Punta de Balasto | |
|---|---|
Municipality and village | |
| Country | |
| Province | Catamarca Province |
| Time zone | UTC−3 (ART) |
Punta de Balasto is a village and municipality in Catamarca Province in northwestern Argentina. [1]
Punta de Balasto | |
|---|---|
Municipality and village | |
| Country | |
| Province | Catamarca Province |
| Time zone | UTC−3 (ART) |
Punta de Balasto is a village and municipality in Catamarca Province in northwestern Argentina. [1]

The Arctic Archipelago, also known as the Canadian Arctic Archipelago, is an archipelago lying to the north of the Canadian continental mainland, excluding Greenland and Iceland.

Palmer Land is the portion of the Antarctic Peninsula, Antarctica that lies south of a line joining Cape Jeremy and Cape Agassiz. This application of Palmer Land is consistent with the 1964 agreement between the Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names and the UK Antarctic Place-Names Committee, in which the name Antarctic Peninsula was approved for the major peninsula of Antarctica, and the names Graham Land and Palmer Land for the northern and southern portions, respectively. The line dividing them is roughly 69° S.

The Aldermen Islands are a small group of rocky islets to the southeast of Mercury Bay in the North Island of New Zealand. They are located off the coast of the Coromandel Peninsula, 20 kilometres (12 mi) east of the mouth of the Tairua River.

Palacios de la Sierra is a small town and municipality in the Spanish province of Burgos. The local economy is primarily based on agriculture and logging.

Alonso de Ibáñez is a province in the northern parts of the Bolivian Potosí Department. Its capital is Sacaca.

Northeast Glacier is a steep, heavily crevassed glacier on the west side of Hemimont Plateau, 21 km (13 mi) long and 8 km (5 mi) wide at its mouth, which flows from McLeod Hill westward and then south-westwards into Marguerite Bay between the Debenham Islands and Roman Four Promontory, on the west coast of Graham Land, Antarctica. Northeast Glacier was first surveyed in 1936 by the British Graham Land Expedition (BGLE) under John Riddoch Rymill. It was resurveyed in 1940 by members of the United States Antarctic Service (USAS), who first used the glacier as a sledging route, and so named by them because it lay on the north-eastern side of their base at Stonington Island.
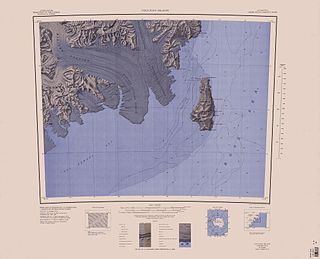
Borchgrevink Glacier is a large glacier in the Victory Mountains, Victoria Land, draining south between Malta Plateau and Daniell Peninsula, and thence projecting into Glacier Strait, Ross Sea, as a floating glacier tongue, the Borchgrevink Glacier Tongue, just south of Cape Jones. It was named by the New Zealand Geological Survey Antarctic Expedition, 1957–58, for Carsten Borchgrevink, leader of the British Antarctic Expedition, 1898–1900. Borchgrevink visited the area in February 1900 and first observed the seaward portion of the glacier.

The Prince Charles Mountains are a major group of mountains in Mac. Robertson Land in Antarctica, including the Athos Range, the Porthos Range, and the Aramis Range. The highest peak is Mount Menzies, with a height of 3,228 m (10,591 ft). Other prominent peaks are Mount Izabelle and Mount Stinear. These mountains, together with other scattered peaks, form an arc about 420 km (260 mi) long, extending from the vicinity of Mount Starlight in the north to Goodspeed Nunataks in the south.

Grenadines is an administrative parish of Saint Vincent and the Grenadines, comprising the islands of the Grenadines other than those belonging to Grenada. The capital is Port Elizabeth.
Extension Reef is a reef which encompasses a large number of small islands and rocks, extending 10 miles (16 km) southwest from the south end of Rabot Island, in the Biscoe Islands. It was first charted and named by the British Graham Land Expedition, 1934–37, under John Rymill.

HNLMS Isaac Sweers was one of four Gerard Callenburgh-class destroyer built for the Royal Netherlands Navy during World War II.
Bredbo River, a perennial stream that is part of the Murrumbidgee catchment within the Murray–Darling basin, is located in the Monaro region of New South Wales, Australia.

Gaspar, Santa Catarina is a municipality in the state of Santa Catarina in the South region of Brazil.

Breitfuss Glacier is a glacier 10 nautical miles (19 km) long, which flows southeast from Avery Plateau into Mill Inlet to the west of Cape Chavanne, on the east coast of Graham Land. It was charted by the Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey (FIDS) and photographed from the air by the Ronne Antarctic Research Expedition in 1947. It was named by the FIDS for Leonid Breitfuss, a German polar explorer, historian, and author of many polar bibliographies.
Neff Nunatak is a nunatak rising to about 1,500 m, located 1 nautical mile (1.9 km) southeast of Schmutzler Nunatak in the southeast end of the Grossman Nunataks, Palmer Land. Mapped by United States Geological Survey (USGS) from U.S. Navy aerial photographs taken 1965–68. Named by Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names (US-ACAN) in 1988 after Richard J. Neff, USGS cartographer, a member of the winter party at Australia's Casey Station, 1975.

Plummer Glacier is a short glacier descending east through the Enterprise Hills to the north of Lippert Peak and the Douglas Peaks, in the Heritage Range in Antarctica. Mapped by United States Geological Survey (USGS) from surveys and U.S. Navy air photos, 1961–66. Named by Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names (US-ACAN) for Charles C. Plummer, United States Antarctic Research Program (USARP) glaciologist at Palmer Station in 1965.
Field Glacier is a glacier on Pernik Peninsula, Loubet Coast in Graham Land, situated south of Salmon Cove, and flowing west into Lallemand Fjord just south of Kanchov Peak. It was mapped from air photos taken by the Falkland Islands and Dependencies Aerial Survey Expedition, 1956–57. In association with the names of glaciologists grouped in this area, it was named by the UK Antarctic Place-Names Committee after William B.O. Field, an American glaciologist and surveyor, sometime Research Fellow of the American Geographical Society.
Squires Glacier is a tributary glacier between the Playfair and Hutton Mountains, flowing east-northeast to Swann Glacier, in Palmer Land. Mapped by United States Geological Survey (USGS) from surveys and U.S. Navy air photos, 1961–67. Named by Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names (US-ACAN) for Peter L. Squires, glaciologist at Byrd Station, summer 1965–66.

The Laputa Nunataks are a range of nunataks and snow-covered hills with minor rock outcrops, rising from about 500 metres (1,600 ft) to over 1,000 metres (3,300 ft), and located 6 nautical miles (11 km) northwest of Adie Inlet on the east side of Graham Land, Antarctica. They were first charted by the Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey and photographed from the air by the Ronne Antarctic Research Expedition in 1947. They were named by the UK Antarctic Place-Names Committee after Laputa, the flying island in Jonathan Swift's Gulliver's Travels.