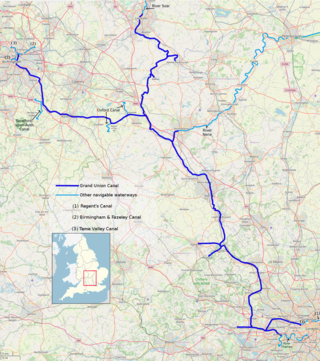
The Grand Union Canal in England is part of the British canal system. It is the principal navigable waterway between London and the Midlands. Starting in London, one arm runs to Leicester and another ends in Birmingham, with the latter stretching for 137 miles (220 km) with 166 locks from London. The Birmingham line has a number of short branches to places including Slough, Aylesbury, Wendover, and Northampton. The Leicester line has two short arms of its own, to Market Harborough and Welford.

The Birmingham and Fazeley Canal is a canal of the Birmingham Canal Navigations in the West Midlands of England. Its purpose was to provide a link between the Coventry Canal and Birmingham and thereby connect Birmingham to London via the Oxford Canal.

The Coventry Canal is a navigable narrow canal in the Midlands of England.

Birmingham Canal Navigations (BCN) is a network of canals connecting Birmingham, Wolverhampton, and the eastern part of the Black Country. The BCN is connected to the rest of the English canal system at several junctions. It was owned and operated by the Birmingham Canal Navigations Company from 1767 to 1948.

The Gravelly Hill Interchange, popularly known as Spaghetti Junction, is a road junction in Birmingham, England. It is junction 6 of the M6 motorway where it meets the A38(M) Aston Expressway in the Gravelly Hill area of Birmingham. The interchange was opened on 24 May 1972.

Erdington is a suburb and ward of Birmingham in the West Midlands County, England. Historically part of Warwickshire and located 5 miles (8 km) northeast of central Birmingham, bordering Sutton Coldfield. It was also a council constituency, managed by its own district committee. The former council district consisted of the ward of Erdington, and Tyburn,, Stockland Green and Kingstanding, although all of Kingstanding and most of both Tyburn and Stockland Green wards lie outside the historical boundaries of Erdington. Stockland Green was formerly part of Aston, Kingstanding part of Perry Barr and Tyburn partially split between Aston and Hodge Hill. Erdington (ward) was part of the Sutton Coldfield constituency before 1974.

Gravelly Hill is an area of Birmingham, United Kingdom.

The Warwickshire ring is a connected series of canals forming a circuit around the West Midlands area of England. The ring is formed from the Coventry Canal, the Oxford Canal, the Grand Union Canal, the Stratford-upon-Avon Canal and the Birmingham and Fazeley Canal. It is a popular route with tourists due to its circular route and mixture of urban and rural landscapes.

The A5127 is a major road in England which runs between Birmingham and Lichfield, Staffordshire. For much of the route the road follows the old route of the A38 which has since been moved in order to by-pass places such as Erdington and Sutton Coldfield and form a relief road from Birmingham city centre to Spaghetti Junction.

The Tame Valley Canal is a relatively late (1844) canal in the West Midlands of England. It forms part of the Birmingham Canal Navigations. It takes its name from the roughly-parallel River Tame.

The Digbeth Branch Canal in Birmingham, England is a short canal which links the mainline of the Birmingham and Fazeley Canal at Aston Junction and the Grand Union Canal at Digbeth Junction in Digbeth, a district in Birmingham, England.

Fazeley Junction is the name of the canal junction where the authorised Birmingham and Fazeley Canal terminates and meets the Coventry Canal at Fazeley, near Tamworth, Staffordshire, England.

Aston Junction is the name of the canal junction where the Digbeth Branch Canal terminates and meets the Birmingham and Fazeley Canal near to Aston, Birmingham, England.

Bordesley Junction is a canal junction where the Grand Union Canal splits near to Bordesley, Birmingham, England. It opened in 1844, when the Birmingham and Warwick Junction Canal was built as part of a scheme to bypass the congestion at the Farmers Bridge flight of locks.

The Walsall Canal is a narrow canal, seven miles (11 km) long, forming part of the Birmingham Canal Navigations, and passing around the western side of Walsall, West Midlands, England.

Rushall Junction is the southern limit of the Rushall Canal where it meets the Tame Valley Canal in the West Midlands, England. It opened in 1847, when the Rushall Canal was built to create connections between the Birmingham Canal Navigations system and the Wyrley and Essington Canal, following the amalgamation of the two companies in 1840.

Tame Valley Junction, also known as Doe Bank Junction, is a canal junction at the western limit of the Tame Valley Canal where it meets the Walsall Canal, south of Walsall, in the West Midlands, England.

Bromford is an industrial and residential area of Birmingham, situated between Ward End, Alum Rock, Hodge Hill, Washwood Heath, Shard End, Stechford, Castle Bromwich and Tyburn. The industrial area is predominantly situated on the north side of the M6 motorway, including The Bromford Gate industrial park, Fort Shopping Park, and Fort Dunlop, with one industrial site sitting east of the M6 called Bromford Central. The residential area sits adjacent to the East of the M6 comprising two neighbourhoods, Bromford built along Bromford Drive, and The Firs built along Chipperfield Road. The industrial and residential areas have increasingly become two separate distinguishable places, and not recognised locally as joined or one. This is signified by the M6 & River Tame dividing the two areas, poor public transport links between the two areas, and the areas sitting within three different local authority wards, and two parliamentary constituencies (industrial area situated within Birmingham Erdington and residential area situated within Birmingham Hodge Hill.

The Birmingham and Warwick Junction Canal is a short canal connecting the Digbeth Branch of the Birmingham and Fazeley Canal in the centre of Birmingham to the Warwick and Birmingham Canal near Gravelly Hill Interchange. It was authorized in 1840 by Act of Parliament to relieve pressure on this connection to the Grand Junction Canal leading to London and opened in 1844. It is 2.5 miles long and has 6 locks.

Aston Reservoir, sometimes known as Salford Lake, Salford Park Pool or Salford Bridge Reservoir, is a 19th-century reservoir, formerly used for drinking water extracted from the River Tame, in Birmingham, England. It was built by the Birmingham Waterworks Company and was at that time situated in the parish of Aston. On 1 January 1876 the company was purchased by Birmingham Corporation Water Department.





















