
Tar Rocks are coastal rocks on the west side of the Isle of Portland, Dorset, England. [1] The rocks become mostly covered at high tide.

Tar Rocks are coastal rocks on the west side of the Isle of Portland, Dorset, England. [1] The rocks become mostly covered at high tide.

The Solent is a strait between the Isle of Wight and Great Britain. It is about 20 miles long and varies in width between 2+1⁄2 and 5 mi, although the Hurst Spit which projects 1+1⁄2 mi (2.4 km) into the Solent narrows the sea crossing between Hurst Castle and Colwell Bay to just over 1 mi (1.6 km).

The Isle of Portland is a tied island, 6 kilometres (4 mi) long by 2.7 kilometres (1.7 mi) wide, in the English Channel. The southern tip, Portland Bill lies 8 kilometres (5 mi) south of the resort of Weymouth, forming the southernmost point of the county of Dorset, England. A barrier beach called Chesil Beach joins Portland with mainland England. The A354 road passes down the Portland end of the beach and then over the Fleet Lagoon by bridge to the mainland. The population of Portland is 12,797.

Durdle Door is a natural limestone arch on the Jurassic Coast near Lulworth in Dorset, England. Although privately owned by the Lulworth Estate, it is open to the public.

RFA Green Ranger was a fleet support tanker of the Royal Fleet Auxiliary.

Dancing Ledge is part of the Jurassic Coast near Langton Matravers in the Isle of Purbeck in Dorset, England. Dancing Ledge is a flat area of rock at the base of a small cliff. A little scrambling is required for access. It is signposted on the South West Coast Path a few kilometres west of Swanage. Dancing Ledge is so called because at certain stages of the tide when the waves wash over the horizontal surface, the surface undulations cause the water to bob about making the ledge appear to dance.
Lyme Bay is an area of the English Channel off the south coast of England, situated between Start Point in the west and Portland Bill in the east. The south western counties of Devon and Dorset front onto the bay.

Pulpit Rock is a coastal feature at Portland Bill, the southern tip of the Isle of Portland, Dorset, England. Representing an open bible leaning on a pulpit, Pulpit Rock was formed in the 1870s after a natural arch was cut away by quarrymen at Bill Quarry. As a quarrying relic, the rock is similar to that of Nicodemus Knob, another quarrying landmark on the island.

Compton Bay is a bay located on the southwest section of the Isle of Wight, England. Its northwestern edge is defined by the distinctive white chalk cliff of Freshwater Cliff, named after adjacent Freshwater Bay, which forms a small cove with the village of Freshwater situated just behind. Its northeastern edge is formed from the soft red and orange lower cretaceous rocks of Brook Bay, which are rapidly eroding.

Newton's Cove is a small cove, 0.5 kilometres (0.3 mi) south of Weymouth, Dorset, England. Overlooking Portland Harbour, the cove is close to Nothe Gardens and the Nothe Fort.

Man o' War Cove lies on the Dorset coast in southern England and is flanked by the rocky, steep and slightly projecting headlands of Durdle Door to the west and Man O War Head to the east.

Hallelujah Bay is a bay located on the west side of the Isle of Portland, Dorset, England. The bay is situated below West Weares, with Clay Ope, Blacknor Point and Mutton Cove further south. Near the cove is a large mound of rock and earth beneath the clifftops known locally as the Green Hump.
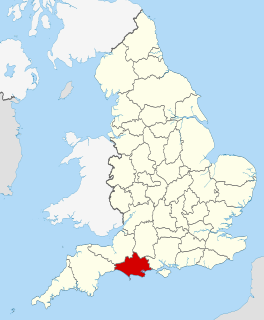
Dorset is a county located in the middle of the south coast of England. It lies between the latitudes 50.512°N and 51.081°N and the longitudes 1.682°W and 2.958°W, and occupies an area of 2,653 km2. It spans 90 kilometres (56 mi) from east to west and 63 kilometres (39 mi) from north to south.

Nicodemus Knob is a 30-feet pillar of Portland stone, left as a landmark and quarrying relic at East Cliff on the Isle of Portland, Dorset, England. A similar artificial pillar formed through quarrying is Pulpit Rock at Portland Bill.

The Trinity House Obelisk, also known as the Trinity House Landmark, is a 19th-century obelisk located at Portland Bill, on the Isle of Portland, Dorset, England. Built as a daymark, it has been Grade II Listed since 1978.

Wallsend Cove is a cove, located on the Isle of Portland, Dorset, England; part of the Jurassic Coast. It is found on the west side of Portland, further south from Mutton Cove, and situated between Southwell Business Park and Portland Bill. The cliff tops above the cove are part of the South West Coast Path.

Cave Hole is a large cave on the south east side of the Isle of Portland, a large peninsular in Dorset, England. It has a blowhole and a wooden crane, known as Broad Ope Crane on the cliff top. It is 1⁄2 mile (800 m) north-east of Portland Bill, has an interior measuring 50 feet (15 m) square and 21 feet (6.4 m) high.

Portland Raised Beach refers to small raised beaches on each side of Portland Bill, on the Isle of Portland, part of the Jurassic Coast in Dorset, England. The main one is known as the West Pleistocene Raised Beach; nearby is the East Pleistocene Raised Beach.

The Great Southwell Landslip occurred in 1734 on the Isle of Portland, Dorset, England near the southerly village of Southwell and extended for a length of 1.5 miles (2.4 km) between Durdle Pier and Freshwater Bay. It remains Britain's second largest recorded historical landslide.

The Salt Pans are two salt pans on the Isle of Portland, Dorset, England. Both pans sit next to one another, and are situated on the coastline of East Weares, the east side of Portland. The pans sit directly below the Young Offenders Institution HM Prison Portland, and are found close to various old historic relics such as the East Weare Rifle Range, Folly Pier, King's Pier and the remains of the Folly Pier Waterworks. The East Weares area, including the Salt Pans, has been labelled a Site of Special Scientific Interest (SSSI), largely due to the scrub and wildlife being of high nature conservation value.
Coordinates: 50°33′02.4″N2°27′10.88″W / 50.550667°N 2.4530222°W