
Dugongidae is a family in the order of Sirenia. The family has one surviving species, the dugong, one recently extinct species, Steller's sea cow, and a number of extinct genera known from fossil records.

Moeritherium is an extinct genus of basal proboscideans from the Eocene of North and West Africa. It was related to elephants and, more distantly, to sea cows and hyraxes.
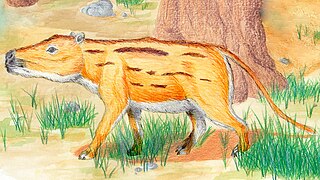
Didolodus is an extinct genus of mammals from Middle Eocene Argentina. It is an ungulate mammal of uncertain affinities, possibly related to Litopterna, though this is uncertain due to the lack of reliable post-cranial remains, and for now remains Meridiungulata incertae sedis. Its remains were found in the Sarmiento Formation of Patagonia.
Numidotheriidae is an extinct family of primitive proboscideans that lived from the late Paleocene to the early Oligocene periods of North Africa.

Sirenia is the order of placental mammals which comprises modern "sea cows" and their extinct relatives. They are the only extant herbivorous marine mammals and the only group of herbivorous mammals to have become completely aquatic. Sirenians are thought to have a 50-million-year-old fossil record. They attained modest diversity during the Oligocene and Miocene, but have since declined as a result of climatic cooling, oceanographic changes, and human interference. Two genera and four species are extant: Trichechus, which includes the three species of manatee that live along the Atlantic coasts and in rivers and coastlines of the Americas and western Africa, and Dugong, which is found in the Indian and Pacific oceans.

Ailuravus is a genus of prehistoric rodents in the family Ischyromyidae.

Cow Head is a town in the Canadian province of Newfoundland and Labrador. The town had a population of 478 in the Canada 2016 Census.

Eotheroides is an extinct genus of Eocene sirenian. It is an early member of the family Dugongidae, which includes the extant dugong. Fossils have been found from Egypt, India, and Madagascar. Eotheroides was first described by Richard Owen in 1875 under the name Eotherium, which was replaced by the current name in 1899.

Protosiren is an extinct early genus of the order Sirenia. Protosiren existed throughout the Lutetian to Priabonian stages of the Middle Eocene. Fossils have been found in the far-flung locations like the United States, Africa (Egypt), Europe and Asia.

Umayodus is an extinct genus of "condylarth" mammal from the late Paleocene or the earliest Eocene. It is a didolodontid which lived in what is now Peru. It is known from the holotype LU3-801, an isolated right third molar, which was found in the Muñani Formation of Laguna Umayo, Peru. It was first named by Javier N. Gelfo and Bernard Sigé in 2011 and the type species is Umayodus raimondi.

Eosiren is an extinct genus of sea cow that lived during the Late Eocene to Early Oligocene (Rupelian). Several fossils have been found in Egypt. It seems like the species E. abeli were contemporaneous with Protosiren and Eotheroides. like them, Eosiren closely resembled modern sirenians. It differs from them by having somewhat larger innominates and possess thigh bones.
This list, 2013 in molluscan paleontology, is a list of new taxa of ammonites and other fossil cephalopods, as well as fossil gastropods, bivalves and other molluscs that have been described during the year 2013.

Didolodontidae is a possibly paraphyletic family of "condylarth" mammals known from the Paleogene of South America, with most specimens known from Argentina. They were generally small-medium in body size, and had a bunodont dentition. A close relationship with litopterns has been suggested by some studies. They range in age from the early Paleocene (Selandian/Peligran) to late Eocene (Priabonian/Mustersan). The attribution of Salladolodus deuterotheroides from the Late Oligocene of Bolivia to the family is doubtful.

Mont-Saint-Aubert is a village of Wallonia and a district of the municipality of Tournai, located in the province of Hainaut, Belgium.
Paralitherium was an early sea cow from the late Eocene of Hungary (Felsotarkany).
Anisosiren was an early sea cow from the Middle Eocene of Hungary.
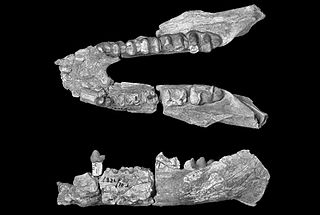
Arcanotherium is an extinct genus of early proboscidean belonging to the family Numidotheriidae that lived in north Africa during the late Eocene/early Oligocene interval.

Harmatia is an extinct genus of sea snails, marine gastropod mollusks, in the subfamily Muricinae, the murex snails or rock snails.
Colbertia is an extinct genus of oldfieldthomasiid notoungulate. It lived from the Early to the Middle Eocene, and its fossilized remains were discovered in Argentina and Brazil.
Acteon dudariensis is an extinct species of sea snail, a marine gastropod mollusc in the family Acteonidae.














