
Astrology is a range of divinatory practices, recognized as pseudoscientific since the 18th century, that claim to discern information about human affairs and terrestrial events by studying the apparent positions of celestial objects. Different cultures have employed forms of astrology since at least the 2nd millennium BCE, these practices having originated in calendrical systems used to predict seasonal shifts and to interpret celestial cycles as signs of divine communications. Most, if not all, cultures have attached importance to what they observed in the sky, and some—such as the Hindus, Chinese, and the Maya—developed elaborate systems for predicting terrestrial events from celestial observations. Western astrology, one of the oldest astrological systems still in use, can trace its roots to 19th–17th century BCE Mesopotamia, from where it spread to Ancient Greece, Rome, the Islamic world, and eventually Central and Western Europe. Contemporary Western astrology is often associated with systems of horoscopes that purport to explain aspects of a person's personality and predict significant events in their lives based on the positions of celestial objects; the majority of professional astrologers rely on such systems.

The zodiac is a belt-shaped region of the sky that extends approximately 8° north and south of the ecliptic, which is the apparent path of the Sun across the celestial sphere over the course of the year. The orbital paths of the Moon and major planets are within the belt of the zodiac.

A horoscope is an astrological chart or diagram representing the positions of the Sun, Moon, planets, astrological aspects and sensitive angles at the time of an event, such as the moment of a person's birth. The word horoscope is derived from the Greek words ōra and scopos meaning "time" and "observer". It is claimed by proponents of astrology that a horoscope can be used as a method of divination regarding events relating to the point in time it represents, and it forms the basis of the horoscopic traditions of astrology, although practices surrounding astrology have been recognized as pseudoscientific since the 18th century. Horoscope columns are often featured in print and online newspapers.

Western astrology is the system of astrology most popular in Western countries. Western astrology is historically based on Ptolemy's Tetrabiblos, which in turn was a continuation of Hellenistic and ultimately Babylonian traditions.

Most horoscopic traditions of astrology systems divide the horoscope into a number of houses whose positions depend on time and location rather than on date. In Hindu astrological tradition these are known as Bhāvas. The houses of the horoscope represent different fields of experience wherein the energies of the signs and planets operate—described in terms of physical surroundings as well as personal life experiences.
Hindu astrology, also called Indian astrology, or Jyotisha ; from jyót “light, heavenly body", and more recently Vedic astrology, is the traditional Hindu system of astrology. It is one of the six auxiliary disciplines in Hinduism that is connected with the study of the Vedas.

In astrology, sidereal and tropical are terms that refer to two different systems of ecliptic coordinates used to divide the ecliptic into twelve "signs". Each sign is divided into 30 degrees, making a total of 360 degrees. The terms sidereal and tropical may also refer to two different definitions of a year, applied in sidereal solar calendars or tropical solar calendars.

In Western astrology, astrological signs are the twelve 30-degree sectors that make up Earth's 360-degree orbit around the Sun. The signs enumerate from the first day of spring, known as the First Point of Aries, which is the vernal equinox. The astrological signs are Aries, Taurus, Gemini, Cancer, Leo, Virgo, Libra, Scorpio, Sagittarius, Capricorn, Aquarius, and Pisces. The Western zodiac originated in Babylonian astrology, and was later influenced by the Hellenistic culture. Each sign was named after a constellation the sun annually moved through while crossing the sky. This observation is emphasized in the simplified and popular sun sign astrology. Over the centuries, Western astrology's zodiacal divisions have shifted out of alignment with the constellations they were named after by axial precession of the Earth while Hindu astrology measurements correct for this shifting. Astrology was developed in Chinese and Tibetan cultures as well but these astrologies are not based upon the zodiac but deal with the whole sky.

Electional astrology, also known as event astrology, is a branch found in most traditions of astrology according to which a practitioner decides the most appropriate time for an event based on the astrological auspiciousness of that time. It differs from horary astrology because, while horary astrologers seek to find the answer to a question based on the time the question was asked, electional astrologers seek to find a period of time which will result in the most preferable outcome for an event being planned.

