
The common dace is a species of freshwater and brackish water ray-finned fish from the family Cyprinidae which is native to Europe but which has been introduced to other parts of the world. It is a quarry species for coarse anglers.

The round goby is a euryhaline bottom-dwelling species of fish of the family Gobiidae. It is native to Central Eurasia, including the Black Sea and the Caspian Sea. Round gobies have established large non-native populations in the Baltic Sea, several major Eurasian rivers, and the North American Great Lakes.

Eucyclogobius newberryi, the northern tidewater goby, is a species of goby native to lagoons of streams, marshes, and creeks along the coast of California, United States. The northern tidewater goby is one of six native goby species of California. It is protected under the Endangered Species Act as an endangered species of the United States since 1994.

Benthophiloides brauneri is a species of goby, a benthophilic fish native to the fresh and brackish waters of the Black Sea, the Caspian Sea and the Sea of Azov as well as their surrounding rivers and estuaries. Despite the wide distribution, very few observations overall of this fish exist, and just one from the Caspian basin. It has been found in still waters at depths down to around 15 metres (49 ft). Males of this species can reach a length of 7.2 centimetres (2.8 in) SL while females only reach 5.1 centimetres (2.0 in) SL. This fish only lives for one year.

Neogobius is a genus of goby native to Black Sea and the Caspian Sea basins. It is part of the broader Benthophilinae subfamily which is also endemic to the same region. Nevertheless, two Neogobius species have recently turned out to be highly invasive and spread across Europe and even to the Great Lakes of North America.

The racer goby is a species of goby native to fresh, sometimes brackish, waters, of the Black Sea basin. It is a Ponto-Caspian relict species. The species is placed a monotypic genus, Babka, which was once considered a subgenus of genus Neogobius, but was then elevated to genus-status based on the molecular analysis.
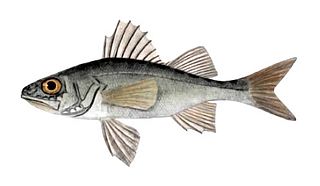
Common percarina is a species of fish in the family Percidae. It is found in northwestern Black Sea basin in estuaries and coastal lakes, and in the lower reaches of the rivers that drain into that part of the Black Sea. It is a carnivorous species.

The Chinese sleeper, also known as the Amur sleeper, is a species of freshwater sleeper native to the Amur River basin in eastern Asia with introduced populations in other regions of Eurasia. It is currently the only known member of its genus.

The Chornaya tubenose goby is a species of goby endemic to Crimea, Ukraine where it is only found in a short stretch of River Chornaya. Water is extracted in large quantities for irrigation could cause the stream to completely dry out in summer and thus poses a critical risk of extinction in a near future.

The western tubenose goby is a species of goby native to fresh waters of the Black Sea and Aegean Sea basins. It has recently spread as an invasive species to Central and Western Europe and to North America. Previously Proterorhinus semilunaris was considered as a junior synonym of Proterorhinus marmoratus, but was confirmed as a distinct species based on molecular analysis.

Ponticola is a genus of gobies native mostly to fresh waters of the Black Sea - Caspian Sea region in Eurasia. Some species occur in the brackish-water Black and Caspian seas themselves. It was considered to be part of the broader goby subfamily Benthophilinae, also endemic to the same region, although the 5th edition of Fishes of the World does not list any subfamilies in the Gobiidae. Originally, Ponticola was described as subgenus of Neogobius.

Proterorhinus semipellucidus is a species of gobiid fish, a tubenose goby originally described from the Gharasu River near Gorgan Bay of the Caspian Sea in Iran. Following the systematic decomposition of the tubenose gobies it was suggested to be a more widespread and invasive taxon distributed in the fresh waters of the Caspian Sea basin. It may be the same species as that known as Proterorhinus nasalis.

Proterorhinus is a genus of fishes, known as the tubenose gobies. These gobiid fish are native to Eurasia where they occur in the region of the Caspian and Black seas, inhabiting marine, brackish and fresh waters. The species Proterorhinus semilunaris was introduced to the St. Clair River in Michigan during the late 1990s. Until recently, the genus was considered monotypic, comprising only the tubenose goby. Following molecular and further morphological investigations it has been split into several taxa, with distinct distributions in marine vs. fresh waters and in the Black Sea vs. Caspian Sea basins.

The eastern tubenose goby is a species of gobiid fish native to fresh and brackish waters of the basins of the Sea of Azov and the Caspian Sea and has invaded the upper reaches of the Volga River from its native occurrence in the delta. This species prefers slow flowing rivers or still waters with plentiful rocks or vegetation. It can reach a length of 9 centimetres (3.5 in) SL. It is probably the same species as that recently treated as Proterorhinus semipellucidus.

The Black Sea tadpole-goby is a species of goby native to the basin of the Black Sea. Found in the Gulf of Tendra and limans of the north-western Black Sea, lakes of the Danube Delta. In the rivers of the Black Sea basin: Danube up to Iron Gate dam, Dniester up to Tighina, Dnieper up to Kyiv, Southern Bug. This species is mostly a denizen of fresh and slightly brackish bodies of water, preferring rivers and deltas, limans and coastal lakes. This fish can reach a length of 15 centimetres (5.9 in) TL.
Neogobius pallasi, the Caspian sand goby or the Caspian monkey goby, is a species of fish native to fresh and brackish waters of the Caspian Sea basin including the Volga drainage up to the vicinity of Moscow. It has been introduced into the Aral basin. This species of goby can reach a length of 20 centimetres (7.9 in) SL. It is also important to local commercial fisheries.

Neogobius bathybius is a species of goby endemic to the Caspian Sea, where it occurs in depths down to 200 metres (660 ft). It is strictly confined to the brackish-water basin and does not enter fresh waters. It can grow up to a length of 25 centimetres (9.8 in) TL.
Carol Ann Stepien is an American ecologist at the National Museum of Natural History of the Smithsonian Institution. She was elected a fellow of the American Association for the Advancement of Science in 2016.
Holostephanus cobitidis is a species of parasitic trematode in the family Cyathocotylidae.

















