Thiamine, also known as thiamin and vitamin B1, is a vitamin, an essential micronutrient for humans and animals. It is found in food and commercially synthesized to be a dietary supplement or medication. Phosphorylated forms of thiamine are required for some metabolic reactions, including the breakdown of glucose and amino acids.

Vitamins are organic molecules that are essential to an organism in small quantities for proper metabolic function. Essential nutrients cannot be synthesized in the organism in sufficient quantities for survival, and therefore must be obtained through the diet. For example, vitamin C can be synthesized by some species but not by others; it is not considered a vitamin in the first instance but is in the second. Most vitamins are not single molecules, but groups of related molecules called vitamers. For example, there are eight vitamers of vitamin E: four tocopherols and four tocotrienols.

Biotin (also known as vitamin B7 or vitamin H) is one of the B vitamins. It is involved in a wide range of metabolic processes, both in humans and in other organisms, primarily related to the utilization of fats, carbohydrates, and amino acids. The name biotin, borrowed from the German Biotin, derives from the Ancient Greek word βίοτος (bíotos; 'life') and the suffix "-in" (a suffix used in chemistry usually to indicate 'forming'). Biotin appears as a white, needle-like crystalline solid.
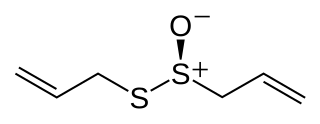
Allicin is an organosulfur compound obtained from garlic and leeks. When fresh garlic is chopped or crushed, the enzyme alliinase converts alliin into allicin, which is responsible for the aroma of fresh garlic. Allicin is unstable and quickly changes into a series of other sulfur-containing compounds such as diallyl disulfide. Allicin is an antifeedant, i.e. the defense mechanism against attacks by pests on the garlic plant.
B vitamins are a class of water-soluble vitamins that play important roles in cell metabolism and synthesis of red blood cells. They are a chemically diverse class of compounds.
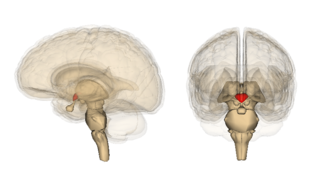
Wernicke encephalopathy (WE), also Wernicke's encephalopathy, or wet brain is the presence of neurological symptoms caused by biochemical lesions of the central nervous system after exhaustion of B-vitamin reserves, in particular thiamine (vitamin B1). The condition is part of a larger group of thiamine deficiency disorders that includes beriberi, in all its forms, and alcoholic Korsakoff syndrome. When it occurs simultaneously with alcoholic Korsakoff syndrome it is known as Wernicke–Korsakoff syndrome.

Pyritinol also called pyridoxine disulfide or pyrithioxine (European drug names Encephabol, Encefabol, Cerbon 6) is a semi-synthetic water-soluble analog of vitamin B6 (Pyridoxine HCl). It was produced in 1961 by Merck Laboratories by bonding 2 vitamin B6 compounds (pyridoxine) together with a disulfide bridge. Since the 1970s, it has been a prescription and OTC drug in several countries for cognitive disorders, rheumatoid arthritis, and learning disorders in children. Since the early 1990s it has been sold as a nootropic dietary supplement in the United States.
Thiazole, or 1,3-thiazole, is a 5-membered heterocyclic compound that contains both sulfur and nitrogen. The term 'thiazole' also refers to a large family of derivatives. Thiazole itself is a pale yellow liquid with a pyridine-like odor and the molecular formula C3H3NS. The thiazole ring is notable as a component of the vitamin thiamine (B1).
Food fortification is the addition of micronutrients to food products. Food enrichment specifically means adding back nutrients lost during food processing, while fortification includes adding nutrients not naturally present. Food manufacturers and governments have used these practices since the 1920s to help prevent nutrient deficiencies in populations. Common nutrient deficiencies in a region often result from local soil conditions or limitations of staple foods. The addition of micronutrients to staples and condiments can prevent large-scale deficiency diseases in these cases.

