
Aerodynamics, from Greek ἀήρ aero (air) + δυναμική (dynamics), is the study of motion of air, particularly when affected by a solid object, such as an airplane wing. It is a sub-field of fluid dynamics and gas dynamics, and many aspects of aerodynamics theory are common to these fields. The term aerodynamics is often used synonymously with gas dynamics, the difference being that "gas dynamics" applies to the study of the motion of all gases, and is not limited to air. The formal study of aerodynamics began in the modern sense in the eighteenth century, although observations of fundamental concepts such as aerodynamic drag were recorded much earlier. Most of the early efforts in aerodynamics were directed toward achieving heavier-than-air flight, which was first demonstrated by Otto Lilienthal in 1891. Since then, the use of aerodynamics through mathematical analysis, empirical approximations, wind tunnel experimentation, and computer simulations has formed a rational basis for the development of heavier-than-air flight and a number of other technologies. Recent work in aerodynamics has focused on issues related to compressible flow, turbulence, and boundary layers and has become increasingly computational in nature.

An electric current is a stream of charged particles, such as electrons or ions, moving through an electrical conductor or space. It is measured as the net rate of flow of electric charge through a surface or into a control volume. The moving particles are called charge carriers, which may be one of several types of particles, depending on the conductor. In electric circuits the charge carriers are often electrons moving through a wire. In semiconductors they can be electrons or holes. In a electrolyte the charge carriers are ions, while in plasma, an ionized gas, they are ions and electrons.

In physics and engineering, fluid dynamics is a subdiscipline of fluid mechanics that describes the flow of fluids—liquids and gases. It has several subdisciplines, including aerodynamics and hydrodynamics. Fluid dynamics has a wide range of applications, including calculating forces and moments on aircraft, determining the mass flow rate of petroleum through pipelines, predicting weather patterns, understanding nebulae in interstellar space and modelling fission weapon detonation.

Mach number is a dimensionless quantity in fluid dynamics representing the ratio of flow velocity past a boundary to the local speed of sound.

The Nile is a major north-flowing river in northeastern Africa. The longest river in Africa, it has historically been considered the longest river in the world, though this has been contested by research suggesting that the Amazon River is slightly longer, the Nile is amongst the smallest in the world by measure of cubic metres flowing annually. About 6,650 km (4,130 mi) long, its drainage basin covers eleven countries: Tanzania, Uganda, Rwanda, Burundi, the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Kenya, Ethiopia, Eritrea, South Sudan, Republic of the Sudan, and Egypt. In particular, the Nile is the primary water source of Egypt and Sudan.

The Rhine is one of the major European rivers, and has its sources in Switzerland and flows in a mostly northerly direction through Germany and the Netherlands, emptying into the North Sea. The river begins in the Swiss canton of Graubünden in the southeastern Swiss Alps, forms part of the Swiss-Liechtenstein, Swiss-Austrian, Swiss-German and then the Franco-German border, then flows through the German Rhineland and the Netherlands and eventually empties into the North Sea.

A volcano is a rupture in the crust of a planetary-mass object, such as Earth, that allows hot lava, volcanic ash, and gases to escape from a magma chamber below the surface.
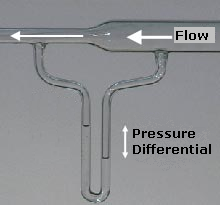
In fluid dynamics, Bernoulli's principle states that an increase in the speed of a fluid occurs simultaneously with a decrease in static pressure or a decrease in the fluid's potential energy. The principle is named after Daniel Bernoulli who published it in his book Hydrodynamica in 1738. Although Bernoulli deduced that pressure decreases when the flow speed increases, it was Leonhard Euler who derived Bernoulli's equation in its usual form in 1752. The principle is only applicable for isentropic flows: when the effects of irreversible processes and non-adiabatic processes are small and can be neglected.
In fluid dynamics, turbulence or turbulent flow is fluid motion characterized by chaotic changes in pressure and flow velocity. It is in contrast to a laminar flow, which occurs when a fluid flows in parallel layers, with no disruption between those layers.

A pyroclastic flow is a fast-moving current of hot gas and volcanic matter that flows along the ground away from a volcano at average speeds of 100 km/h (62 mph) but is capable of reaching speeds up to 700 km/h (430 mph). The gases and tephra can reach temperatures of about 1,000 °C (1,830 °F).
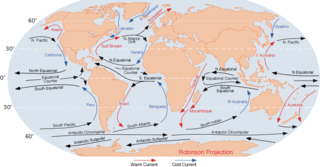
An ocean current is a continuous, directed movement of sea water generated by a number of forces acting upon the water, including wind, the Coriolis effect, breaking waves, cabbeling, and temperature and salinity differences. Depth contours, shoreline configurations, and interactions with other currents influence a current's direction and strength. Ocean currents are primarily horizontal water movements.

A flowchart is a type of diagram that represents a workflow or process. A flowchart can also be defined as a diagrammatic representation of an algorithm, a step-by-step approach to solving a task.

In positive psychology, a flow state, also known colloquially as being inthe zone, is the mental state in which a person performing some activity is fully immersed in a feeling of energized focus, full involvement, and enjoyment in the process of the activity. In essence, flow is characterized by the complete absorption in what one does, and a resulting transformation in one's sense of time.

Ampasinambo is a town and commune in Madagascar. It belongs to the district of Nosy Varika, which is a part of Vatovavy-Fitovinany Region. The population of the commune was estimated to be approximately 25,000 in 2001 commune census.

A river is a natural flowing watercourse, usually freshwater, flowing towards an ocean, sea, lake or another river. In some cases, a river flows into the ground and becomes dry at the end of its course without reaching another body of water. Small rivers can be referred to using names such as stream, creek, brook, rivulet, and rill. There are no official definitions for the generic term river as applied to geographic features, although in some countries or communities a stream is defined by its size. Many names for small rivers are specific to geographic location; examples are "run" in some parts of the United States, "burn" in Scotland and northeast England, and "beck" in northern England. Sometimes a river is defined as being larger than a creek, but not always: the language is vague.

Lava is molten rock (magma) that has been expelled from the interior of a terrestrial planet or a moon. Magma is generated by the internal heat of the planet or moon and it is erupted as lava at volcanoes or through fractures in the crust, usually at temperatures from 800 to 1,200 °C. The volcanic rock resulting from subsequent cooling is also often described as lava.

The Reynolds number helps predict flow patterns in different fluid flow situations. At low Reynolds numbers, flows tend to be dominated by laminar (sheet-like) flow, while at high Reynolds numbers flows tend to be turbulent. The turbulence results from differences in the fluid's speed and direction, which may sometimes intersect or even move counter to the overall direction of the flow. These eddy currents begin to churn the flow, using up energy in the process, which for liquids increases the chances of cavitation. Reynolds numbers are an important dimensionless quantity in fluid mechanics.

The Sakaleona Falls are the highest waterfalls of Madagascar, with a height of 200 metres (660 ft).

TensorFlow is a free and open-source software library for machine learning. It can be used across a range of tasks but has a particular focus on training and inference of deep neural networks.


















