The RGB color model is an additive color model in which the red, green and blue primary colors of light are added together in various ways to reproduce a broad array of colors. The name of the model comes from the initials of the three additive primary colors, red, green, and blue.
ANSI escape sequences are a standard for in-band signaling to control cursor location, color, font styling, and other options on video text terminals and terminal emulators. Certain sequences of bytes, most starting with an ASCII escape character and a bracket character, are embedded into text. The terminal interprets these sequences as commands, rather than text to display verbatim.
Gamma correction or gamma is a nonlinear operation used to encode and decode luminance or tristimulus values in video or still image systems. Gamma correction is, in the simplest cases, defined by the following power-law expression:
Y′UV, also written YUV, is the color model found in the PAL analogue color TV standard. A color is described as a Y′ component (luma) and two chroma components U and V. The prime symbol (') denotes that the luma is calculated from gamma-corrected RGB input and that it is different from true luminance. Today, the term YUV is commonly used in the computer industry to describe colorspaces that are encoded using YCbCr.

An RGB color space is one of many specific additive colorimetric color spaces based on the RGB color model.
Color management is the process of ensuring consistent and accurate colors across various devices, such as monitors, printers, and cameras. It involves the use of color profiles, which are standardized descriptions of how colors should be displayed or reproduced.

HSL and HSV are alternative representations of the RGB color model, designed in the 1970s by computer graphics researchers. In these models, colors of each hue are arranged in a radial slice, around a central axis of neutral colors which ranges from black at the bottom to white at the top.

The CIELAB color space, also referred to as L*a*b*, is a color space defined by the International Commission on Illumination in 1976. It expresses color as three values: L* for perceptual lightness and a* and b* for the four unique colors of human vision: red, green, blue and yellow. CIELAB was intended as a perceptually uniform space, where a given numerical change corresponds to a similar perceived change in color. While the LAB space is not truly perceptually uniform, it nevertheless is useful in industry for detecting small differences in color.

In color reproduction, including computer graphics and photography, the gamut, or color gamut, is a certain complete subset of colors. The most common usage refers to the subset of colors that can be accurately represented in a given circumstance, such as within a given color space or by a certain output device.
In digital photography, computer-generated imagery, and colorimetry, a grayscale image is one in which the value of each pixel is a single sample representing only an amount of light; that is, it carries only intensity information. Grayscale images, a kind of black-and-white or gray monochrome, are composed exclusively of shades of gray. The contrast ranges from black at the weakest intensity to white at the strongest.

sRGB is a standard RGB color space that HP and Microsoft created cooperatively in 1996 to use on monitors, printers, and the World Wide Web. It was subsequently standardized by the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) as IEC 61966-2-1:1999. sRGB is the current defined standard colorspace for the web, and it is usually the assumed colorspace for images that are neither tagged for a colorspace nor have an embedded color profile.
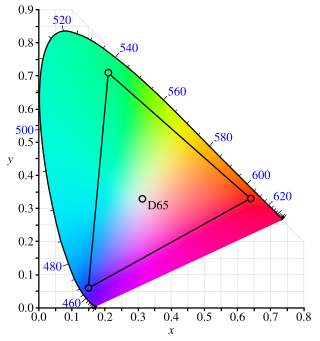
The Adobe RGB (1998) color space or opRGB is a color space developed by Adobe Inc. in 1998. It was designed to encompass most of the colors achievable on CMYK color printers, but by using RGB primary colors on a device such as a computer display. The Adobe RGB (1998) color space encompasses roughly 50% of the visible colors specified by the CIELAB color space – improving upon the gamut of the sRGB color space, primarily in cyan-green hues. It was subsequently standardized by the IEC as IEC 61966-2-5:1999 with a name opRGB and is used in HDMI.

In photography and image processing, color balance is the global adjustment of the intensities of the colors. An important goal of this adjustment is to render specific colors – particularly neutral colors like white or grey – correctly. Hence, the general method is sometimes called gray balance, neutral balance, or white balance. Color balance changes the overall mixture of colors in an image and is used for color correction. Generalized versions of color balance are used to correct colors other than neutrals or to deliberately change them for effect. White balance is one of the most common kinds of balancing, and is when colors are adjusted to make a white object appear white and not a shade of any other colour.

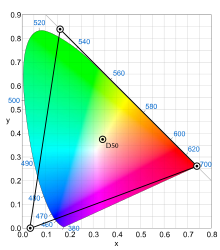
The CIE 1931 color spaces are the first defined quantitative links between distributions of wavelengths in the electromagnetic visible spectrum, and physiologically perceived colors in human color vision. The mathematical relationships that define these color spaces are essential tools for color management, important when dealing with color inks, illuminated displays, and recording devices such as digital cameras. The system was designed in 1931 by the "Commission Internationale de l'éclairage", known in English as the International Commission on Illumination.

Photo CD is a system designed by Kodak for digitizing and saving photos onto a CD. Launched in 1991, the discs were designed to hold nearly 100 high quality images, scanned prints and slides using special proprietary encoding. Photo CDs are defined in the Beige Book and conform to the CD-ROM XA and CD-i Bridge specifications as well. They were intended to play on CD-i players, Photo CD players, and any computer with a suitable software.

Histogram equalization is a method in image processing of contrast adjustment using the image's histogram.
xvYCC or extended-gamut YCbCr is a color space that can be used in the video electronics of television sets to support a gamut 1.8 times as large as that of the sRGB color space. xvYCC was proposed by Sony, specified by the IEC in October 2005 and published in January 2006 as IEC 61966-2-4. xvYCC extends the ITU-R BT.709 tone curve by defining over-ranged values. xvYCC-encoded video retains the same color primaries and white point as BT.709, and uses either a BT.601 or BT.709 RGB-to-YCC conversion matrix and encoding. This allows it to travel through existing digital limited range YCC data paths, and any colors within the normal gamut will be compatible. It works by allowing negative RGB inputs and expanding the output chroma. These are used to encode more saturated colors by using a greater part of the RGB values that can be encoded in the YCbCr signal compared with those used in Broadcast Safe Level. The extra-gamut colors can then be displayed by a device whose underlying technology is not limited by the standard primaries.
The Academy Color Encoding System (ACES) is a color image encoding system created under the auspices of the Academy of Motion Picture Arts and Sciences. ACES is characterised by a color accurate workflow, with "seamless interchange of high quality motion picture images regardless of source".

ICTCP, ICtCp, or ITP is a color representation format specified in the Rec. ITU-R BT.2100 standard that is used as a part of the color image pipeline in video and digital photography systems for high dynamic range (HDR) and wide color gamut (WCG) imagery. It was developed by Dolby Laboratories from the IPT color space by Ebner and Fairchild. The format is derived from an associated RGB color space by a coordinate transformation that includes two matrix transformations and an intermediate nonlinear transfer function that is informally known as gamma pre-correction. The transformation produces three signals called I, CT, and CP. The ICTCP transformation can be used with RGB signals derived from either the perceptual quantizer (PQ) or hybrid log–gamma (HLG) nonlinearity functions, but is most commonly associated with the PQ function.
The European Color Initiative (ECI) is an expert group that is concerned with media-neutral reproduction of color data in digital publication systems. It was formed in June 1996 by German publishers Bauer, Burda, Gruner + Jahr and Springer in Hamburg.