Related Research Articles

The Nasdaq Stock Market is an American stock exchange based in New York City. It is the most active stock trading venue in the US by volume, and ranked second on the list of stock exchanges by market capitalization of shares traded, behind the New York Stock Exchange. The exchange platform is owned by Nasdaq, Inc., which also owns the Nasdaq Nordic stock market network and several U.S.-based stock and options exchanges.

Market capitalization, sometimes referred to as market cap, is the total value of a publicly traded company's outstanding common shares owned by stockholders.

Pump and dump (P&D) is a form of securities fraud that involves artificially inflating the price of an owned stock through false and misleading positive statements (pump), in order to sell the cheaply purchased stock at a higher price (dump). Once the operators of the scheme "dump" (sell) their overvalued shares, the price falls and investors lose their money. This is most common with small-cap cryptocurrencies and very small corporations/companies, i.e. "microcaps".

A public company is a company whose ownership is organized via shares of stock which are intended to be freely traded on a stock exchange or in over-the-counter markets. A public company can be listed on a stock exchange, which facilitates the trade of shares, or not. In some jurisdictions, public companies over a certain size must be listed on an exchange. In most cases, public companies are private enterprises in the private sector, and "public" emphasizes their reporting and trading on the public markets.
Small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) or small and medium-sized businesses (SMBs) are businesses whose personnel and revenue numbers fall below certain limits. The abbreviation "SME" is used by international organizations such as the World Bank, the OECD, European Union, the United Nations, and the World Trade Organization (WTO).
Penny stocks are common shares of small public companies that trade for less than one dollar per share. The U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) uses the term "Penny stock" to refer to a security, a financial instrument which represents a given financial value, issued by small public companies that trade at less than $5 per share. Penny stocks are priced over-the-counter, rather than on the trading floor. The term "penny stock" refers to shares that, prior to the SEC's classification, traded for "pennies on the dollar". In 1934, when the United States government passed the Securities Exchange Act to regulate any and all transactions of securities between parties which are "not the original issuer", the SEC at the time disclosed that equity securities which trade for less than $5 per share could not be listed on any national stock exchange or index.
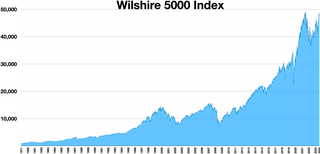
The Wilshire 5000 Total Market Index, or more simply the Wilshire 5000, is a market-capitalization-weighted index of the market value of all American stocks actively traded in the United States. As of September 30, 2023, the index contained 3,427 components. The index is intended to measure the performance of most publicly traded companies headquartered in the United States, with readily available price data. Hence, the index includes a majority of the common stocks and REITs traded primarily through New York Stock Exchange, NASDAQ, or the American Stock Exchange. Limited partnerships and ADRs are not included. It can be tracked by following the ticker ^W5000.
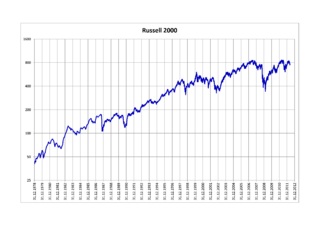
The Russell 2000 Index is a small-cap U.S. stock market index that makes up the smallest 2,000 stocks in the Russell 3000 Index. It was started by the Frank Russell Company in 1984. The index is maintained by FTSE Russell, a subsidiary of the London Stock Exchange Group (LSEG).
Russell indexes are a family of global stock market indices from FTSE Russell that allow investors to track the performance of distinct market segments worldwide. Many investors use mutual funds or exchange-traded funds based on the FTSE Russell Indexes as a way of gaining exposure to certain portions of the U.S. stock market. Additionally, many investment managers use the Russell Indexes as benchmarks to measure their own performance. Russell's index design has led to more assets benchmarked to its U.S. index family than all other U.S. equity indexes combined.
The OTC (Over-The-Counter) Bulletin Board or OTCBB was a United States quotation medium operated by the Financial Industry Regulatory Authority (FINRA) for its subscribing members. FINRA closed the OTCBB on November 8, 2021.
Authorities provide differing definitions of the middle-market or mid-market companies. While some authorities look to revenue generated by companies to define the middle market, other sources regard either asset size or number of employees as a better metric for comparing company sizes.

Securities fraud, also known as stock fraud and investment fraud, is a deceptive practice in the stock or commodities markets that induces investors to make purchase or sale decisions on the basis of false information. The setups are generally made to result in monetary gain for the deceivers, and generally result in unfair monetary losses for the investors. They are generally violating securities laws.
A capitalization-weightedindex, also called a market-value-weighted index is a stock market index whose components are weighted according to the total market value of their outstanding shares. Every day an individual stock's price changes and thereby changes a stock index's value. The impact that individual stock's price change has on the index is proportional to the company's overall market value, in a capitalization-weighted index. In other types of indices, different ratios are used.
In business and investing, term microcap stock refers to the stock of public companies in the United States which have a market capitalization of roughly $50 million to $250 million. The shares of companies with a market capitalization of less than $50 million are typically referred to as nano-cap stocks. Many micro-cap and nano-cap stocks are traded over-the-counter with their prices quoted on the OTCBB, OTC Link LLC, or the Pink Sheets. The larger, more established micro-caps are listed on the NASDAQ Capital Market or American Stock Exchange (AMEX).

Microcap stock fraud is a form of securities fraud involving stocks of "microcap" companies, generally defined in the United States as those with a market capitalization of under $250 million. Its prevalence has been estimated to run into the billions of dollars a year. Many microcap stocks are penny stocks, which the SEC defines as a security that trades at less than $5 per share, is not listed on a national exchange, and fails to meet other specific criteria.
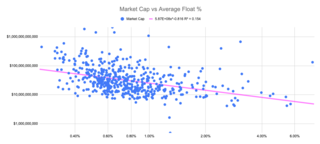
In the context of stock markets, the public float or free float represents the portion of shares of a corporation that are in the hands of public investors as opposed to locked-in shares held by promoters, company officers, controlling-interest investors, or governments. This number is sometimes seen as a better way of calculating market capitalization, because it provides a more accurate reflection of what public investors consider the company to be worth. In this context, the float may refer to all the shares outstanding that can be publicly traded.

In finance, a stock index, or stock market index, is an index that measures the performance of a stock market, or of a subset of a stock market. It helps investors compare current stock price levels with past prices to calculate market performance.

Big Tech, also known as the Tech Giants, are the largest information technology companies. The term most often refers to the Big Five tech companies in the United States: Alphabet (Google), Amazon, Apple, Meta, and Microsoft. In China, Baidu, Alibaba, Tencent, and Xiaomi (BATX) are the equivalent of the Big Five. Big Tech can also include smaller tech companies with high valuations, such as Netflix, or non-tech companies with high-tech practices, such as the automaker Tesla.
Megacap stocks are stocks with a capitalization or market value over $200 billion. In business and investing the market capitalization term megacap stock is also referred to as mega-cap in the United States. The companies are the largest publicly traded companies in the world. Capitalization is the total value of the outstanding common shares owned by stockholders. Stocks under $200 billion are Large cap stocks. Megacap stocks are listed on the NASDAQ Capital Market or American Stock Exchange (AMEX). Market caps term may be different outside the United States.
References
- ↑ "Market Cap Explained | FINRA.org". www.finra.org.
- ↑ Bowman, Jeremy. "3 Best Small-Cap Stocks to Buy in 2023". The Motley Fool.
- ↑ Tucker, Hank. "The Best And Worst Small Cap Stocks Of First Half 2023". Forbes.