Related Research Articles

In celestial mechanics, the Lagrange points are points of equilibrium for small-mass objects under the gravitational influence of two massive orbiting bodies. Mathematically, this involves the solution of the restricted three-body problem.

The Large Binocular Telescope (LBT) is an optical telescope for astronomy located on 10,700-foot (3,300 m) Mount Graham, in the Pinaleno Mountains of southeastern Arizona, United States. It is a part of the Mount Graham International Observatory.
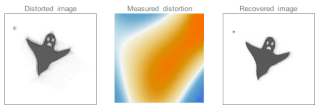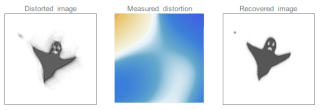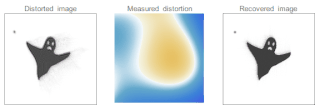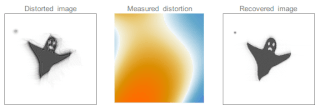
Adaptive optics (AO) is a technique of precisely deforming a mirror in order to compensate for light distortion. It is used in astronomical telescopes and laser communication systems to remove the effects of atmospheric distortion, in microscopy, optical fabrication and in retinal imaging systems to reduce optical aberrations. Adaptive optics works by measuring the distortions in a wavefront and compensating for them with a device that corrects those errors such as a deformable mirror or a liquid crystal array.

Aden B. Meinel was an American astronomer. He retired in 1993 as a distinguished scientist at the Jet Propulsion Laboratory. He also held the rank of professor emeritus at the University of Arizona College of Optical Sciences. His research interests have included upper atmospheric physics, glass technology, optical design, instrumentation and space systems.
A space sunshade or sunshield is a parasol that diverts or otherwise reduces some of the Sun's radiation, preventing it from hitting a spacecraft or planet and thereby reducing its insolation, which results in reduced heating. Light can be diverted by different methods. The concept of the construction of sunshade as a method of climate engineering dates back to the years 1923, 1929, 1957 and 1978 by the physicist Hermann Oberth. Space mirrors in orbit around the Earth with a diameter of 100 to 300 km, as designed by Hermann Oberth, are intended to focus sunlight on individual regions of the Earth’s surface or deflect it into space so that the solar radiation is weakened in a specifically controlled manner for individual regions on the Earth’s surface. First proposed in 1989, another space sunshade concept involves putting a large occulting disc, or technology of equivalent purpose, between the Earth and Sun.

A coronagraph is a telescopic attachment designed to block out the direct light from a star or other bright object so that nearby objects – which otherwise would be hidden in the object's bright glare – can be resolved. Most coronagraphs are intended to view the corona of the Sun, but a new class of conceptually similar instruments are being used to find extrasolar planets and circumstellar disks around nearby stars as well as host galaxies in quasars and other similar objects with active galactic nuclei (AGN).

McMath–Pierce solar telescope is a 1.6 m f/54 reflecting solar telescope at Kitt Peak National Observatory in Arizona, United States. Built in 1962, the building was designed by American architect Myron Goldsmith and Bangladeshi-American structural engineer Fazlur Rahman Khan. It was the largest solar telescope and the largest unobstructed aperture optical telescope in the world. It is named after the astronomers Robert Raynolds McMath and Keith Pierce.

The MMT Observatory (MMTO) is an astronomical observatory on the site of Fred Lawrence Whipple Observatory. The Whipple observatory complex is located on Mount Hopkins, Arizona, US in the Santa Rita Mountains. The observatory is operated by the University of Arizona and the Smithsonian Institution, and has a visitor center in nearby Amado, Arizona. The MMTO is the home of the MMT, which has a primary mirror 6.5 m in diameter. The name comes from the six smaller mirrors originally used before the single primary mirror was installed in 1998. The primary mirror has a special lightweight honeycomb design made by the University of Arizona's Steward Observatory Mirror Laboratory. The MMT is housed in a building which allows the walls and roof around the telescope to be completely rolled back, allowing it to cool down very quickly in order to improve observation.
The Gregorian telescope is a type of reflecting telescope designed by Scottish mathematician and astronomer James Gregory in the 17th century, and first built in 1673 by Robert Hooke. James Gregory was a contemporary of Isaac Newton, and both often worked simultaneously on similar projects. Gregory's design was published in 1663 and pre-dates the first practical reflecting telescope, the Newtonian telescope, built by Sir Isaac Newton in 1668. However, Gregory's design was only a theoretical description, and he never actually constructed the telescope. It was not successfully built until five years after Newton's first reflecting telescope.

An X-ray telescope (XRT) is a telescope that is designed to observe remote objects in the X-ray spectrum. X-rays are absorbed by the Earth's atmosphere, so instruments to detect X-rays must be taken to high altitude by balloons, sounding rockets, and satellites.
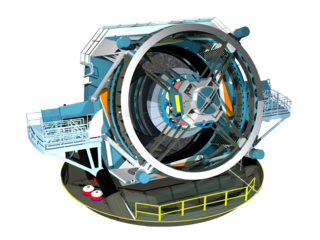
The Vera C. Rubin Observatory, formerly known as the Large Synoptic Survey Telescope (LSST), is an astronomical observatory under construction in Chile. Its main task will be carrying out a synoptic astronomical survey, the Legacy Survey of Space and Time. The word "synoptic" is derived from the Greek words σύν and ὄψις, and describes observations that give a broad view of a subject at a particular time. The observatory is located on the El Peñón peak of Cerro Pachón, a 2,682-meter-high mountain in Coquimbo Region, in northern Chile, alongside the existing Gemini South and Southern Astrophysical Research Telescopes. The LSST Base Facility is located about 100 kilometres away from the observatory by road, in the town of La Serena. The observatory is named for Vera Rubin, an American astronomer who pioneered discoveries about galaxy rotation rates.

