
Frontotemporal lobar degeneration (FTLD) is a pathological process that occurs in frontotemporal dementia. It is characterized by atrophy in the frontal lobe and temporal lobe of the brain, with sparing of the parietal and occipital lobes.
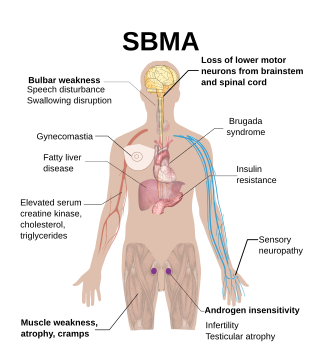
Spinal and bulbar muscular atrophy (SBMA), popularly known as Kennedy's disease, is a rare, adult-onset, X-linked recessive lower motor neuron disease caused by trinucleotide CAG repeat expansions in exon 1 of the androgen receptor (AR) gene, which results in both loss of AR function and toxic gain of function.

Congenital muscular dystrophies are autosomal recessively-inherited muscle diseases. They are a group of heterogeneous disorders characterized by muscle weakness which is present at birth and the different changes on muscle biopsy that ranges from myopathic to overtly dystrophic due to the age at which the biopsy takes place.

Progressive muscular atrophy (PMA), also called Duchenne–Aran disease and Duchenne–Aran muscular atrophy, is a disorder characterised by the degeneration of lower motor neurons, resulting in generalised, progressive loss of muscle function.

Spinal muscular atrophy (SMA) is a rare neuromuscular disorder that results in the loss of motor neurons and progressive muscle wasting. It is usually diagnosed in infancy or early childhood and if left untreated it is the most common genetic cause of infant death. It may also appear later in life and then have a milder course of the disease. The common feature is progressive weakness of voluntary muscles, with arm, leg and respiratory muscles being affected first. Associated problems may include poor head control, difficulties swallowing, scoliosis, and joint contractures.
Dejerine–Sottas disease, also known as, Dejerine–Sottas syndrome, hereditary motor and sensory polyneuropathy type III, and Charcot–Marie–Tooth disease type 3, is a hereditary neurological disorder characterized by damage to the peripheral nerves, demyelination, and resulting progressive muscle wasting and somatosensory loss. The condition is caused by mutations in various genes and currently has no known cure.

Distal myopathy is a group of rare genetic disorders that cause muscle damage and weakness, predominantly in the hands and/or feet. Mutation of many different genes can be causative. Many types involve dysferlin.

Spinocerebellar ataxia type 6 (SCA6) is a rare, late-onset, autosomal dominant disorder, which, like other types of SCA, is characterized by dysarthria, oculomotor disorders, peripheral neuropathy, and ataxia of the gait, stance, and limbs due to cerebellar dysfunction. Unlike other types, SCA 6 is not fatal. This cerebellar function is permanent and progressive, differentiating it from episodic ataxia type 2 (EA2) where said dysfunction is episodic. In some SCA6 families, some members show these classic signs of SCA6 while others show signs more similar to EA2, suggesting that there is some phenotypic overlap between the two disorders. SCA6 is caused by mutations in CACNA1A, a gene encoding a calcium channel α subunit. These mutations tend to be trinucleotide repeats of CAG, leading to the production of mutant proteins containing stretches of 20 or more consecutive glutamine residues; these proteins have an increased tendency to form intracellular agglomerations. Unlike many other polyglutamine expansion disorders expansion length is not a determining factor for the age that symptoms present.
Episodic ataxia (EA) is an autosomal dominant disorder characterized by sporadic bouts of ataxia with or without myokymia. There are seven types recognized but the majority are due to two recognized entities. Ataxia can be provoked by psychological stress or startle, or heavy exertion, including exercise. Symptoms can first appear in infancy. There are at least six loci for EA, of which 4 are known genes. Some patients with EA also have migraine or progressive cerebellar degenerative disorders, symptomatic of either familial hemiplegic migraine or spinocerebellar ataxia. Some patients respond to acetazolamide though others do not.