Astrological belief in correspondences between celestial observations and terrestrial events have influenced various aspects of human history, including world-views, language and many elements of social culture.

Astrology and astronomy were archaically treated together, but gradually distinguished through the Late Middle Ages into the Age of Reason. Developments in 17th century philosophy resulted in astrology and astronomy operating as independent pursuits by the 18th century.

An astrological age is a time period which, according to astrology, parallels major changes in the development of human society, culture, history, and politics. There are twelve astrological ages corresponding to the twelve zodiacal signs in western astrology. One cycle of the twelve astrological ages is called a Great Year, comprising 25,772 solar years, at the end of which another cycle begins.

Natal astrology, also known as genethliac astrology or genethlialogy, is a system of astrology that claims to shed light on an individual’s personality or path in life based on constructing a horoscope or natal chart that includes the exact date, time, and location of an individual's birth. Natal astrology is found in the Indian, Chinese, Hellenistic and Western astrological traditions.

In astrology, exaltation is one of the five essential dignities of a planet. The exaltation is a place of awareness for the planet, whereas the fall is a position of weakness concerning the function of the planet. The sign position directly opposite a planet's sign of exaltation is considered to be its fall.

Essential dignity, in the context of an astrological horoscope or natal chart, refers to the relative “strength” or “weakness” of a planet based on its zodiac sign and specific degree. This strength or weakness is referred to as the planet’s essence—what the 17th-century astrologer William Lilly called "the strength, fortitude or debility of the Planets [or] significators."

In astrology, a planet's domicile is the zodiacal sign over which it has rulership. This is a separate concept from the houses of the horoscope. A planetary ruler is given to each sign, over which the planet is said to have a more powerful influence when positioned therein. The ruling planet associated with a sign is also used as an implied focus of interpretation for the signs on house cusps in a chart. A planet is considered to be in domal dignity when it is positioned in the sign it rules. This is the strongest of the five essential dignities of a planet. Domicile is an archaic term in infrequent, specialist uses today; most astrologers use the simpler term "sign".

Horoscopic astrology is a form of astrology that uses a horoscope, a visual representation of the heavens, for a specific moment in time to interpret the purported meaning behind the alignment of the planets at that moment. The idea is that the placement of the planets at any given moment in time supposedly reflects the nature of that moment and especially anything that is born then, and proponents claim that this can be analyzed using the chart and a variety of rules for interpreting the "language" or symbols therein.

Psychological astrology, or astropsychology, is the result of the cross-fertilisation of the fields of astrology with depth psychology, humanistic psychology and transpersonal psychology. There are several methods of analyzing the horoscope in the contemporary psychological astrology: the horoscope can be analysed through the archetypes within astrology or the analyses can be rooted in the psychological need and motivational theories. There might exist other astrological methods and approaches rooted in psychology. Astrologer and psychotherapist Glenn Perry characterises psychological astrology as "both a personality theory and a diagnostic tool".

Astrology consists of a number of belief systems that hold that there is a relationship between astronomical phenomena and events or descriptions of personality in the human world. Astrology has been rejected by the scientific community as having no explanatory power for describing the universe. Scientific testing has found no evidence to support the premises or purported effects outlined in astrological traditions.
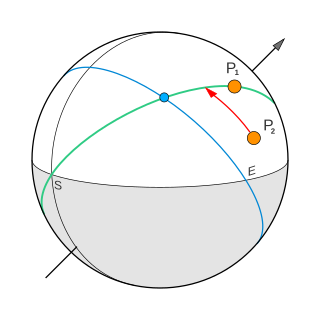
Primary direction is a term in astrology for referencing one of the oldest methods of predicting events. It indicates the year of life in which an event shown by the birth chart will occur. This method has been around for over 1800 years and is mentioned in the Tetrabiblos of Claudius Ptolemy in the section on calculating the length of life. It gained widespread popularity in medieval Europe and was thoroughly described by Jean-Baptiste Morin in the 22nd book of his Astrologia Gallica.





