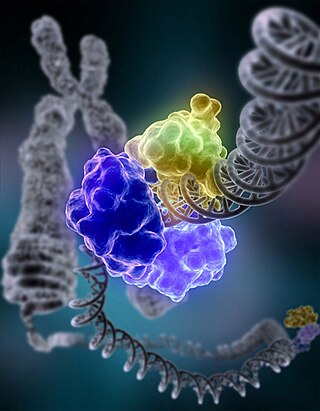
DNA ligase is a type of enzyme that facilitates the joining of DNA strands together by catalyzing the formation of a phosphodiester bond. It plays a role in repairing single-strand breaks in duplex DNA in living organisms, but some forms may specifically repair double-strand breaks. Single-strand breaks are repaired by DNA ligase using the complementary strand of the double helix as a template, with DNA ligase creating the final phosphodiester bond to fully repair the DNA.

A cloning vector is a small piece of DNA that can be stably maintained in an organism, and into which a foreign DNA fragment can be inserted for cloning purposes. The cloning vector may be DNA taken from a virus, the cell of a higher organism, or it may be the plasmid of a bacterium. The vector contains features that allow for the convenient insertion of a DNA fragment into the vector or its removal from the vector, for example through the presence of restriction sites. The vector and the foreign DNA may be treated with a restriction enzyme that cuts the DNA, and DNA fragments thus generated contain either blunt ends or overhangs known as sticky ends, and vector DNA and foreign DNA with compatible ends can then be joined by molecular ligation. After a DNA fragment has been cloned into a cloning vector, it may be further subcloned into another vector designed for more specific use.
A cDNA library is a combination of cloned cDNA fragments inserted into a collection of host cells, which constitute some portion of the transcriptome of the organism and are stored as a "library". cDNA is produced from fully transcribed mRNA found in the nucleus and therefore contains only the expressed genes of an organism. Similarly, tissue-specific cDNA libraries can be produced. In eukaryotic cells the mature mRNA is already spliced, hence the cDNA produced lacks introns and can be readily expressed in a bacterial cell. While information in cDNA libraries is a powerful and useful tool since gene products are easily identified, the libraries lack information about enhancers, introns, and other regulatory elements found in a genomic DNA library.

In molecular biology, a library is a collection of genetic material fragments that are stored and propagated in a population of microbes through the process of molecular cloning. There are different types of DNA libraries, including cDNA libraries, genomic libraries and randomized mutant libraries. DNA library technology is a mainstay of current molecular biology, genetic engineering, and protein engineering, and the applications of these libraries depend on the source of the original DNA fragments. There are differences in the cloning vectors and techniques used in library preparation, but in general each DNA fragment is uniquely inserted into a cloning vector and the pool of recombinant DNA molecules is then transferred into a population of bacteria or yeast such that each organism contains on average one construct. As the population of organisms is grown in culture, the DNA molecules contained within them are copied and propagated.
A DNA construct is an artificially-designed segment of DNA borne on a vector that can be used to incorporate genetic material into a target tissue or cell. A DNA construct contains a DNA insert, called a transgene, delivered via a transformation vector which allows the insert sequence to be replicated and/or expressed in the target cell. This gene can be cloned from a naturally occurring gene, or synthetically constructed. The vector can be delivered using physical, chemical or viral methods. Typically, the vectors used in DNA constructs contain an origin of replication, a multiple cloning site, and a selectable marker. Certain vectors can carry additional regulatory elements based on the expression system involved.
A restriction digest is a procedure used in molecular biology to prepare DNA for analysis or other processing. It is sometimes termed DNA fragmentation, though this term is used for other procedures as well. In a restriction digest, DNA molecules are cleaved at specific restriction sites of 4-12 nucleotides in length by use of restriction enzymes which recognize these sequences.

A multiple cloning site (MCS), also called a polylinker, is a short segment of DNA which contains many restriction sites - a standard feature of engineered plasmids. Restriction sites within an MCS are typically unique, occurring only once within a given plasmid. The purpose of an MCS in a plasmid is to allow a piece of DNA to be inserted into that region.

A plasmid preparation is a method of DNA extraction and purification for plasmid DNA. It is an important step in many molecular biology experiments and is essential for the successful use of plasmids in research and biotechnology. Many methods have been developed to purify plasmid DNA from bacteria. During the purification procedure, the plasmid DNA is often separated from contaminating proteins and genomic DNA.
A genomic library is a collection of overlapping DNA fragments that together make up the total genomic DNA of a single organism. The DNA is stored in a population of identical vectors, each containing a different insert of DNA. In order to construct a genomic library, the organism's DNA is extracted from cells and then digested with a restriction enzyme to cut the DNA into fragments of a specific size. The fragments are then inserted into the vector using DNA ligase. Next, the vector DNA can be taken up by a host organism - commonly a population of Escherichia coli or yeast - with each cell containing only one vector molecule. Using a host cell to carry the vector allows for easy amplification and retrieval of specific clones from the library for analysis.
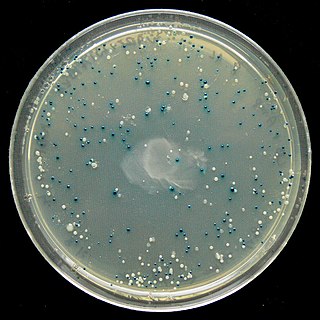
The blue–white screen is a screening technique that allows for the rapid and convenient detection of recombinant bacteria in vector-based molecular cloning experiments. This method of screening is usually performed using a suitable bacterial strain, but other organisms such as yeast may also be used. DNA of transformation is ligated into a vector. The vector is then inserted into a competent host cell viable for transformation, which are then grown in the presence of X-gal. Cells transformed with vectors containing recombinant DNA will produce white colonies; cells transformed with non-recombinant plasmids grow into blue colonies.
Fragmentation describes the process of splitting into several pieces or fragments. In cell biology, fragmentation is useful for a cell during both DNA cloning and apoptosis. DNA cloning is important in asexual reproduction or creation of identical DNA molecules, and can be performed spontaneously by the cell or intentionally by laboratory researchers. Apoptosis is the programmed destruction of cells, and the DNA molecules within them, and is a highly regulated process. These two ways in which fragmentation is used in cellular processes describe normal cellular functions and common laboratory procedures performed with cells. However, problems within a cell can sometimes cause fragmentation that results in irregularities such as red blood cell fragmentation and sperm cell DNA fragmentation.

