| Subularia | |
|---|---|
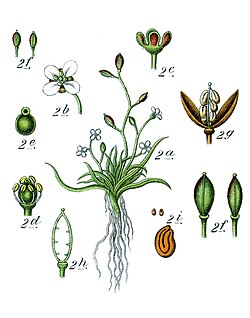 | |
| Illustration of Subularia aquatica | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Eudicots |
| Clade: | Rosids |
| Order: | Brassicales |
| Family: | Brassicaceae |
| Genus: | Subularia L. (1753) |
| Type species | |
| Subularia aquatica [1] L. | |
| Species [2] | |
| |
Subularia is a genus of plants in the family Brassicaceae. Subularia species are annual herbs that grow in moist or even flooded soils. There are only two species of the genus: Subularia aquatica , which is widespread in North America and Europe; and Subularia monticola , from Africa mountains. [3] Awlwort is a common name for plants in this genus. [4]