
Acipenseriformes is an order of basal ray-finned fishes that includes living and fossil sturgeons and paddlefishes (Acipenseroidei), as well as the extinct families Chondrosteidae and Peipiaosteidae. They are the second earliest diverging group of living ray-finned fish after the bichirs. Despite being early diverging, they are highly derived, having only weakly ossified skeletons that are mostly made of cartilage, and in modern representatives highly modified skulls.

Paddlefish are a family of ray-finned fish belonging to order Acipenseriformes, and one of two living groups of the order alongside sturgeons (Acipenseridae). They are distinguished from other fish by their elongated rostra, which are thought to enhance electroreception to detect prey. Paddlefish have been referred to as "primitive fish" because the Acipenseriformes are among the earliest diverging lineages of ray-finned fish, having diverged from all other living groups over 300 million years ago. Paddlefish are almost exclusively North American and Chinese, both extant and in the fossil record.

The Chinese paddlefish, also known as the Chinese swordfish, is an extinct species of fish that was formerly native to the Yangtze and Yellow River basins in China. With records of specimens over three metres and possibly 7 m (23 ft) in length, it was one of the largest species of freshwater fish. It was the only species in the genus Psephurus and one of two recent species of paddlefish (Polyodontidae), the other being the American paddlefish. It was an anadromous species, meaning that it spent part of its adult life at sea, while migrating upriver to spawn.

Chondrosteus is a genus of extinct actinopterygian belonging to the family Chondrosteidae. It lived during the Sinemurian in what is now England. Chondrosteus is related to sturgeons and paddlefishes as part of the clade Acipenseriformes. Similar to sturgeons, the jaws of Chondrosteus were free from the rest of the skull. Its scale cover was reduced to the upper lobe of the caudal fin like in paddlefish.

Lycoptera is an extinct genus of fish that lived from Lower Cretaceous, Barremian to Aptian in present-day China, North Korea, Mongolia and Siberia. Although there is record from Jurassic Formation in Siberia, its age remains questionable. It is known from abundant fossils representing sixteen species, which serve as important index fossil used to date geologic formations in China. Along with the genus Peipiaosteus, Lycoptera has been considered a defining member of the Jehol Biota, a prehistoric ecosystem famous for its feathered dinosaurs, which flourished for 20 million years during the Early Cretaceous, where it occurs abundantly in often monospecific beds, where they are thought to have died in seasonal mass death events. Lycoptera is a crown group teleost belonging to an early diverging lineage of the Osteoglossomorpha, which contains living mooneyes, arapaima, arowana, elephantfish and knifefish/featherbacks.
Protoscaphirhynchus squamosus is an extinct sturgeon from the Late Cretaceous of North America. It is known from a single poorly preserved specimen found in the Maastrichtian aged Hell Creek Formation in Montana. Due to its poor preservational state, it has few diagnostic characters.
Palaeopsephurus is an extinct genus of paddlefish (Polyodontidae). At present the genus contains the single species Palaeopsephurus wilsoni. The genus is known from the Late Cretaceous (Maastrichtian) aged Hell Creek Formation of Montana.
Styracopterus is an extinct genus of prehistoric bony fish that lived during the Tournaisian stage of the Mississippian epoch of Scotland and Eastern European Platform, Russia.

Strongylosteus is an extinct genus of prehistoric ray-finned fish that lived during the early Toarcian age of the Early Jurassic epoch. Its type species is Strongylosteus hindenburgi (monotypy). It is related to modern sturgeon and paddlefish (Acipenseroidei), but with a different kind of mouth than common species, made for hunting prey in open waters, with a strong lower jaw, similar to modern beluga.

Cyranorhis is an extinct genus of prehistoric bony fish that lived during the Serpukhovian age of the Carboniferous period in what is now Montana, United States.

Peipiaosteus is an extinct genus of prehistoric chondrostean ray-finned fish. Its fossils are found in the Early Cretaceous Jiufotang Formation, Pani Lake, Liaoning Province, China.

Protopsephurus is an extinct genus of paddlefish containing the single species Protopsephurus liui, known from the Yixian Formation in Liaoning, northern China from the Barremian to Aptian ages of the Early Cretaceous period around 125-120 million years ago. It is currently the oldest and most basal paddlefish known.
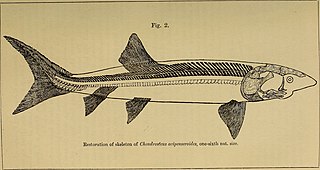
Chondrosteidae is a family of extinct marine actinopterygian fishes in the order Acipenseriformes. Three genera are known from the Early Jurassic of Europe, Chondrosteus, Gyrosteus, and Strongylosteus. Included species were of large size, with body lengths ranging from 2 metres (6.6 ft) up to 7 metres (23 ft). Their skeleton was largely made up of bones, but ossification was reduced compared to other ray-fins.

Archaeomaenidae is an extinct family of stem-teleost fish found in freshwater environments of Jurassic New South Wales of Australia, China, and Antarctica, and in Lower Cretaceous New South Wales and Mongolia.

Crossopholis is an extinct fish known from the early Eocene (Ypresian) of North America, approximately 52 million years ago. It is a close relative of the contemporary American paddlefish, belonging to the paddlefish family Polyodontidae.
This list of fossil fishes described in 2020 is a list of new taxa of jawless vertebrates, placoderms, acanthodians, fossil cartilaginous fishes, bony fishes, and other fishes of every kind that were described during the year 2020, as well as other significant discoveries and events related to paleoichthyology that occurred in 2020.
Eochondrosteus is a genus of extinct actinopterygian, comprising one species, E. sinensis (monotypy) from the Early Triassic strata in Gansu Province, China. It is suggested to be the most basal acipenseriform. It was originally described in 2005, and then redescribed in 2020 in Chinese. Other authors have considered the placement of Eochondrosteus within the Acipenseriformes as tentative.

Peipiaosteidae is an extinct family of fish, known from the Late Jurassic and Early Cretaceous of Asia. They are members of Acipenseriformes, related to sturgeons (Acipenseridae) and paddlefish (Polyodontidae). Fossils have been found in freshwater deposits in China, Russia, Kazakhstan, and Mongolia. They are generally considered either the earliest diverging group of Acipenseriformes, or the sister group to the clade containing Acipenseridae and Polyodontidae. At least Yanosteus was likely to have been piscivorous, based on a specimen of Lycoptera found in the mouth of one specimen.
Priscosturion is a genus of sturgeon from the Judith River Formation. It lived during the Campanian stage of the Late Cretaceous some 77.5 million years ago. Initially called Psammorhynchus, its describers Lance Grande and Eric J. Hilton renamed the animal in 2009. The fish belongs to the subfamily Priscosturioninae within the larger family Acipenseridae. Priscosturion is only known from one species, P. longipinnis.
Parapsephurus is an extinct genus of paddlefish in the family Polyodontidae. Currently the only known species in this genus is the type species, Parapsephurus willybemisi.P. willybemisi is known a nearly complete specimen from the Tanis locality of the Hell Creek Formation in North Dakota, USA, which dates to the late Maastrichtian stage of the Late Cretaceous, approximately 66 million years ago.













