The McDonnell FH Phantom is a twinjet, straight-wing, carrier-based fighter aircraft designed and first flown during late World War II for the United States Navy. As a first-generation jet fighter, the Phantom was the first purely jet-powered aircraft to land on an American aircraft carrier and the first jet deployed by the United States Marine Corps. Although only 62 FH-1s were built it helped prove the viability of carrier-based jet fighters. As McDonnell's first successful fighter, it led to the development of the follow-on F2H Banshee, which was one of the two most important naval jet fighters of the Korean War; combined, the two established McDonnell as an important supplier of navy aircraft.

The McDonnell XF-88 Voodoo was a long-range, twinjet fighter aircraft designed for the United States Air Force. Although it never entered production, its design was adapted for the subsequent supersonic F-101 Voodoo.

The Bell P-59 Airacomet is a single-seat, twin jet-engine fighter aircraft that was designed and built by Bell Aircraft during World War II. It was the first jet produced in the United States. As the British were further along in jet engine development, they donated an engine for the United States to copy in 1941 that became the basis for the General Electric J31 jet engine used by the P-59 a year later. Because the plane was underpowered, the United States Army Air Forces (USAAF) was not impressed by its performance and canceled half of the original order for 100 fighters, using the completed aircraft as trainers. The USAAF would instead go on to select the Lockheed P-80 Shooting Star as its first operational jet fighter. Although no P-59s entered combat, the aircraft paved the way for later generations of U.S. turbojet-powered aircraft.

The Martin P4M Mercator was a maritime reconnaissance aircraft built by the Glenn L. Martin Company. The Mercator was an unsuccessful contender for a United States Navy requirement for a long-range maritime patrol bomber, with the Lockheed P2V Neptune chosen instead. It saw a limited life as a long-range electronic reconnaissance aircraft. Its most unusual feature was that it was powered by a combination of piston engines and turbojets, the latter being in the rear of the engine nacelles.

The Convair R3Y Tradewind was an American 1950s turboprop-powered flying boat designed and built by Convair.

The Ryan FR Fireball is an American mixed-power fighter aircraft designed by Ryan Aeronautical for the United States Navy during World War II. It was the Navy's first aircraft with a jet engine. Only 66 aircraft were built before Japan surrendered in August 1945. The FR-1 Fireball equipped a single squadron before the war's end, but did not see combat. The aircraft ultimately proved to lack the structural strength required for operations aboard aircraft carriers and was withdrawn in mid-1947.

The Douglas A2D Skyshark was an American turboprop-powered attack aircraft built by the Douglas Aircraft Company for the United States Navy. The program was substantially delayed by engine reliability problems, and was canceled because more promising jet attack aircraft had entered development and the smaller escort carriers the A2D was intended to utilize were being phased out.

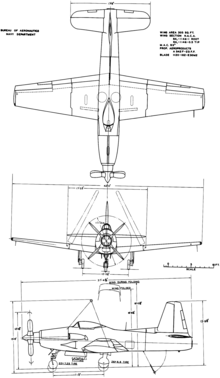
The Consolidated Vultee XP-81 is a development of the Consolidated Vultee Aircraft Corporation to build a single seat, long range escort fighter that combined use of both turbojet and turboprop engines. Although promising, the lack of suitable engines combined with the end of World War II doomed the project.

The Douglas Skystreak is an American single-engine jet research aircraft of the 1940s. It was designed in 1945 by the Douglas Aircraft Company for the U.S. Navy Bureau of Aeronautics, in conjunction with the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA). The Skystreak was a turbojet-powered aircraft that took off from the ground under its own power and had unswept flying surfaces.

The Hiller X-18 was an experimental cargo transport aircraft designed to be the first testbed for tiltwing and V/STOL technology.

The Curtiss XP-46 was a 1940s American prototype fighter aircraft. It was a development of the Curtiss-Wright Corporation in an effort to introduce the best features found in European fighter aircraft in 1939 into a fighter aircraft which could succeed the Curtiss P-40, then in production.

The General Electric J31 was the first jet engine to be mass-produced in the United States.

The VL Humu (Whirlwind) is a Finnish fighter aircraft, designed by Valtion lentokonetehdas in 1944, and based on the American Brewster F2A Buffalo.
The Sukhoi Su-5 or I-107 was a Soviet mixed-power prototype fighter aircraft built toward the end of World War II.

The NDN Firecracker is a single-engine aircraft designed as a military trainer.

The Fuji T-5 or KM-2Kai is a Japanese turboprop-driven primary trainer aircraft, which is a development of the earlier Fuji KM-2. The student and the instructor sit side-by-side.

The Kawasaki P-2J is a maritime patrol and ASW aircraft developed for the Japan Maritime Self-Defense Force. A twin turboprop-powered version of the radial-engined P-2 Neptune, the P-2J was developed as an alternative to buying the larger and more expensive P-3 Orion, which would eventually replace the P-2J in the 1980s.

The SIAI-Marchetti SM.1019 is an Italian STOL liaison monoplane built by SIAI-Marchetti for the Italian Army. It is a turboprop-powered derivative of the Cessna O-1 Bird Dog.

The Curtiss XF15C-1 is a mixed-propulsion fighter prototype of the 1940s. It was among a number of similar designs ordered by the US Navy before pure-jet aircraft had demonstrated their ability to operate from carriers and the mixed-propulsion designs were abandoned. Only three prototypes were constructed, the first one having crashed in testing while the second was scrapped and the last survives to this day.

The General Electric T31 was the first turboprop engine designed and built in the United States.