
Apiaceae or Umbelliferae is a family of mostly aromatic flowering plants named after the type genus Apium and commonly known as the celery, carrot or parsley family, or simply as umbellifers. It is the 16th-largest family of flowering plants, with more than 3,800 species in about 446 genera, including such well-known and economically important plants as ajwain, angelica, anise, asafoetida, caraway, carrot, celery, chervil, coriander, cumin, dill, fennel, lovage, cow parsley, parsley, parsnip and sea holly, as well as silphium, a plant whose identity is unclear and which may be extinct.

The Araliaceae are a family of flowering plants composed of about 43 genera and around 1500 species consisting of primarily woody plants and some herbaceous plants. The morphology of Araliaceae varies widely, but it is predominantly distinguishable based on its woody habit, tropical distribution, and the presence of simple umbels.

In botany a capsule is a type of simple, dry, though rarely fleshy dehiscent fruit produced by many species of angiosperms.

Smyrnium olusatrum, common name alexanders is an edible flowering plant of the family Apiaceae (Umbelliferae), which grows on waste ground and in hedges around the Mediterranean and Atlantic coastal regions of Europe. It was formerly widely grown as a pot herb, but is now appreciated mostly by foragers.

Hydrocotyle, also called floating pennywort, water pennywort, Indian pennywort, dollar weed, marsh penny, thick-leaved pennywort and even white rot is a genus of prostrate, perennial aquatic or semi-aquatic plants formerly classified in the family Apiaceae, now in the family Araliaceae.
Carlesia sinensis is a species of flowering plant in the Apiaceae and is the only member of the genus Carlesia. It is endemic to eastern China.

Scandix pecten-veneris is a species of edible plant belonging to the family Apiaceae. It is native to Eurasia, but is known to occur elsewhere. It is named for its long fruit, which has a thickened body up to 1.5 centimeters long and a beak which can measure up to 7 centimeters long and is lined with comblike bristles.

Chaerophyllum temulum, the rough chervil, is a species of flowering plant in the family Apiaceae.

Sium suave, the water parsnip or hemlock waterparsnip, is a perennial wildflower in the family Apiaceae. It is native to many areas of both Asia and North America. The common name water parsnip is due to its similarity to parsnip and its wetland habitat. The alternate common name hemlock waterparsnip is due to its similarity to the highly poisonous spotted water hemlock.

Oenanthe pimpinelloides is a species of flowering plant in the family Apiaceae known by the common name corky-fruited water-dropwort. It is a plant of damp or dry grassland and more ruderal tall herb communities.

Angelica acutiloba is a perennial herb from the family Apiaceae or Umbelliferous. It is predominately in Japan and perhaps endemic (unique). It is now distributed widely and cultivated in Jilin, China, Korea, Taiwan and Indonesia.

Thapsia villosa, commonly known as the villous deadly carrot, is a species of poisonous herbaceous plants in the genus Thapsia. It grows to about 70 to 190 cm in height. It has pinnate hairy leaves with sheath-like petioles. The flowers are yellow in color and borne on compound umbels. They develop into fruits with four wings characteristic of the genus. It is native to southwestern Europe and northwestern Africa surrounding the Mediterranean Sea. The plant was used extensively for traditional medicine since around the 3rd century BC.
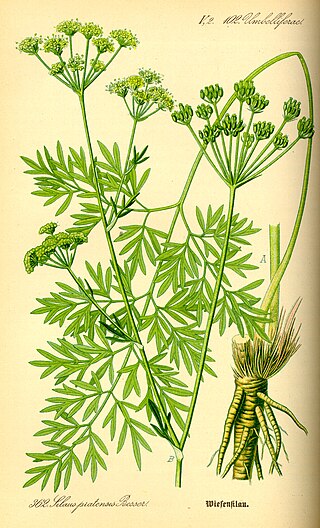
Silaum silaus, commonly known as pepper-saxifrage, is a perennial plant in the family Apiaceae (Umbelliferae) found across south-eastern, central, and western Europe, including the British Isles. It grows in damp grasslands on neutral soils.

Tordylium maximum, known as hartwort, is an annual or biennial flowering plant in the carrot family (Apiaceae).
Saposhnikovia is a monotypic genus of flowering plants in the family Apiaceae. Its only species is Saposhnikovia divaricata, known as fángfēng防風 in Chinese, bangpung in Korean, and siler in English. The plant is still frequently referenced under the obsolete genus name Ledebouriella in many online sources devoted to traditional Chinese medicine. It was first described as Stenocoelium divaricatum by Nikolai Turczaninow in 1844, and transferred to Saposhnikovia in 1951.

Seseli libanotis, also known by the common names moon carrot, mountain stone-parsley, or säfferot, is a species of herb in the genus Seseli of the carrot family, Apiaceae. It is native to Eurasia, throughout which it is widespread.

Oenanthe aquatica, fine-leaved water-dropwort, is an aquatic flowering plant in the carrot family. It is widely distributed from the Atlantic coast of Europe to central Asia.

Neogaya is a monotypic genus of flowering plants belonging to the family Apiaceae. It just contains one species, Neogaya simplex(L.) Meisn. It can be found in Europe, in the Alps, the western and southern Carpathians, also former Yugoslavia, Belarus and the European parts of Russia. It is also found in Asia, within Kazakhstan, China, and western Siberia.

Scandia is a genus of flowering plants belonging to the family Apiaceae. It is also in tribe Aciphylleae, with plants, Gingidia Dawson and Lignocarpa Dawson, with all three genera being native to New Zealand. They are scrambling shrubs with white flowers.

Zosima is a genus of flowering plants belonging to the family Apiaceae.


















