| Ring-necked duck | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Drake (male) | |
 | |
| Hen (female) | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Aves |
| Order: | Anseriformes |
| Family: | Anatidae |
| Genus: | Aythya |
| Species: | A. collaris |
| Binomial name | |
| Aythya collaris (Donovan, 1809) | |
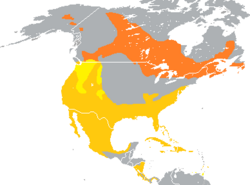 | |
| Range of A. collaris Breeding range Year-round range Wintering range | |
| Synonyms [2] | |
| |
The ring-necked duck (Aythya collaris) is a diving duck from North America commonly found in freshwater ponds and lakes. [3] The scientific name is derived from Greek aithuia, an unidentified seabird mentioned by authors including Hesychius and Aristotle, and Latin collaris, "of the neck" from collum, "neck". [4]



