 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
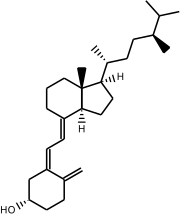
| IUPAC name (3S,5Z,7E)-9,10-Secoergosta-5,7,10(19)-trien-3-ol | |
| Systematic IUPAC name (1S,3Z)-3-[(2E)-2-{(1R,3aS,7aR)-1-[(2R,5S)-5,6-Dimethylheptan-2-yl]-7a-methyloctahydro-4H-inden-4-ylidene}ethylidene]-4-methylidenecyclohexan-1-ol | |
| Other names (5Z,7E)-(3S)-9,10-seco-5,7,10(19)-ergostatrien-3-ol (24S)-Methylcalciol 22,23-Dihydroercalciol [1] Vitamin D4 | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.007.389 |
PubChem CID | |
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C28H46O | |
| Molar mass | 398.675 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
22-Dihydroergocalciferol is a form of vitamin D, also known as vitamin D4. [2] It has the systematic name (5Z,7E)-(3S)-9,10-seco-5,7,10(19)-ergostatrien-3-ol. [1]
Contents
Vitamin D4 is found in certain mushrooms, being produced from ergosta-5,7-dienol (22,23-dihydroergosterol) instead of ergosterol. [3]