BioBrick parts are DNA sequences which conform to a restriction-enzyme assembly standard. These building blocks are used to design and assemble larger synthetic biological circuits from individual parts and combinations of parts with defined functions, which would then be incorporated into living cells such as Escherichia coli cells to construct new biological systems. Examples of BioBrick parts include promoters, ribosomal binding sites (RBS), coding sequences and terminators.
Artificial gene synthesis, or simply gene synthesis, refers to a group of methods that are used in synthetic biology to construct and assemble genes from nucleotides de novo. Unlike DNA synthesis in living cells, artificial gene synthesis does not require template DNA, allowing virtually any DNA sequence to be synthesized in the laboratory. It comprises two main steps, the first of which is solid-phase DNA synthesis, sometimes known as DNA printing. This produces oligonucleotide fragments that are generally under 200 base pairs. The second step then involves connecting these oligonucleotide fragments using various DNA assembly methods. Because artificial gene synthesis does not require template DNA, it is theoretically possible to make a completely synthetic DNA molecule with no limits on the nucleotide sequence or size.
The Gateway cloning method is a method of molecular cloning invented and commercialized by Invitrogen since the late 1990s, which makes use of the integration and excision recombination reactions that take place when bacteriophage lambda infects bacteria. This technology provides a fast and highly efficient way to transport DNA sequences into multi-vector systems for functional analysis and protein expression using Gateway att sites and two proprietary enzyme mixes called BP Clonase and LR Clonase. In vivo, these recombination reactions are facilitated by the recombination of attachment sites from the lambda/phage chromosome (attP) and the bacteria (attB). As a result of recombination between the attP and attB sites, the phage integrates into the bacterial genome flanked by two new recombination sites. The removal of the phage from the bacterial chromosome and the regeneration of attP and attB sites can both result from the attL and attR sites recombining under specific circumstances.
Ligation-independent cloning (LIC) is a form of molecular cloning that can be performed without the use of restriction endonucleases or DNA ligase. The technique was developed in the early 1990s as an alternative to restriction enzyme/ligase cloning. This allows genes to be cloned without the requirement of a restriction site for cloning that is absent from the gene insert. LIC uses long complementary overhangs on the vector and the DNA insert to create a stable association between them.
Diversity Arrays Technology (DArT) is a high-throughput genetic marker technique that can detect allelic variations to provide comprehensive genome coverage without any DNA sequence information for genotyping and other genetic analysis. The general steps involve reducing the complexity of the genomic DNA with specific restriction enzymes, choosing diverse fragments to serve as representations for the parent genomes, amplify via polymerase chain reaction (PCR), inserting fragments into a vector to be placed as probes within a microarray, and then fluorescent targets from a reference sequence will be allowed to hybridize with probes and put through an imaging system. The objective is to identify and quantify various forms of DNA polymorphism within genomic DNA of sampled species.

Molecular cloning is a set of experimental methods in molecular biology that are used to assemble recombinant DNA molecules and to direct their replication within host organisms. The use of the word cloning refers to the fact that the method involves the replication of one molecule to produce a population of cells with identical DNA molecules. Molecular cloning generally uses DNA sequences from two different organisms: the species that is the source of the DNA to be cloned, and the species that will serve as the living host for replication of the recombinant DNA. Molecular cloning methods are central to many contemporary areas of modern biology and medicine.

Genetic engineering techniques allow the modification of animal and plant genomes. Techniques have been devised to insert, delete, and modify DNA at multiple levels, ranging from a specific base pair in a specific gene to entire genes. There are a number of steps that are followed before a genetically modified organism (GMO) is created. Genetic engineers must first choose what gene they wish to insert, modify, or delete. The gene must then be isolated and incorporated, along with other genetic elements, into a suitable vector. This vector is then used to insert the gene into the host genome, creating a transgenic or edited organism.

Ligation is the joining of two nucleotides, or two nucleic acid fragments, into a single polymeric chain through the action of an enzyme known as a ligase. The reaction involves the formation of a phosphodiester bond between the 3'-hydroxyl terminus of one nucleotide and the 5'-phosphoryl terminus of another nucleotide, which results in the two nucleotides being linked consecutively on a single strand. Ligation works in fundamentally the same way for both DNA and RNA. A cofactor is generally involved in the reaction, usually ATP or NAD+. Eukaryotic ligases belong to the ATP type, while the NAD+ type are found in bacteria (e.g. E. coli).

Golden Gate Cloning or Golden Gate assembly is a molecular cloning method that allows a researcher to simultaneously and directionally assemble multiple DNA fragments into a single piece using Type IIS restriction enzymes and T4 DNA ligase. This assembly is performed in vitro. Most commonly used Type IIS enzymes include BsaI, BsmBI, and BbsI.












