Factitious disorder imposed on self, also known as Munchausen syndrome, is a factitious disorder in which those affected feign or induce disease, illness, injury, abuse, or psychological trauma to draw attention, sympathy, or reassurance to themselves. Munchausen syndrome fits within the subclass of factitious disorder with predominantly physical signs and symptoms, but patients also have a history of recurrent hospitalization, travelling, and dramatic, extremely improbable tales of their past experiences. The term Munchausen syndrome derives its name from the fictional character Baron Munchausen.
In psychology, false memory syndrome (FMS) was a proposed "pattern of beliefs and behaviors" in which a person's identity and relationships are affected by false memories of psychological trauma, recollections which are strongly believed by the individual, but contested by the accused. False memory syndrome was proposed to be the result of recovered memory therapy, a scientifically discredited form of therapy intended to recover memories. Originally conceptualized by the False Memory Syndrome Foundation, the organization sought to understand what they understood as a general pattern of behaviors that followed after a patient underwent recovered memory therapy and to come up with a term to explain the pattern. The principle that individuals can hold false memories and the role that outside influence can play in their formation is widely accepted by scientists, but there is debate over whether this effect can lead to the kinds of detailed memories of repeated sexual abuse and significant personality changes typical of cases that FMS has historically been applied to. FMS is not listed as a psychiatric illness in any medical manuals including the ICD-11, or the DSM-5. The most influential figure in the genesis of the theory is psychologist Elizabeth Loftus.

Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) is a functional gastrointestinal disorder characterized by a group of symptoms that commonly include abdominal pain, abdominal bloating and changes in the consistency of bowel movements. These symptoms may occur over a long time, sometimes for years. IBS can negatively affect quality of life and may result in missed school or work or reduced productivity at work. Disorders such as anxiety, major depression, and chronic fatigue syndrome are common among people with IBS.

Kernicterus is a bilirubin-induced brain dysfunction. The term was coined in 1904 by Christian Georg Schmorl. Bilirubin is a naturally occurring substance in the body of humans and many other animals, but it is neurotoxic when its concentration in the blood is too high, a condition known as hyperbilirubinemia. Hyperbilirubinemia may cause bilirubin to accumulate in the grey matter of the central nervous system, potentially causing irreversible neurological damage. Depending on the level of exposure, the effects range from clinically unnoticeable to severe brain damage and even death.

Chorea is an abnormal involuntary movement disorder, one of a group of neurological disorders called dyskinesias. The term chorea is derived from the Ancient Greek: χορεία, as the quick movements of the feet or hands are comparable to dancing.

Athetosis is a symptom characterized by slow, involuntary, convoluted, writhing movements of the fingers, hands, toes, and feet and in some cases, arms, legs, neck and tongue. Movements typical of athetosis are sometimes called athetoid movements. Lesions to the brain are most often the direct cause of the symptoms, particularly to the corpus striatum. This symptom does not occur alone and is often accompanied by the symptoms of cerebral palsy, as it is often a result of this physical disability. Treatments for athetosis are not very effective, and in most cases are simply aimed at managing the uncontrollable movement, rather than the cause itself.
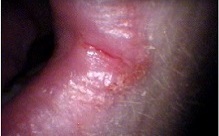
Plummer–Vinson syndrome is a rare disease characterized by dysphagia, iron-deficiency anemia, glossitis, cheilosis, and esophageal webs. Treatment with iron supplementation and mechanical widening of the esophagus generally leads to excellent outcomes.
Hepatosplenomegaly is the simultaneous enlargement of both the liver (hepatomegaly) and the spleen (splenomegaly). Hepatosplenomegaly can occur as the result of acute viral hepatitis, infectious mononucleosis, and histoplasmosis or it can be the sign of a serious and life-threatening lysosomal storage disease. Systemic venous hypertension can also increase the risk for developing hepatosplenomegaly, which may be seen in those patients with right-sided heart failure.

The intergluteal cleft or just gluteal cleft, also known by a number of synonyms, including natal cleft and cluneal cleft, is the groove between the buttocks that runs from just below the sacrum to the perineum, so named because it forms the visible border between the external rounded protrusions of the gluteus maximus muscles. Other names are the anal cleft, crena analis, crena interglutealis, and rima ani. Colloquially, the intergluteal cleft is known as bum crack (UK) or butt crack (US). The intergluteal cleft is located superior to the anus.