Thiamine deficiency is a medical condition of low levels of thiamine (vitamin B1). A severe and chronic form is known as beriberi. The name beriberi was possibly borrowed in the 18th century from the Sinhalese phrase බැරි බැරි (bæri bæri, “I cannot, I cannot”), owing to the weakness caused by the condition. The two main types in adults are wet beriberi and dry beriberi. Wet beriberi affects the cardiovascular system, resulting in a fast heart rate, shortness of breath, and leg swelling. Dry beriberi affects the nervous system, resulting in numbness of the hands and feet, confusion, trouble moving the legs, and pain. A form with loss of appetite and constipation may also occur. Another type, acute beriberi, found mostly in babies, presents with loss of appetite, vomiting, lactic acidosis, changes in heart rate, and enlargement of the heart.

Sulbutiamine sold under the brand names Arcalion, Enerion, and Sulbuxin is a synthetic derivative of thiamine (vitamin B1). In France, it is used to treat symptoms of weakness or fatigue. In Uruguay, it is prescribed when there is thiamine deficiency, mainly in patients with asthenia, overwork, apathy, depressive states, memory disorders, and iatrogenic disorders of wakefulness. It is also sold as a dietary supplement. Sulbutiamine was discovered in Japan as part of an effort to develop useful thiamine derivatives.

Thiamine triphosphate (ThTP) is a biomolecule found in most organisms including bacteria, fungi, plants and animals. Chemically, it is the triphosphate derivative of the vitamin thiamine.

Benfotiamine is a synthetic, fat-soluble, S-acyl derivative of thiamine that is approved in some countries as a medication or dietary supplement to treat diabetic sensorimotor polyneuropathy. Benfotiamine was developed in late 1950s in Japan.

Allithiamine (thiamine allyl disulfide or TAD) is a lipid-soluble form of vitamin B1 which was discovered in garlic (Allium sativum) in the 1950s along with its homolog prosultiamine. They were both investigated for their ability to treat Wernicke–Korsakoff syndrome and beriberi better than thiamine.

Nutritional neuroscience is the scientific discipline that studies the effects various components of the diet such as minerals, vitamins, protein, carbohydrates, fats, dietary supplements, synthetic hormones, and food additives have on neurochemistry, neurobiology, behavior, and cognition.

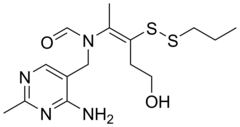
Fursultiamine is a medication and vitamin used to treat thiamine deficiency. Chemically, it is a disulfide derivative of thiamine and is similar in structure to allithiamine.

Lipase inhibitors are substances used to reduce the activity of lipases found in the intestine. Lipases are secreted by the pancreas when fat is present. The primary role of lipase inhibitors is to decrease the gastrointestinal absorption of fats. Fats then tend to be excreted in feces rather than being absorbed to be used as a source of caloric energy, and this can result in weight loss in individuals. These inhibitors could be used for the treatment of obesity, which can subsequently lead to Type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular diseases if not managed. An example of a lipase inhibitor is orlistat.

Intravenous Ascorbic Acid or PAA, pharmacologic ascorbic acid, is a process that delivers soluble ascorbic acid directly into the bloodstream. It is not approved for use to treat any medical condition.

Russell Morse Wilder Sr. was an American physician, diabetologist, epileptologist, and medical researcher, known as one of the originators of the ketogenic diet as a therapy for both epilepsy and diabetes. He coined the term "ketogenic diet." He was also among the first American physicians to use insulin for patients with diabetes.
Gary E. Gibson is an American neuroscientist specializing in mitochondrial biology and metabolic dysfunction related to neurodegeneration. He serves as the Lab Director of the Laboratory for Mitochondrial Biology and Metabolic Dysfunction in Neurodegeneration at the Burke Neurological Institute and holds the position of Professor of Neuroscience with tenure at the Brain and Mind Research Institute of Weill Cornell Medicine. He also served as associate director of the Dementia Research Service.