
The Amur River or Heilong River is a perennial river in Northeast Asia, forming the natural border between the Russian Far East and Northeast China. The Amur proper is 2,824 km (1,755 mi) long, and has a drainage basin of 1,855,000 km2 (716,000 sq mi). If including its main stem tributary, the Argun, the Amur is 4,444 km (2,761 mi) long, making it the world's tenth longest river.
Sturgeon is the common name for the 28 species of fish belonging to the family Acipenseridae. The earliest sturgeon fossils date to the Late Cretaceous, and are descended from other, earlier acipenseriform fish, which date back to the Early Jurassic period, some 174 to 201 million years ago. They are one of two living families of the Acipenseriformes alongside paddlefish (Polyodontidae). The family is grouped into four genera: Acipenser, Huso, Scaphirhynchus, and Pseudoscaphirhynchus. Two species may be extinct in the wild, and one may be entirely extinct. Sturgeons are native to subtropical, temperate and sub-Arctic rivers, lakes and coastlines of Eurasia and North America. A Maastrichtian-age fossil found in Morocco shows that they also once lived in Africa.

Acipenseriformes is an order of basal ray-finned fishes that includes living and fossil sturgeons and paddlefishes (Acipenseroidei), as well as the extinct families Chondrosteidae and Peipiaosteidae. They are the second earliest diverging group of living ray-finned fish after the bichirs. Despite being early diverging, they are highly derived, having only weakly ossified skeletons that are mostly made of cartilage, and in modern representatives highly modified skulls.

The Chinese paddlefish, also known as the Chinese swordfish, is an extinct species of fish that was formerly native to the Yangtze and Yellow River basins in China. With records of specimens over three metres and possibly 7 m (23 ft) in length, it was one of the largest species of freshwater fish. It was the only species in the genus Psephurus and one of two recent species of paddlefish (Polyodontidae), the other being the American paddlefish. It was an anadromous species, meaning that it spent part of its adult life at sea, while migrating upriver to spawn.
Chondrostei is a group of non-neopterygian ray-finned fish. While the term originally referred to the paraphyletic grouping of all non-neopterygian ray-finned fish, it was redefined by Patterson in 1982 to be a clade comprising the Acipenseriformes and their extinct relatives.

Caviar is a food consisting of salt-cured roe of the family Acipenseridae. Caviar is considered a delicacy and is eaten as a garnish or spread. Traditionally, the term caviar refers only to roe from wild sturgeon in the Caspian Sea and Black Sea. The term caviar can also describe the roe of other species of sturgeon or other fish such as paddlefish, salmon, steelhead, trout, lumpfish, whitefish, or carp.

The beluga, also known as the beluga sturgeon or great sturgeon, is a species of anadromous fish in the sturgeon family (Acipenseridae) of the order Acipenseriformes. It is found primarily in the Caspian and Black Sea basins, and formerly in the Adriatic Sea. Based on maximum size, it is the third-most-massive living species of bony fish. Heavily fished for the female's valuable roe, known as beluga caviar, wild populations have been greatly reduced by overfishing and poaching, leading IUCN to classify the species as critically endangered.

The kaluga, also known as the river beluga, is a large predatory sturgeon found in the Amur River basin from Russia to China and near Hokkaido in Japan. With a maximum size of at least 1,000 kg (2,205 lb) and 5.6 m (18 ft), the kaluga is one of the biggest of the sturgeon family. Like the slightly larger beluga, it spends part of its life in salt water. Unlike the beluga, this fish has 5 major rows of dermal scutes and feeds on salmon and other fish in the Amur with its nail like teeth in its jaws. They have gray-green to black backs with a yellowish green-white underbelly.
Acipenser is a genus of sturgeons. With 17 living species, it is the largest genus in the order Acipenseriformes. The genus is paraphyletic, containing all sturgeons that do not belong to Huso, Scaphirhynchus, or Pseudoscaphirhynchus, with many species more closely related to the other three genera than they are to other species of Acipenser. They are native to freshwater and estuarine systems of Eurasia and North America, and most species are threatened. Several species also known to enter near-shore marine environments in the Atlantic, Arctic and Pacific oceans.
The Chinese sturgeon is a critically endangered member of the family Acipenseridae in the order Acipenseriformes. Historically, this anadromous fish was found in China, Japan, and the Korean Peninsula, but it has been extirpated from Korea, Japan, and most regions in China due to habitat loss and overfishing.

