
The Kariba Dam is a double curvature concrete arch dam in the Kariba Gorge of the Zambezi river basin between Zambia and Zimbabwe. The dam stands 128 metres (420 ft) tall and 579 metres (1,900 ft) long. The dam forms Lake Kariba, which extends for 280 kilometres (170 mi) and holds 185 cubic kilometres (150,000,000 acre⋅ft) of water.

Victoria Falls is a waterfall on the Zambezi River in southern Africa, which provides habitat for several unique species of plants and animals. It is located on the border between Zambia and Zimbabwe and is one of the world's largest waterfalls, with a width of 1,708 m (5,604 ft).

Mica Dam is a hydroelectric embankment dam spanning the Columbia River 135 kilometres north of Revelstoke, British Columbia, Canada. It was built as one of three Canadian projects under the terms of the 1964 Columbia River Treaty and is operated by BC Hydro. Completed in 1973, the Mica powerhouse had an original generating capacity of 1,805 megawatts (MW). Mica Dam, named after the nearby settlement of Mica Creek and its associated stream, in turn named after the abundance of mica minerals in the area, is one of the largest earthfill dams in the world. The reservoir created by the dam is Kinbasket Lake. Water from the dam flows south directly into Revelstoke Lake, the reservoir for the Revelstoke Dam. Mica Dam is the tallest dam in Canada and second tallest in North America after the Chicoasén Dam in Mexico and it is the farthest upstream dam on the Columbia River. The dam's underground powerhouse was the second largest in the world at the time of its construction, and was the first 500 kV installation of sulphur hexafluoride (SF6) insulated switchgear in the world.

Kwekwe, formerly known as Que Que, is a city in the Midlands province in central Zimbabwe. The city has a population of 119,863 within the city limits, as of the 2022 census, making it the 7th-largest city in Zimbabwe and the second-most populous city in the Midlands, behind Gweru.
Zhombe, originally known as Jombe, is a rural communal area in Kwekwe District, Midlands Province, Zimbabwe. It is an area of mixed Shona and Northern Ndebele People. It lies along the Mnyathi border line between Midlands and Mashonaland Provinces. There are a few commercial farms within its borders and a handful of resettlement areas. Most of it is within the Zhombe Constituency. Its administrative centre is the Zhombe Joel Growth Point, and it is under the Zibagwe Rural District Council.

Kwekwe, originally known as Que Que, is a district in Zimbabwe. 197,062 people live in Kwekwe rural and 119,863 live in Kwekwe town.
Zimbabwe Iron and Steel Company is the largest steel works in Zimbabwe. It is located just outside Kwekwe, in Redcliff, Kwekwe District. Over the years the company has faced many operational problems and corruption scandals.
Silobela is an agricultural village in Kwekwe District in the Midlands Province of Zimbabwe. It is located about 60 kilometres (37 mi) west of Kwekwe town, 80 kilometres (50 mi) north-west of Gweru town, and bordering Nkayi on the west.

Sebakwe River or Zibagwe River is a river in Zimbabwe.

Columbina Rural Service Center is a populated place in Zhombe. It is 95 km northwest of Kwekwe and 67 km southwest of Kadoma.
Ngondoma Irrigation Scheme is located in Zhombe, Kwekwe District in Zimbabwe's Agro-Ecological Region Three. The average annual rainfall for the location is 550 mm. The scheme area is 44.4 4 hectares. Of the 179 farmers in the scheme, 134 are women. It comprises members from various villages, including villagers from Chief Njelele side, Gokwe District on the other side of Ngondoma River.
Empress Mine Township is a populated place in the area formerly known as Salakuhle in Zhombe Communal Land, Kwekwe District of the Midlands Province in Zimbabwe. It is Zhombe's largest growth point yet officially it is rated second after Zhombe Joel, the current Zhombe District capital.
Commoner, Zimbabwe is a populated place and a place where highly deformed and folded quartz reef structure gold ore is extracted. It is about 50 km west-southwest of Kadoma by air and 68 km by road. It is 67 km north-west of Kwekwe by air and 96 km by road. It is in Zhombe Kwekwe District, Midlands Province, Zimbabwe. Commoner is not to be confused with Commoner Gold Mine near Kadoma in Mashonaland West Province.

Ngondoma Dam is a dam on the Ngondoma River located 500 meters west of the Empress Mine Township in the Midlands Province of Zimbabwe. The dam is 67 kilometers northwest of the Kwekwe and 54 km southwest of Kadoma.
The Kwekwe-Gokwe Highway or the R84-7 Highway is an all-weather bitumen macadam highway in Zimbabwe running from Kwekwe to Gokwe passing through Zhombe. As a trunk road it is officially designated as the P11 Highway.
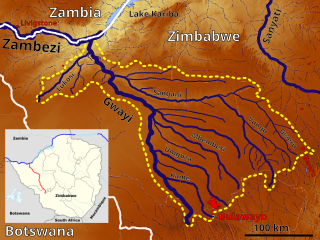
Gweru River is a river in Midlands Province of Zimbabwe.
Globe and Phoenix Mine is a gold mine in Zimbabwe. It is just outside Kwekwe CBD.
The Gaika Mine, now known as the Gaika Gold Fields, is situated in what was Chicago Farm just about 2 kilometres (1.2 mi) south of Kwekwe CBD. The Gaika Mine was the earliest mine developed in 1894, then Globe and Phoenix in 1895-1900, the Eldorado in 1905, the Antelope in 1908, the Cam and Motor Mine in 1909, the Shamva Mine in 1909-1910, and numerous others during the period 1895-1911.
The A5 Highway is a national road in Zimbabwe. It joins the cities of Harare and Bulawayo, and is hence known as the Harare-Bulawayo Highway. It is one of the two routes that form the R2 Route, which connects Harare with the Plumtree Border with Botswana.

Mutange Dam, across Mutange River, is a manmade earth fill embarkment dam located in Chisina Village, 30 km east of Gokwe and 35 km northwest of Empress Mine, in the Midlands Province of Zimbabwe. Mutange Dam is 42 km by road from Gokwe and 49 km from Empress, 117 km from Kadoma and 146 km from Kwekwe via Empress. It is owned and operated by the Ministry of Water Resources and Development.











