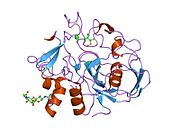
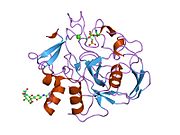
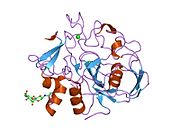
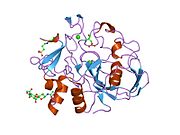
Uroporphyrinogen III decarboxylase is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the UROD gene.
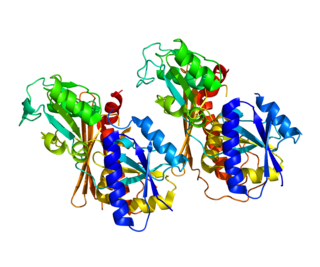
Porphobilinogen deaminase (hydroxymethylbilane synthase, or uroporphyrinogen I synthase) is an enzyme (EC 2.5.1.61) that in humans is encoded by the HMBS gene. Porphobilinogen deaminase is involved in the third step of the heme biosynthetic pathway. It catalyzes the head to tail condensation of four porphobilinogen molecules into the linear hydroxymethylbilane while releasing four ammonia molecules:
Galactosylceramidase, EC 3.2.1.46, is an enzyme that removes galactose from ceramide derivatives (galactosylceramides) by catalysing the hydrolysis of galactose ester bonds of galactosylceramide, galactosylsphingosine, lactosylceramide, and monogalactosyldiglyceride.

Arylsulfatase A is an enzyme that breaks down sulfatides, namely cerebroside 3-sulfate into cerebroside and sulfate. In humans, arylsulfatase A is encoded by the ARSA gene.

Steroid sulfatase (STS), or steryl-sulfatase, formerly known as arylsulfatase C, is a sulfatase enzyme involved in the metabolism of steroids. It is encoded by the STS gene.
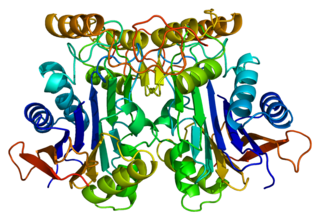
N(4)-(beta-N-acetylglucosaminyl)-L-asparaginase is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the AGA gene.

Trifunctional enzyme subunit beta, mitochondrial (TP-beta) also known as 3-ketoacyl-CoA thiolase, acetyl-CoA acyltransferase, or beta-ketothiolase is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the HADHB gene.

N-acetylgalactosamine-6-sulfatase is an enzyme that, in humans, is encoded by the GALNS gene.

Phosphorylase b kinase regulatory subunit alpha, liver isoform is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PHKA2 gene.

Ceroid-lipofuscinosis neuronal protein 6 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CLN6 gene.

Sulfatase-modifying factor 2 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the SUMF2 gene.

Molybdenum cofactor biosynthesis protein 1 is a protein that in humans and other animals, fungi, and cellular slime molds, is encoded by the MOCS1 gene.

Acetylcholinesterase collagenic tail peptide also known as AChE Q subunit, acetylcholinesterase-associated collagen, or ColQ is the collagen-tail subunit of acetylcholinesterase found in the neuromuscular junction. In humans it is encoded by the COLQ gene.

Adenylyltransferase and sulfurtransferase MOCS3 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the MOCS3 gene.

Heparan-α-glucosaminide N-acetyltransferase is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the HGSNAT gene.
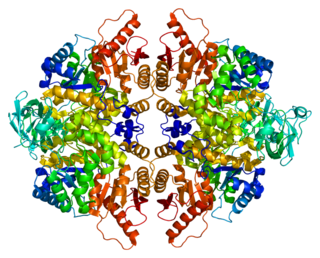
Pyruvate kinase PKLR is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PKLR gene.

Multiple sulfatase deficiency (MSD), also known as Austin disease, or mucosulfatidosis, is a very rare autosomal recessive lysosomal storage disease caused by a deficiency in multiple sulfatase enzymes, or in formylglycine-generating enzyme, which activates sulfatases. It is similar to mucopolysaccharidosis.

Arylsulfatase L is an enzyme that, in humans, is encoded by the ARSL gene.

Formylglycine-generating enzyme (FGE), located at 3p26.1 in humans, is the name for an enzyme present in the endoplasmic reticulum that catalyzes the conversion of cysteine to formylglycine (fGly). There are two main classes of FGE, aerobic and anaerobic. FGE activates sulfatases, which are essential for the degradation of sulfate esters. The catalytic activity of sulfatases is dependent upon a formylglycine residue in the active site.
An aldehyde tag is a short peptide tag that can be further modified to add fluorophores, glycans, PEG chains, or reactive groups for further synthesis. A short, genetically-encoded peptide with a consensus sequence LCxPxR is introduced into fusion proteins, and by subsequent treatment with the formylglycine-generating enzyme (FGE), the cysteine of the tag is converted to a reactive aldehyde group. This electrophilic group can be targeted by an array of aldehyde-specific reagents, such as aminooxy- or hydrazide-functionalized compounds.