A telescope is a device used to observe distant objects by their emission, absorption, or reflection of electromagnetic radiation. Originally, it was an optical instrument using lenses, curved mirrors, or a combination of both to observe distant objects – an optical telescope. Nowadays, the word "telescope" is defined as a wide range of instruments capable of detecting different regions of the electromagnetic spectrum, and in some cases other types of detectors.

Roger David Blandford, FRS, FRAS is a British theoretical astrophysicist, best known for his work on black holes.
Daniel Apai is a professor and astrophysicist at The University of Arizona in Tucson, Arizona. He is known for his studies of astrobiology, extrasolar planets, and the formation of planetary systems. He is the principal investigator of the Earths in Other Solar Systems team of NASA's Nexus for Exoplanet System Studies and the Hubble Space Telescope Cloud Atlas Treasury program, and Project EDEN, a large survey for habitable planets in the immediate solar neighborhood. He is leading the Nautilus Space Observatory space telescope concept and co-leading the technology development underpinning it.
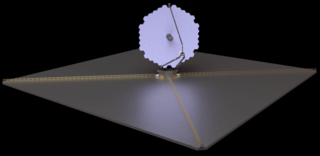
The Large Ultraviolet Optical Infrared Surveyor, commonly known as LUVOIR, is a multi-wavelength space telescope concept being developed by NASA under the leadership of a Science and Technology Definition Team. It is one of four large astrophysics space mission concepts studied in preparation for the National Academy of Sciences 2020 Astronomy and Astrophysics Decadal Survey.
Nautilus Deep Space Observatory (NDSO) is a proposed deep space fleet of space telescopes designed to search for biosignatures of life in the atmospheres of exoplanets.

The ExoLife Finder (ELF) telescope is an under-development hybrid interferometric telescope being designed at the Instituto de Astrofisica de Canarias (IAC) for the direct detection and imaging of exoplanets and potentially water-bearing exoplanets. Developed by a collaboration of scientists and engineers including the PLANETS Foundation, the ELF aims to analyze the surfaces and atmospheres of exoplanets for evidence of life, focusing on nearby star systems within 25 light years of Earth. The telescope’s design features non-redundant circular arrays of 5-meter-scale mirrors and tensegrity-based mechanical support with an outer diameter of 35m. It uses multiple layers of advanced atmospheric wavefront sensing and control. It is a scalable optical concept, and could be built within a 10 year timeframe. A 3.5-meter precursor called the Small ELF (SELF) is currently being built in the Canary Islands. The ELF's first targets will include nearby stars cooler than the Sun.

Lobster-eye optics are a biomimetic design, based on the structure of the eyes of a lobster with an ultra wide field of view, used in X-ray optics. This configuration allows X-ray light to enter from multiple angles, capturing more X-rays from a larger area than other X-ray telescopes. The idea was originally proposed for use in X-ray astronomy by Roger Angel in 1979, with a similar idea presented earlier by W. K. H. Schmidt in 1975. It was first used by NASA on a sub-orbital sounding rocket experiment in 2012. The Lobster Eye Imager for Astronomy, a Chinese technology demonstrator satellite, was launched in 2022. The Chinese Einstein Probe, launched in 2024, is the first major space telescope to use lobster-eye optics. Several other such space telescopes are currently under development or consideration.
References
- 1 2 3 "Roger Angel | American astronomer | Britannica".
- ↑ Gibbs, Wayt (December 1, 2005). "Breaking the Mold". Scientific American.
- 1 2 "J. Roger Angel | Professor of Astronomy". Wyant College of Optical Sciences. The University of Arizona. Retrieved April 2, 2024.
- ↑ Angel, Roger (1967-08-15). "Direct Measurement of an Atomic Quadrupole Moment". The Journal of Chemical Physics. 47 (4): 1552–1553. Bibcode:1967JChPh..47.1552A. doi:10.1063/1.1712116.
- ↑ "Book of Members, 1780-2010: Chapter A" (PDF). American Academy of Arts and Sciences . Retrieved April 18, 2011.
- ↑ Hartline, Beverly Karplus (4 January 1980). "Lobster-Eye X-ray Telescope Envisioned". Science. 207 (4426): 47. Bibcode:1980Sci...207...47K. doi:10.1126/science.207.4426.47. ISSN 0036-8075 . Retrieved 29 December 2023.
- ↑ Angel, Roger (2006-11-14). "Feasibility of cooling the Earth with a cloud of small spacecraft near the inner Lagrange point (L1)". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 103 (46): 17184–17189. Bibcode:2006PNAS..10317184A. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0608163103 . ISSN 0027-8424. PMC 1859907 . PMID 17085589.
- ↑ Palca, Joe (2012-08-23). "Telescope Innovator Shines His Genius On New Fields". NPR .
- ↑ "Fellowships Reward Bright Stars", Associated Press, The Free Lance-Star, Terri Likens, June 19, 1996
- ↑ "Optical Society of America Confers 17 General and Specialty Awards for 2007 | Optica". www.optica.org. Retrieved 2024-06-11.
- ↑ "J. Roger P. Angel - Lightweight Mirrors for Astronomical Telescopes". National Inventors Hall of Fame . Retrieved June 4, 2016.