
Semnopithecus is a genus of Old World monkeys native to the Indian subcontinent, with all species with the exception of two being commonly known as gray langurs. Traditionally only one species Semnopithecus entellus was recognized, but since about 2001, additional species have been recognized. The taxonomy has been in flux, but currently eight species are recognized.

Trachypithecus is a genus of Old World monkeys containing species known as lutungs, langurs, or leaf monkeys. Their range is much of Southeast Asia.

Gee's golden langur, also known as simply the golden langur, is an Old World monkey found in a small region of Western Assam, India and in the neighboring foothills of the Black Mountains of Bhutan. Long considered sacred by many Himalayan people, the golden langur was first brought to the attention of the Western world by the naturalist Edward Pritchard Gee in the 1950s. Adult males have a cream to golden coat with darker flanks while the females and juveniles are lighter. The golden langur has a black face and a long tail up to 50 cm (19.69 in) in length. It lives in high trees and has a herbivorous diet of fruits, leaves, seeds, buds and flowers. The average group size is eight individuals, with a ratio of several females to each adult male. It is one of the most endangered primate species of India and Bhutan.

The Nilgiri langur is a langur. This primate has glossy black fur on its body and golden brown fur on its head. It is similar in size and long-tailed like the gray langurs. Females have a white patch of fur on the inner thigh. It typically lives in troops of nine to ten monkeys. Its diet consists of fruits, shoots and leaves. The species is classified as vulnerable due to habitat destruction and poaching for its fur and flesh, the latter believed to have aphrodisiac properties.

The Hatinh langur is a highly threatened Old World monkey found in limestone forests in Vietnam, primarily in the Quảng Bình Province. A recent survey discovered a small population living in the Quảng Trị Province. Contrary to its name, it is not known from the Hà Tĩnh Province. The local Van Kieu minority refer to this monkey as the 'Con Cung', which roughly translates as "black, cliff-dwelling monkey with a long tail". It resembles the closely related François' langur, but its white cheek-stripes typically extend behind the ears onto the nape, and the overall black colour is non-glossy and has a brownish tinge.

The silvery lutung, also known as the silvered leaf monkey or the silvery langur, is an Old World monkey. It is arboreal, living in coastal, mangrove, and riverine forests in Peninsular Malaysia, Sumatra, Borneo, Java, and other nearby islands.

The East Javan langur, also known as the ebony lutung, Javan langur or Javan lutung, is an Old World monkey from the Colobinae subfamily. It is most commonly glossy black with a brownish tinge to its legs, sides, and "sideburns". It is found on the island of Java, as well as on several of the surrounding Indonesian islands. The Latin word auratus in its scientific name means "golden", and refers to a less common color variant. Note that the common name golden langur is used for a different species.

Delacour's langur or Delacour's lutung is a critically endangered species of Old World monkey endemic to northern Vietnam. It is named for French-American ornithologist Jean Théodore Delacour.

The heath mouse is a species of mouse in the subfamily Murinae, the Old World rats and mice, found in Australia.

Phayre's leaf monkey, also known as Phayre's langur, is a species of Old World monkey native to South Asia and Southeast Asia, namely India, Bangladesh, and Myanmar. Populations from further east are now thought to belong to other species. It is listed as Endangered on the IUCN Red List and is threatened by hunting and loss of habitat. The species epithet commemorates Arthur Purves Phayre.

Shortridge's mouse is a species of rodent in the family Muridae. It is found in Cambodia, Laos, Myanmar, Thailand, and Vietnam.
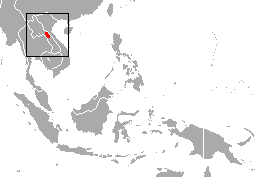
The Laotian langur or white-browed black langur is a species of primate in the family Cercopithecidae. It is endemic to Laos. Its natural habitat is subtropical or tropical dry forests. Genetically the Indochinese black and Hatinh langurs are very close to the Laotian langur, and consequently it has been suggested they should be considered subspecies of it.

The dusky leaf monkey, also known as the spectacled langur or the spectacled leaf monkey, is a species of primate in the family Cercopithecidae. It is found in Peninsular Malaysia, Myanmar and Thailand, and can occasionally be found in Singapore. During the day, these small, folivorous primates divide in sub-groups and forage for vegetation and fruit throughout the tropical forests. According to the IUCN, the dusky leaf monkey's population is declining due to habitat loss, poaching, and anthropogenic land use, which prompted the IUCN to classify the species as endangered in 2015.

The capped langur is a species of primate in the family Cercopithecidae. It is native to Bangladesh, Bhutan, India, and Myanmar. Its natural habitat is subtropical or tropical dry forests. It is threatened by habitat loss. They are arboreal and gregarious by nature. A herd of capped langurs consists of 2 to 14 langurs led by a single male. They are herbivorous, eating leaves, twigs, buds and fruits.

Germain's langur is an Old World monkey native to Thailand, Myanmar, Cambodia, Laos and Vietnam. The monkey was previously included in Trachypithecus cristatus and Trachypithecus villosus.
The Indochinese black langur is a poorly known Old World monkey native to Laos and adjacent Vietnam. It was originally described as a subspecies of T. auratus, but was later found to be a member of the T. francoisi group, with some maintaining it as a subspecies of that species. In 2001, it was recommended treating it as a separate species.

The World's 25 Most Endangered Primates is a list of highly endangered primate species selected and published by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) Species Survival Commission (SSC) Primate Specialist Group (PSG), the International Primatological Society (IPS), Global Wildlife Conservation (GWC), and Bristol Zoological Society (BZS). The IUCN/SSC PSG worked with Conservation International (CI) to start the list in 2000, but in 2002, during the 19th Congress of the International Primatological Society, primatologists reviewed and debated the list, resulting in the 2002–2004 revision and the endorsement of the IPS. The publication was a joint project between the three conservation organizations until the 2012–2014 list when BZS was added as a publisher. The 2018–2020 list was the first time Conservation International was not among the publishers, replaced instead by GWC. The list has been revised every two years following the biannual Congress of the IPS. Starting with the 2004–2006 report, the title changed to "Primates in Peril: The World's 25 Most Endangered Primates". That same year, the list began to provide information about each species, including their conservation status and the threats they face in the wild. The species text is written in collaboration with experts from the field, with 60 people contributing to the 2006–2008 report and 85 people contributing to the 2008–2010 report. The 2004–2006 and 2006–2008 reports were published in the IUCN/SSC PSG journal Primate Conservation,, since then they have been published as independent publications.


















