
Megabats constitute the family Pteropodidae of the order Chiroptera (bats). They are also called fruit bats, Old World fruit bats, or—especially the genera Acerodon and Pteropus—flying foxes. They are the only member of the superfamily Pteropodoidea, which is one of two superfamilies in the suborder Yinpterochiroptera. Internal divisions of Pteropodidae have varied since subfamilies were first proposed in 1917. From three subfamilies in the 1917 classification, six are now recognized, along with various tribes. As of 2018, 197 species of megabat had been described.

The New World leaf-nosed bats (Phyllostomidae) are found from southern North America to South America, specifically from the Southwest United States to northern Argentina. They are ecologically the most varied and diverse family within the order Chiroptera. Most species are insectivorous, but the phyllostomid bats include within their number true predatory species and frugivores. For example, the spectral bat, the largest bat in the Americas, eats vertebrate prey, including small, dove-sized birds. Members of this family have evolved to use food groups such as fruit, nectar, pollen, insects, frogs, other bats, and small vertebrates, and in the case of the vampire bats, even blood.

The Philippine naked-backed fruit bat or Philippine bare-backed fruit bat is a megabat that mostly lives on Negros Island. Two small populations were also found on Cebu Island in the Philippines. Like other bare-backed fruit bats, its wings meet along the midline of their bodies, making it a very agile flier. It roosted in caves, in areas where little light penetrated the gloom. It was so abundant once that it left piles of guano, which were used by miners as fertiliser.

The little red flying-fox is a megachiropteran bat native to northern and eastern Australia. The species weighs about half a kilogram, one US pound, and is the smallest species of Pteropus at the Australian mainland. P. scapulatus occurs at the coast and further inland, camping and flying to the tropical to temperate regions that provide them with an annual source of nectar. They exhibit an unusual method of obtaining drinking water during dry periods, skimming a stream's surface to gather it onto their fur while they are in flight.
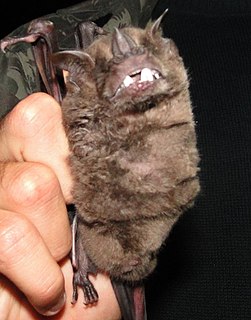
The fringed fruit-eating bat, is a species of bat native to South America.

The silver fruit-eating bat is a South American bat species of the family Phyllostomidae.

The dwarf little fruit bat is a species of leaf-nosed bat from South America.

The black flying fox or black fruit bat is a bat in the family Pteropodidae. It is among the largest bats in the world, but is considerably smaller than the largest species in its genus, Pteropus. The black flying fox is native to Australia, Papua New Guinea, and Indonesia. It is not a threatened species.

The Neotropical fruit bats (Artibeus) are a genus of bats within the subfamily Stenodermatinae. The genus consists of 12 species, which are native to Central and South America, as well as parts of the Caribbean.
Aethalops is a genus of megabats in the family Pteropodidae. It contains two species:

The Honduran fruit-eating bat is a species of bat in the family Phyllostomidae. It is found in El Salvador, Honduras, and Nicaragua.

The Madagascan fruit bat is a species of bat in the family Pteropodidae. It is endemic to Madagascar and is listed as "Vulnerable" by the IUCN because it is hunted as bushmeat.

Buettikofer's epauletted fruit bat is a species of megabat in the family Pteropodidae. It is found in Ivory Coast, Ghana, Guinea, Guinea-Bissau, Liberia, Nigeria, Senegal, and Sierra Leone. Its natural habitats are subtropical or tropical moist lowland forests, dry savanna, and moist savanna. It is threatened by habitat loss.
Myonycteris is a genus of bat in the family Pteropodidae.

The little collared fruit bat is a species of megabat in the family Pteropodidae found in Angola, Cameroon, the Central African Republic, the Republic of the Congo, the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Ivory Coast, Equatorial Guinea, Gabon, Ghana, Guinea, Liberia, Nigeria, Rwanda, Sierra Leone, South Sudan, Togo, and Uganda. Its natural habitats are subtropical or tropical moist lowland forests and moist savanna.

The demonic tube-nosed fruit bat is a species of bat in the family Pteropodidae. It is endemic to Papua New Guinea. The holotype specimen was collected in 1979 on New Ireland, in the Bismarck Archipelago. It was described as a new species in 1983. The range of the species may extend to other islands, however the extent of the range is not presently known.

The little golden-mantled flying fox is a species of bat in the family Pteropodidae. It is found in Indonesia and the Philippines. Its natural habitat is subtropical or tropical dry forests. It is threatened by hunting and habitat loss, as well as pollution.

Carolliinae is a subfamily of bats.
Thomas's fruit-eating bat, sometimes also popularly called Watson's fruit-eating bat, is a species of bat in the family Phyllostomidae. It is found in southern Mexico, Belize, Guatemala, Honduras, Nicaragua, Costa Rica, Panama and Colombia. Its South American range is to the west of the Andes. The species name is in honor of H. J. Watson, a plantation owner in western Panama who used to send specimens to the British Natural History Museum, where Oldfield Thomas would often describe them.















