
Thiamine, also known as thiamin and vitamin B1, is a vitamin, an essential micronutrient for humans and animals. It is found in food and commercially synthesized to be a dietary supplement or medication. Phosphorylated forms of thiamine are required for some metabolic reactions, including the breakdown of glucose and amino acids.

Vitamin K is a family of structurally similar, fat-soluble vitamers found in foods and marketed as dietary supplements. The human body requires vitamin K for post-synthesis modification of certain proteins that are required for blood coagulation or for controlling binding of calcium in bones and other tissues. The complete synthesis involves final modification of these so-called "Gla proteins" by the enzyme gamma-glutamyl carboxylase that uses vitamin K as a cofactor.

Vitamin B6 is one of the B vitamins, and is an essential nutrient for humans. The term essential nutrient refers to a group of six chemically similar compounds, i.e., "vitamers", which can be interconverted in biological systems. Its active form, pyridoxal 5′-phosphate, serves as a coenzyme in more than 140 enzyme reactions in amino acid, glucose, and lipid metabolism.

Methionine is an essential amino acid in humans.

In chemistry, a hydrochloride is an acid salt resulting, or regarded as resulting, from the reaction of hydrochloric acid with an organic base. An alternative name is chlorhydrate, which comes from French. An archaic alternative name is muriate, derived from hydrochloric acid's ancient name: muriatic acid.

Trimethylglycine is an amino acid derivative with the formula (CH3)3N+CH2CO−2. A colorless, water-soluble solid, it occurs in plants. Trimethylglycine is a zwitterion: the molecule contains both a quaternary ammonium group and a carboxylate group. Trimethylglycine was the first betaine discovered; originally it was simply called betaine because it was discovered in sugar beets. Several other betaines are now known.

Alfuzosin, sold under the brand name Uroxatral among others, is a medication of the α1 blocker class. It is used to treat benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH).
In organic chemistry, an azo coupling is an reaction between a diazonium compound and another aromatic compound that produces an azo compound. In this electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction, the aryldiazonium cation is the electrophile, and the activated carbon, serves as a nucleophile. Classical coupling agents are phenols and naphthols. Usually the diazonium reagent attacks at the para position of the coupling agent. When the para position is occupied, coupling occurs at a ortho position, albeit at a slower rate.

Menadione is a synthetic organic compound with the formula C6H4(CO)2C2H(CH3). It is an analog of 1,4-naphthoquinone with a methyl group in the 2-position. It is sometimes called vitamin K3. Use is allowed as a nutritional supplement in animal feed because of its vitamin K activity.

Methyltransferases are a large group of enzymes that all methylate their substrates but can be split into several subclasses based on their structural features. The most common class of methyltransferases is class I, all of which contain a Rossmann fold for binding S-Adenosyl methionine (SAM). Class II methyltransferases contain a SET domain, which are exemplified by SET domain histone methyltransferases, and class III methyltransferases, which are membrane associated. Methyltransferases can also be grouped as different types utilizing different substrates in methyl transfer reactions. These types include protein methyltransferases, DNA/RNA methyltransferases, natural product methyltransferases, and non-SAM dependent methyltransferases. SAM is the classical methyl donor for methyltransferases, however, examples of other methyl donors are seen in nature. The general mechanism for methyl transfer is a SN2-like nucleophilic attack where the methionine sulfur serves as the leaving group and the methyl group attached to it acts as the electrophile that transfers the methyl group to the enzyme substrate. SAM is converted to S-Adenosyl homocysteine (SAH) during this process. The breaking of the SAM-methyl bond and the formation of the substrate-methyl bond happen nearly simultaneously. These enzymatic reactions are found in many pathways and are implicated in genetic diseases, cancer, and metabolic diseases. Another type of methyl transfer is the radical S-Adenosyl methionine (SAM) which is the methylation of unactivated carbon atoms in primary metabolites, proteins, lipids, and RNA.

