
The hammerjaw, Omosudis lowii, is a small deep-sea aulopiform fish, found worldwide in tropical and temperate waters to 4,000 m (13,000 ft) depth. It is the only representative of its family, Omosudidae.
This glossary of ichthyology is a list of definitions of terms and concepts used in ichthyology, the study of fishes.

The greenback flounder is a righteye flounder of the genus Rhombosolea, found around southern Australia and New Zealand.

Cynoscion acoupa, the acoupa weakfish, blacktail basher or grey snapper, is a species of marine ray-finned fish belonging to the family Sciaenidae, the drums and croakers. This fish is found in the western Atlantic.

Brachypterois serrulata, the sawcheek scorpionfish or pygmy lionfish, is a species of scorpionfish native to the northwestern Pacific Ocean.

The yellowtail trumpeter is a common species of coastal marine fish of the grunter family, Terapontidae. The yellowtail trumpeter is native to Australia and Papua New Guinea, ranging from Cape Leeuwin in Western Australia along the north coast to Bowen, Queensland, and along the southern coast of Papua New Guinea.

The European flounder is a flatfish of European coastal waters from the White Sea in the north to the Mediterranean and the Black Sea in the south. It has been introduced into the United States and Canada accidentally through transport in ballast water. It is caught and used for human consumption.

The shadow trevally, also known as the shadow kingfish, twothread trevally or Aldabra trevally, is a species of inshore marine fish in the jack family Carangidae. The species is patchily distributed throughout the tropical and subtropical waters of the Indian and west Pacific Oceans, from South Africa in the west to Japan and Samoa in the east, reaching as far south as Indonesia and New Caledonia. It is most easily distinguished from similar species by as series of dark rectangular blotches under the second dorsal fin, giving a 'shadowed' appearance, from which its common name is derived. The shadow trevally is a reasonably large fish, growing to 85 cm in length and at least 2.6 kg in weight. It inhabits shallow coastal waters, including reefs, bays, and estuaries, where it takes small fish and benthic crustaceans as prey. Nothing is known of the species' ecology and reproductive biology. It is of little importance to fisheries, and is occasionally taken by bottom trawls and other artisanal fishing gear.

The coachwhip trevally, also known as the oblong trevally or oblique-banded trevally, is a species of inshore marine fish classified in the jack family Carangidae. The coachwhip trevally is distributed through the Indo-west Pacific region, ranging from South Africa in the west to Fiji and Japan in the east. It is a moderately large fish, growing to a known maximum length of 46 cm and can be distinguished from similar species by an array of detailed morphological features including dentition, fin ray counts and scale patterns. The coachwhip trevally inhabits coastal waters throughout its range, known to prefer estuarine waters in a number of localities. Nothing is known of its diet or reproductive biology, and is of little importance to fisheries, occasionally taken as bycatch in trawl and hook and line fisheries.

Magosternarchus is a genus of weakly electric knifefish in the family Apteronotidae, containing two species. They are endemic to Brazil, occurring in large river channels in the Amazon River basin. Both species are unusual benthic predators that specialize in biting off the tails of other knifefishes, and are characterized by their greatly enlarged jaws and teeth. Recent systematic studies indicate that both species should be included in Sternarchella instead of being placed in their own genus.

The sailfin snapper, blue-lined sea bream or blue-lined sea perch is a species of marine ray-finned fish, a snapper belonging to the family Lutjanidae. It is native to the Indo-Pacific region. It is of minor importance to local commercial fisheries and can be found in the aquarium trade. It is currently the only known member of its genus.

The coral hawkfish, the pixy hawkfish or sharp-headed hawkfish, is a species of marine ray-finned fish, a hawkfish belonging to the family Cirrhitidae. It is native to tropical reefs of the Indian Ocean and the Pacific Ocean. It occasionally is found in the aquarium trade.

The snake mackerel is the sole species of fish in the monotypic genus Gempylus, belonging to the family Gempylidae. It is found worldwide in tropical and subtropical oceans between the latitudes of 42°N and 40°S; adults are known to stray into temperate waters. It is found to a depth of 600 meters. Populations of the snake mackerel from the Atlantic and the Indo-Pacific differ in vertebral count and number of first dorsal fin spines, and so may represent separate species.

The smallscale lizardfish(Saurida caribbaea) is a species of lizardfish that lives mainly in the Western Atlantic.

Cirrhibarbis capensis, the barbelled klipfish, is a species of clinid found in subtropical waters of the Atlantic Ocean around South Africa. This species can reach a maximum length of 36 centimetres (14 in) TL. This species preys primarily on benthic crustaceans, mostly amphipods and isopods. It is currently the only known member of its genus.
Gobioclinus gobio is a strictly marine ray finned fish, also called Gobioclinus gobio. Its common name is the palehead blenny, and is sometimes referred to as the goggle-eye blenny. It can be identified by its greenish top, red belly, and multicolored banding. L. gobio is a benthic organism with a wide range, taking up residence in a number of coastal environments from Florida to Brazil. This means the fish can live in equatorial, subtropical, and tropical climatic zones. It is native to coastal areas of the Caribbean. Its diet consists mainly of different molluscs and echinoderms.

The Indian threadfin is a species of marine ray-finned fish from the family Polynemidae, the threadfins. It is a coastal species from south-east Asia which has been recorded in Papua New Guinea.
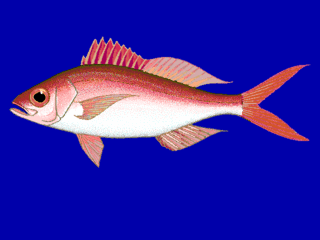
The queen snapper, also known as the night snapper or brim snapper, is a species of ray-finned fish, a snapper belonging to the family Lutjanidae. It is native to the western Atlantic Ocean, and is the only species in the genus Etelis found outside the Indo-Pacific region.

The broomtail grouper or mangrove grouper is a species of ray-finned fish from the family Serranidae which is found in the eastern Pacific along the western coast of the Americas from California to Peru.
Archolaemus luciae is a species of glass knifefish endemic to Brazil where it is found in the Rio Jari, the Rio Trombetas and the Rio Tapajós basins in the eastern Amazon. Also found in the Rio Araguari. This species reaches a length of 49.7 cm (19.6 in).