Glycine—tRNA ligase also known as glycyl–tRNA synthetase is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the GARS1 gene.

Cytoplasmic dynein 1 heavy chain 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the DYNC1H1 gene.

Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), also known as motor neurone disease (MND) or Lou Gehrig's disease in the United States, is a rare but terminal neurodegenerative disorder that results in the progressive loss of both upper and lower motor neurons that normally control voluntary muscle contraction. ALS is the most common form of the motor neuron diseases. ALS often presents in its early stages with gradual muscle stiffness, twitches, weakness, and wasting. Motor neuron loss typically continues until the abilities to eat, speak, move, and, lastly, breathe are all lost. While only 15% of people with ALS also fully develop frontotemporal dementia, an estimated 50% face at least some minor difficulties with thinking and behavior. Depending on which of the aforementioned symptoms develops first, ALS is classified as limb-onset or bulbar-onset.

X-linked spinal muscular atrophy type 2, also known as arthrogryposis multiplex congenita X-linked type 1 (AMCX1), is a rare neurological disorder involving death of motor neurons in the anterior horn of spinal cord resulting in generalised muscle wasting (atrophy). The disease is caused by a mutation in UBA1 gene and is passed in an X-linked recessive manner by carrier mothers to affected sons.

Distal spinal muscular atrophy type 1 (DSMA1), also known as spinal muscular atrophy with respiratory distress type 1 (SMARD1), is a rare neuromuscular disorder involving death of motor neurons in the spinal cord which leads to a generalised progressive atrophy of body muscles.

Spinal muscular atrophy with progressive myoclonic epilepsy (SMA-PME), sometimes called Jankovic–Rivera syndrome, is a very rare neurodegenerative disease whose symptoms include slowly progressive muscle (atrophy), predominantly affecting proximal muscles, combined with denervation and myoclonic seizures. Only 12 known human families are described in scientific literature to have SMA-PME.

Distal spinal muscular atrophy type 2 (DSMA2), also known as Jerash type distal hereditary motor neuropathy (HMNJ), is a very rare childhood-onset genetic disorder characterised by progressive muscle wasting affecting lower and subsequently upper limbs. The disorder has been described in Arab inhabitants of Jerash region in Jordan as well as in a Chinese family.

Monomelic amyotrophy (MMA) is a rare motor neuron disease first described in 1959 in Japan. Its symptoms usually appear about two years after adolescent growth spurt and is significantly more common in males, with an average age of onset between 15 and 25 years. MMA is reported most frequently in Asia but has a global distribution. It is typically marked by insidious onset of muscle atrophy of an upper limb, which plateaus after two to five years from which it neither improves nor worsens. There is no pain or sensory loss associated with MMA. MMA is not believed to be hereditary.
Distal hereditary motor neuropathy type V is a particular type of neuropathic disorder. In general, distal hereditary motor neuropathies affect the axons of distal motor neurons and are characterized by progressive weakness and atrophy of muscles of the extremities. It is common for them to be called "spinal forms of Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease (CMT)", because the diseases are closely related in symptoms and genetic cause. The diagnostic difference in these diseases is the presence of sensory loss in the extremities. There are seven classifications of dHMNs, each defined by patterns of inheritance, age of onset, severity, and muscle groups involved. Type V is a disorder characterized by autosomal dominance, weakness of the upper limbs that is progressive and symmetrical, and atrophy of the small muscles of the hands.

Spinal muscular atrophy with lower extremity predominance 2A (SMALED2A) is a rare neuromuscular disorder characterised by muscle weakness predominantly in legs. The disorder is usually diagnosed shortly after birth; affected children have a delayed motor development, waddling gait, difficulties walking, sometimes develop spasticity. Sensation, swallowing and cognitive development are not affected. The disorder is slowly progressive throughout the lifetime.

Spinal muscular atrophy with lower extremity predominance 2B (SMALED2B) is a rare neuromuscular disorder characterised by generalised muscle weakness.













