 million years ago. It was first described in 1982 by Altangerel Perle, Teresa Maryańska and Halszka Osmólska for a disarticulated skeleton with most of a skull, part of the forelimb and hindlimb, some of the pelvic girdle, and some vertebrae. Perle et al. named the remains Goyocephale lattimorei, from the Mongolian гоё (goyo), meaning "decorated", and the Ancient Greek κεφαλή (kephale), for head. The species name honours Owen Lattimore.

Sphaerotholus is a genus of pachycephalosaurid dinosaur from the Upper Cretaceous of the western United States and Canada. To date, five species have been described: the type species, S. goodwini, from the Den-na-zin Member of the Kirtland Formation and possibly the Fossil Forest Member of the Fruitland Formation of San Juan County, New Mexico, USA; S. buchholtzae, from the Hell Creek Formation of western Carter County, Montana, USA and the Frenchman Formation of Saskatchewan, Canada; S. edmontonensis, from the Horseshoe Canyon Formation of Alberta, Canada; S. lyonsi, from the Dinosaur Park Formation (Campanian) of Alberta, Canada; and S. triregnum from the Hell Creek Formation of Garfield County, Montana, USA.
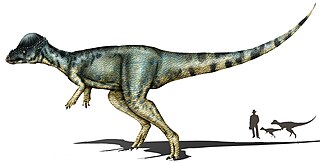
Alaskacephale is an extinct genus of pachycephalosaurid, a group of dome-headed, herbivorous ornithischian dinosaurs, that lived during the Maastrichtian stage of the Late Cretaceous period in what is now northern Alaska The genus is one of the few known Arctic dinosaurs and was found in the Prince Creek Formation, which preserves a menagerie of fossils. The only known specimen, a squamosal bone, was found in 1999 and later described in 2005. However, Alaskacephale was not formally named until the next year.

Halszka Osmólska was a Polish paleontologist who had specialized in Mongolian dinosaurs.
Teresa Maryańska was a Polish paleontologist who specialized in Mongolian dinosaurs, particularly pachycephalosaurians and ankylosaurians. Peter Dodson states that in 1974 Maryanska together with Halszka Osmólska were among the first "women to describe new kinds of dinosaurs". She is considered not only as one of Poland's but also one of the world's leading experts on dinosaurs.

Texacephale is a possibly dubious genus of pachycephalosaurid dinosaur from the Campanian stage of the Late Cretaceous. Its fossils come from the Aguja Formation of Big Bend National Park, in Texas, and were described in 2010 by Longrich, Sankey and Tanke. The generic name means Texas + "head" in reference to its place of discovery, and the specific name langstoni honors Wann Langston. It may be a synonym of Stegoceras.

Foraminacephale is a genus of pachycephalosaurid dinosaur from Late Cretaceous deposits of Canada.

Acrotholus is an extinct genus of pachycephalosaur dinosaur that lived during the Santonian of the late Cretaceous, in the Milk River Formation of Canada. The type species, A. audeti, was named after Roy Audet allowing access to his ranch leading to the discovery of the species. The discovery of this specimen lead to several new revelations in the fossil records questioning the preservation of small-bodied organisms along with the evolution of early pachycephalosaurs. The iconic cranial dome found on Acrotholus makes it one of the earliest indisputable known members of the pachycephalosaur family.

This timeline of pachycephalosaur research is a chronological listing of events in the history of paleontology focused on the pachycephalosaurs, a group of dome-skulled herbivorous marginocephalian dinosaurs. One of the first major events related to the history of pachycephalosaur research actually regards the discovery of an unrelated dinosaur called Troodon, reported from the western United States by Joseph Leidy in 1856. The type specimen of Troodon was simply an unusual tooth, but the close resemblance between Troodon teeth and pachycephalosaur teeth would cause taxonomic confusion for over a century. This was resolved by Phil Currie in 1987, who realized that Troodon belonged to a group of bird-like carnivores then known as saurornithoidids, but since renamed Troodontidae after Troodon itself. The first scientifically documented true pachycephalosaur remains were discovered in Early Cretaceous rocks from England and named Stenopelix not long after Troodon was named in America. Other notable early finds include the well-known pachycephalosaur Stegoceras validum.
Sinocephale is a genus of pachycephalosaurid dinosaur that lived in Inner Mongolia, China during the Cretaceous period. The only species, Sinocephale bexelli, was originally named as a species of the genus Troodon in 1953, and later transferred to the genus Stegoceras. After decades of being considered dubious, it was re-evaluated in 2021 and recognized as a valid taxon, being given a unique generic name. The original holotype was lost, with modern research conducted using rediscovered plaster casts. Scant material makes for limited knowledge of its life appearance, but it is distinguished by an embayment on the back of the domed skull, which would give it a heart shape as seen from above. It is potentially the oldest known pachycephalosaurid and falls within the subset of the family called Pachycephalosaurinae, related to animals such as Pachycephalosaurus and Prenocephale. The geologic context of the species has been historically unclear but it is currently thought to originate in rocks belonging to the Ulansuhai Formation.

Jaculinykus is an extinct genus of alvarezsaurid theropod dinosaur from the Late Cretaceous Baruungoyot Formation of Mongolia. The genus contains a single species, J. yaruui, known from a nearly complete articulated skeleton including bones of the skull. Jaculinykus is notable for its unique hand, which has a hypertrophied first digit and greatly reduced second digit, which is intermediate between the tridactyl hand of Shuvuuia and monodactyl hand of Linhenykus.