Organic brain syndrome, also known as organic brain disease, organic brain damage, organic brain disorder, organic mental syndrome, or organic mental disorder, refers to any syndrome or disorder of mental function whose cause is alleged to be known as organic (physiologic) rather than purely of the mind. These names are older and nearly obsolete general terms from psychiatry, referring to many physical disorders that cause impaired mental function. They are meant to exclude psychiatric disorders. Originally, the term was created to distinguish physical causes of mental impairment from psychiatric disorders, but during the era when this distinction was drawn, not enough was known about brain science for this cause-based classification to be more than educated guesswork labeled with misplaced certainty, which is why it has been deemphasized in current medicine. While mental or behavioural abnormalities related to the dysfunction can be permanent, treating the disease early may prevent permanent damage in addition to fully restoring mental functions. An organic cause to brain dysfunction is suspected when there is no indication of a clearly defined psychiatric or "inorganic" cause, such as a mood disorder.
Factitious disorder imposed on another (FDIA), also known as fabricated or induced illness by carers (FII) and first named as Munchausen syndrome by proxy (MSbP) after Munchausen syndrome, is a mental health disorder in which a caregiver creates the appearance of health problems in another person, typically their child, and sometimes (rarely) when an adult simulates an illness in another adult partner. This might include altering test samples or injuring a child. The caregiver or partner then presents the person as being sick or injured. Permanent injury or death of the victim can occur as a result of the disorder. The behaviour might be motivated by the caregiver or partner seeking sympathy or attention.
Glucose transporter 1, also known as solute carrier family 2, facilitated glucose transporter member 1 (SLC2A1), is a uniporter protein that in humans is encoded by the SLC2A1 gene. GLUT1 facilitates the transport of glucose across the plasma membranes of mammalian cells. This gene encodes a facilitative glucose transporter that is highly expressed in erythrocytes and endothelial cells, including cells of the blood–brain barrier. The encoded protein is found primarily in the cell membrane and on the cell surface, where it can also function as a receptor for human T-cell leukemia virus (HTLV) I and II. GLUT1 accounts for 2 percent of the protein in the plasma membrane of erythrocytes.
Paroxysmal nonkinesigenic dyskinesia (PNKD) is an episodic movement disorder first described by Mount and Reback in 1940 under the name "Familial paroxysmal choreoathetosis". It is a rare hereditary disease that affects various muscular and nervous systems in the body, passing to roughly fifty percent of the offspring.

Costeff syndrome, or 3-methylglutaconic aciduria type III, is a genetic disorder caused by mutations in the OPA3 gene. It is typically associated with the onset of visual deterioration in early childhood followed by the development of movement problems and motor disability in later childhood, occasionally along with mild cases of cognitive deficiency. The disorder is named after Hanan Costeff, the doctor who first described the syndrome in 1989.

DeSanctis–Cacchione syndrome is a genetic disorder characterized by the skin and eye symptoms of xeroderma pigmentosum (XP) occurring in association with microcephaly, progressive intellectual disability, slowed growth and sexual development, deafness, choreoathetosis, ataxia and quadriparesis.
Chorea gravidarum is a rare type of chorea which presents with involuntary abnormal movement, characterized by abrupt, brief, nonrhythmic, nonrepetitive movement of any limb, often associated with nonpatterned facial grimaces. It is a complication of pregnancy which can be associated with eclampsia and its effects upon the basal ganglia. It is not a causal or pathologically distinct entity but a generic term for chorea of any cause starting during pregnancy. It is associated with history of Sydenham's chorea. It mostly occurs in young patients; the average age is 22 years.

Paroxysmal kinesigenic choreoathetosis (PKC) also called paroxysmal kinesigenic dyskinesia (PKD) is a rare hyperkinetic movement disorder characterized by attacks of involuntary movements, which are triggered by sudden voluntary movements. The number of attacks can increase during puberty and decrease in a person's 20s to 30s. Involuntary movements can take many forms such as ballism, chorea or dystonia and usually only affect one side of the body or one limb in particular.

Crack cocaine, commonly known simply as crack, and also known as rock, is a free base form of the stimulant cocaine that can be smoked. Crack offers a short, intense high to smokers. The Manual of Adolescent Substance Abuse Treatment calls it the most addictive form of cocaine.









