
Vespertilionidae is a family of microbats, of the order Chiroptera, flying, insect-eating mammals variously described as the common, vesper, or simple nosed bats. The vespertilionid family is the most diverse and widely distributed of bat families, specialised in many forms to occupy a range of habitats and ecological circumstances, and it is frequently observed or the subject of research. The facial features of the species are often simple, as they mainly rely on vocally emitted echolocation. The tails of the species are enclosed by the lower flight membranes between the legs. Over 300 species are distributed all over the world, on every continent except Antarctica. It owes its name to the genus Vespertilio, which takes its name from a word for bat, vespertilio, derived from the Latin term vesper meaning 'evening'; they are termed "evening bats" and were once referred to as "evening birds".

The New World leaf-nosed bats (Phyllostomidae) are bats found from southern North America to South America, specifically from the Southwest United States to northern Argentina. They are ecologically the most varied and diverse family within the order Chiroptera. Most species are insectivorous, but the phyllostomid bats include within their number true predatory species and frugivores. For example, the spectral bat, the largest bat in the Americas, eats vertebrate prey, including small, dove-sized birds. Members of this family have evolved to use food groups such as fruit, nectar, pollen, insects, frogs, other bats, and small vertebrates, and in the case of the vampire bats, even blood.

The spectral bat, also called the great false vampire bat, great spectral bat, American false vampire bat or Linnaeus's false vampire bat, is a large, carnivorous leaf-nosed bat found in Mexico, Central America, and South America. It is the only member of the genus Vampyrum; its closest living relative is the big-eared woolly bat. It is the largest bat species in the New World, as well as the largest carnivorous bat: its wingspan is 0.7–1.0 m (2.3–3.3 ft). It has a robust skull and teeth, with which it delivers a powerful bite to kill its prey. Birds are frequent prey items, though it may also consume rodents, insects, and other bats.

The Honduran white bat, also called the Caribbean white tent-making bat, is a species of bat in the family Phyllostomatidae. It is the only member of the genus Ectophylla. The genus and the species were both scientifically described for the first time in 1892. It has distinctive, entirely white fur, which is only found in six of the roughly 1,300 known species of bat. It constructs "tents" out of understory plant leaves by strategically cutting the leaf ribs with its teeth; it roosts in these tents during the day. It is a specialist frugivore, consuming almost exclusively the fruits of one species of fig. Females can likely become pregnant twice per year, giving birth to one offspring at a time.
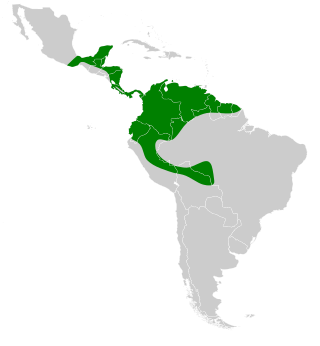
The northern little yellow-eared bat is a bat species found from southern Mexico to Bolivia, the Guianas and western Brazil.

The bidentate yellow-eared bat is a species of bat in the family Phyllostomidae, native to South America. Formerly classified in the Vampyressa genus, phylogenetic analyses support its inclusion in Vampyriscus.

Micronycteris is a genus of leaf-nosed bats.

Chiroderma – big-eyed bats or white-lined bats – is a genus of leaf-nosed bat found in North America, Central America, and South America and the Lesser Antilles.

The genus Chilonatalus of funnel-eared bats is found in South America and the Antilles. It has three species. New mitochondrial and nuclear DNA sequences that were analyzed with published morphological data to see the relationship of extinct natalids. It was found that this fossil taxon's phylogeny that was based on morphological data can be assumed that the Chilonatalus micropus is and one other species is a widespread species

The Mexican long-tongued bat is a species of bat in the family Phyllostomidae. It is the only species within the genus Choeronycteris. The species is found in El Salvador, Guatemala, Honduras, Mexico, and the United States.

The Choco broad-nosed bat is a species of bat in the family Phyllostomidae. It is native to Colombia, Panama, and Ecuador, where it is found in the Choco region lowlands. It is threatened by habitat loss. In 2013, Bat Conservation International listed this species as one of the 35 species of its worldwide priority list of conservation.
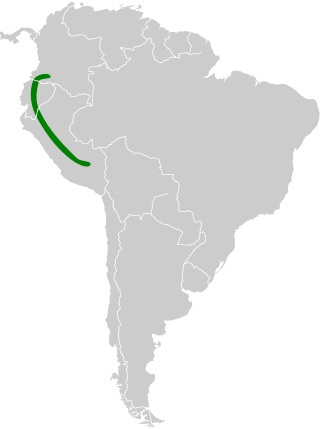
Melissa's yellow-eared bat is a species of bat in the family Phyllostomidae. It is found in southern Colombia, Ecuador and Peru.

Stenodermatinae is a large subfamily of bats in the family Phyllostomidae.

The Cuban greater funnel-eared bat is a species of funnel-eared bat. It is endemic to a cave in westernmost Cuba.

Vampyriscus is a genus of bats in the family Phyllostomidae, the leaf-nosed bats.
Chiroderma vizottoi is a species of frugivorous bat found in the northeast of Brazil.
Kalko's yellow-eared bat is a species of bat in the family Phyllostomidae. It is found in northern Panama.
Villa's little yellow-eared bat is a bat species found in Mexico to the west of the Isthmus of Tehuantepec. It is known from the Mexican states of Oaxaca, Guerrero, and Veracruz.














