
The Bombyliidae are a family of flies, commonly known as bee flies. Adults generally feed on nectar and pollen, some being important pollinators. Larvae are mostly parasitoids of other insects.

The Sepsidae are a family of flies, commonly called the black scavenger flies or ensign flies. Over 300 species are described worldwide. They are usually found around dung or decaying plant and animal material. Many species resemble ants, having a "waist" and glossy black body. Many Sepsidae have a curious wing-waving habit made more apparent by dark patches at the wing end.

The Conopidae, usually known as the thick-headed flies, are a family of flies within the Brachycera suborder of Diptera, and the sole member of the superfamily Conopoidea. Flies of the family Conopidae are distributed worldwide in all the biogeographic realms except for the poles and many of the Pacific islands. About 800 species in 47 genera are described worldwide, about 70 of which are found in North America. The majority of conopids are black and yellow, or black and white, and often strikingly resemble wasps, bees, or flies of the family Syrphidae, themselves notable bee mimics. A conopid is most frequently found at flowers, feeding on nectar with its proboscis, which is often long.

The Anthomyiidae are a large and diverse family of Muscoidea flies. Most look rather like small houseflies. Most species are drab grey to black. Many Pegomya are yellow, and some members of the genera Anthomyia and Eutrichota are patterned in black-and-white or black-and-silvery-grey. Most are difficult to identify, apart from a few groups such as the kelp flies that are conspicuous on beaches.

The Fanniidae are a small group of true flies largely confined to the Holarctic and temperate Neotropical realms; there are 11 Afrotropical species, 29 Oriental, and 14 Australasian.

The Lauxaniidae are a family of acalyptrate flies. They generally are small flies with large compound eyes that often are brightly coloured in life, sometimes with characteristic horizontal stripes, such as in Cestrotus species. Many species have variegated patterns on their wings, but in contrast they generally do not have variegated bodies, except for genera such as Cestrotus, whose camouflage mimics lichens or the texture of granitic rocks.
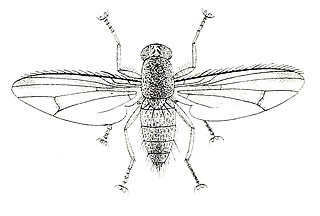
The Curtotonidae or quasimodo flies are a small family of small grey to dark brown humpbacked flies (Diptera) with a worldwide distribution, but with very few species in the Nearctic, Australasian/Oceanian, and Palaearctic regions. Most members of the family are found in tropical to subtropical latitudes in Africa and the Neotropics. Many remain undescribed in collections, since little work on the family has been done since the 1930s.

Hover flies of the genus Microdon are unusual among the Diptera. Like other members of the subfamily, they are myrmecophiles, meaning they inhabit the nests of ants.

Eciton is a New World army ant genus that contains the most familiar species of army ants. The most predominant and well-known species is Eciton burchellii, which is also more commonly known as the army ant and is considered the type species.

Musca is a genus of flies. It includes Musca domestica, as well as Musca autumnalis. It is part of the family Muscidae.

The Pyrgotidae are an unusual family of flies (Diptera), one of only two families of Cyclorrhapha that lack ocelli. Most species are "picture-winged", as is typical among the Tephritoidea, but unlike other tephritoids, they are endoparasitoids; the females pursue scarab beetles in flight, laying an egg on the beetle's back under the elytra where the beetle cannot reach it. The egg hatches and the fly larva enters the body cavity of the beetle, feeding and eventually killing the host before pupating. In the United States, some species of Pyrgota and Sphecomyiella can be quite common in areas where their host beetles are abundant. Like their host beetles, these flies are primarily nocturnal, and are often attracted to artificial lights.

Senostoma is a genus of parasitoid tachinid flies in the family Tachinidae. Endemic to Australasia, the flies are medium-sized, bristly, and long-legged.

Coenosia is a very large genus of true flies of the family Muscidae. Coenosia are known as tiger flies since they are predators and hunt many kinds of insects and other invertebrates.
Nurteria is a genus of flies in the family Dolichopodidae, found in the Afrotropical realm. Three species are currently known in the genus, but there are also numerous undescribed species of the genus from southern Africa. It was originally described in the subfamily Diaphorinae, though it possesses some features of the Sympycninae.
Musca albina is a widespread Old World species of fly, known from the dry areas of the Afrotropical realm, North Africa and the Middle East, Central Asia, India and Sri Lanka. It is a sun-loving species, and adults have been found clustering around domestic animals to feed on sweat and other secretions and on their feces. The Namibian population at least is clearly kleptoparasitic and very specific in its oviposition behaviour, laying eggs only in dung balls being interred by one out of several co-occurring dung-rolling scarab beetle species.
Acemyini is a small but cosmopolitan tribe of flies in the family Tachinidae. Like all tachinid flies, acemyiines are parasitoids of other invertebrates. Specifically, the acemyiines are parasitoids of Orthoptera in the families Acrididae and Eumastacidae.
Diptera is an order of winged insects commonly known as flies. Diptera, which are one of the most successful groups of organisms on Earth, are very diverse biologically. None are truly marine but they occupy virtually every terrestrial niche. Many have co-evolved in association with plants and animals. The Diptera are a very significant group in the decomposition and degeneration of plant and animal matter, are instrumental in the breakdown and release of nutrients back into the soil, and whose larvae supplement the diet of higher agrarian organisms. They are also an important component in food chains.

Physocephala tibialis is a species of thick-headed fly found throughout the eastern United States, often near flowering plants. The adult fly is primarily black with a yellow face and thin white stripes on the abdomen. It is commonly found along the east coast of the United States and is often found near flowering plants.

Exsul singularis, the bat-winged fly, is a species of fly that is endemic to New Zealand, first described by Frederick Hutton in 1901. The males have enormously expanded wings. The species is found in the south-western South Island and occurs mostly in high-altitude meadows near streams. It preys on soft-bodied flying insects and is believed to uses its wings to increase its body temperature to offset the cool temperatures of its alpine habitat.
