White sturgeon is a species of sturgeon in the family Acipenseridae of the order Acipenseriformes. They are an anadromous (migratory) fish species ranging in the Eastern Pacific; from the Gulf of Alaska to Monterey, California. However, some are landlocked in the Columbia River Drainage, Montana, and Lake Shasta in California, with reported sightings in northern Baja California, Mexico.

Chondrosteus is a genus of extinct marine actinopterygian belonging to the family Chondrosteidae. It lived during the Hettangian and Sinemurian in what is now England. Chondrosteus is related to sturgeons and paddlefishes as part of the clade Acipenseriformes, and is one of the earliest known definitive members of the group. Similar to sturgeons, the jaws of Chondrosteus were free from the rest of the skull. Its scale cover was reduced to the upper lobe of the caudal fin like in paddlefish.

The Adriatic sturgeon is a species of fish in the family Acipenseridae. It is native to the Adriatic Sea and large rivers which flow in it of Albania, Greece, Italy, Montenegro, Croatia, Bosnia and Herzegovina and Slovenia. Specimens can be seen in several public aquarium, such the Milan Aquarium, Aquarium Finisterrae, Aquarium of the Po, and Oasis of Sant'Alessio in Lombardy.

The bastard sturgeon, also known as the fringebarbel sturgeon, ship sturgeon, spiny sturgeon, or thorn sturgeon, is a species of fish in the family Acipenseridae. These fish are typically found along the benthos of shallower waters near shorelines or estuaries.

Pseudoscaphirhynchus is a genus of relatively small, highly threatened sturgeons that are restricted to the Aral Sea system, including the Amu Darya and Syr Darya river basins, in Central Asia.

The Amu Darya sturgeon or false shovelnose sturgeon is a critically endangered species of fish in the family Acipenseridae. It is found in Turkmenistan, Uzbekistan, Tajikistan and perhaps Afghanistan. It inhabits quite shallow flowing waters that are turbid and muddy.
Paleopsephurus is an extinct genus of paddlefish (Polyodontidae). At present the genus contains the single species Paleopsephurus wilsoni. The genus is known from the Late Cretaceous (Maastrichtian) aged Hell Creek Formation of Montana.

The Japanese sturgeon or Amur sturgeon is a species of fish in the family Acipenseridae found in the Amur River basin in China and Russia. Claims of its presence in the Sea of Japan need confirmation. The species has 11–16 dorsal, 34–47 lateral, and 7–16 ventral scutes. Their dorsal fins have 38–53 rays and 20–35 anal fin rays. They also have greyish-brown backs and pale ventral sides. The species can reach up to 3 metres (9.8 ft) in length, and weigh over 190 kilograms (420 lb). The species is considered to be critically endangered.
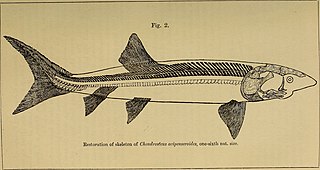
Chondrosteidae is a family of extinct marine actinopterygian fishes, known from the Early Jurassic of Europe. They are closely related to modern sturgeons and paddlefish of the order Acipenseriformes, and are either placed as part of that order or the separate order Chondrosteiformes within the Chondrostei. Three genera are known, Chondrosteus, Gyrosteus, and Strongylosteus. Included species were of large size, with body lengths ranging from 2 metres (6.6 ft) up to 7 metres (23 ft). Their skeleton was largely made up of bones, but ossification was reduced compared to other ray-fins.
Priscosturion is a genus of sturgeon from the Judith River Formation. It lived during the Campanian stage of the Late Cretaceous some 77.5 million years ago. Initially called Psammorhynchus, its describers Lance Grande and Eric J. Hilton renamed the animal in 2009. The fish belongs to the subfamily Priscosturioninae within the larger family Acipenseridae. Priscosturion is only known from one species, P. longipinnis.