Anthranilic acid is an aromatic acid with the formula C6H4(NH2)(CO2H) and has a sweetish taste. The molecule consists of a benzene ring, ortho-substituted with a carboxylic acid and an amine. As a result of containing both acidic and basic functional groups, the compound is amphoteric. Anthranilic acid is a white solid when pure, although commercial samples may appear yellow. The anion [C6H4(NH2)(CO2)]−, obtained by the deprotonation of anthranilic acid, is called anthranilate. Anthranilic acid was once thought to be a vitamin and was referred to as vitamin L1 in that context, but it is now known to be non-essential in human nutrition.

Menatetrenone (INN), also known as menaquinone-4 (MK-4), is one of the nine forms of vitamin K2.
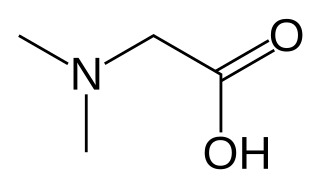
Dimethylglycine (DMG) is a derivative of the amino acid glycine with the structural formula (CH3)2NCH2COOH. It can be found in beans and liver, and has a sweet taste. It can be formed from trimethylglycine upon the loss of one of its methyl groups. It is also a byproduct of the metabolism of choline.

Iproheptine, also known as N-isopropyl-1,5-dimethylhexylamine or N-isopropyloctodrine and sold under the brand names Metron and Susat, is a nasal decongestant which has been marketed in Japan. It is described as a vasoconstrictor and antihistamine. The drug is available over-the-counter in Japan.
1-Naphthol, or α-naphthol, is an organic compound with the formula C10H7OH. It is a fluorescent white solid. 1-Naphthol differs from its isomer 2-naphthol by the location of the hydroxyl group on the naphthalene ring. The naphthols are naphthalene homologues of phenol. Both isomers are soluble in simple organic solvents. They are precursors to a variety of useful compounds.
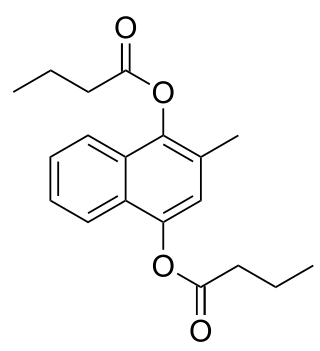
Menadiol is an organic compound with the formula C6H4(COH)2(CH)(CH3). It is formally a derivative of p-hydroquinone. The name vitamin K4 can refer to:
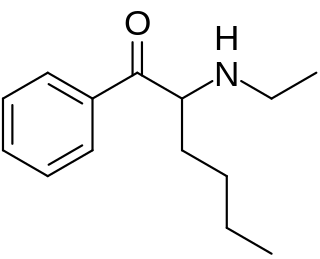
N-Ethylhexedrone (also known as α-ethylaminocaprophenone, N-ethylnorhexedrone, hexen, and NEH) is a stimulant of the cathinone class that acts as a norepinephrine–dopamine reuptake inhibitor (NDRI) with IC50 values of 0.0978 and 0.0467 μM, respectively. N-Ethylhexedrone was first mentioned in a series of patents by Boehringer Ingelheim in the 1960s which led to the development of the better-known drug methylenedioxypyrovalerone (MDPV). Since the mid-2010s, N-ethylhexedrone has been sold online as a designer drug. In 2018, N-ethylhexedrone was the second most common drug of the cathinone class to be identified in Drug Enforcement Administration seizures.

4-Amino-2-methyl-1-naphthol is a menadione analog. Its water-soluble hydrochloride (HCl) salt is often called vitamin K5. The HCl salt has been used as a medicine for vitamin K deficiency under tradenames such as Synkamin, which was sold by Parke-Davis, but has since been discontinued.
The molecular formula C11H11NO (molar mass: 173.211 g/mol, exact mass: 173.0841 u) may refer to:

2-Methylnaphthalene-1,4-diamine is a synthetic menadione analog with vitamin K activity.

















