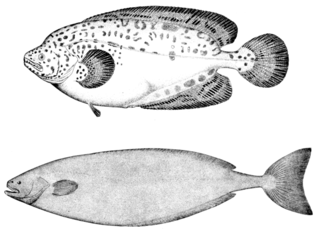
The ragfish is a ray-finned fish of the northern Pacific Ocean; although classified as a bony fish, its skeleton is mostly cartilage, and the larvae have pelvic fins that disappear as they mature. It is the sole member of the family Icosteidae within the order Scombriformes.
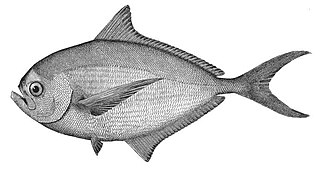
Pomfrets are scombriform fish belonging to the family Bramidae. The family currently includes 20 species across seven genera. Several species are important food sources for humans, especially Brama brama in South Asia. The earlier form of the pomfret's name was "pamflet", a word which probably ultimately comes from Portuguese pampo, referring to various fish such as the blue butterfish. The fish meat is white in color.

The family Stromateidae or butterfish contains 15 species of ray-finned fish in three genera. Butterfishes live in coastal waters off the Americas, western Africa and in the Indo-Pacific.

The big-scale pomfret also known as the long-finned bream, is a species of marine ray-finned fish, a pomfret of the family Bramidae. It is found in the Atlantic ocean, at depths down to 500 metres (1,600 ft). This species is widely distributed in the Pacific, from temperate zones throughout the tropics. They are commonly encountered around seamounts. This species reaches a length of up to 100 centimetres (39 in) SL. This species is of minor importance to the commercial fisheries industry. Bigscale pomfrets are common marketed bycatch species in pelagic longline fisheries targeting Yellowfin tuna or Bigeye tuna. The overall color is dark metallic gray to black. The flesh is white. The pelvic fins are short and black with a brilliant white tip. The caudal fin is a symmetrical crescent with rounded tips. It has a clear white rear edge, widest at the center of the tail, tapering away towards the fin tips. The pectoral fin is transparent gray with a clear white rear edge. From Ireland there are only two records of this fish. The last being from Co. Wicklow. In Hawaii this fish is called “monchong”, along with the Lustrous pomfret.

Caristiidae, the manefishes, are a family of scombriform ray-finned fishes which today includes 19 extant species distributed in four genera. Chalcidichthys malacapterygius and Absalomichthys velifer are extinct species in this family from the Upper Miocene of Southern California.

Ariomma is a genus of deepwater, marine ray-finned fishes belonging to the family Ariommatidae. Members of this genus are found in the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian Oceans. Several members of this genus are of commercial importance as food fish. This genus is currently the only known extant genus in its family.

Scomber is a genus of ray-finned fish in the family Scombridae living in the open ocean found in Atlantic, Indian and Pacific Ocean. The genus Scomber and the genus Rastrelliger comprise the tribe Scombrini, known as the "true mackerels". These fishes have an elongated body, highly streamlined, muscular and agile. The eyes are large, the head is elongated, with a big mouth provided with teeth. They have two triangular dorsal fins, with some stabilizing fins along the caudal peduncle. The basic color is blue-green with a silvery white belly and a darker back, usually black mottled.

The bullet tuna is a species of tuna, in the family Scombridae, found circumglobally in tropical oceans, including the Mediterranean Sea, in open surface waters to depths of 50 m (164 ft). The population of bullet tuna in the Eastern Pacific was classified as a subspecies of A. rochei, A. rochei eudorax, but some authorities regard this as a valid species Auxis eudorax. Its maximum length is 50 centimetres (20 in).
Perissias taeniopterus, the striped-fin flounder, is a species of lefteye flounder native to the eastern Pacific Ocean along the coast of Central America from Mexico to Panama. It is found at depths of from 46 to 157 metres. This species grows to a length of 11 centimetres (4.3 in) TL. This species is the only known member of its genus.

Solea is a genus of soles from the Indo-Pacific and East Atlantic Oceans, and the Mediterranean Sea.

Brama is a genus of marine ray-finned fishes from the family Bramidae, the pomfrets. Currently, there are 8 species within the genus.

Eumegistus is a small genus of pomfrets found in the Atlantic and Pacific oceans.

Pteraclis is a genus of ray-finned fish in the family Bramidae, the pomfrets. They are known commonly as fanfishes. The three species are distributed throughout the oceans of the world.

Pterycombus is a genus of pomfrets distinguished by greatly elongated dorsal and anal fins. Along with the genus Pteraclis, they are commonly referred to as fanfishes. Pterycombus can be distinguished from Pteraclis by examining the dorsal and anal fin rays, which should be relatively uniform in thickness to neighboring rays and by a lack of scales anterior to the dorsal fin.

Taractichthys is a genus of marine ray-finned fishes from the family Bramidae, the pomfrets.

Pampus is a genus of ray-finned fish of the family Stromateidae. They are an important food fish in East and Southeast Asia. In common parlance they are often called pomfrets, although scientifically the term pomfret properly refers to fish of the genus Bramidae. An alternative name for "pomfrets" of the Pampus genus is "pompano".

Scombriformes, also known as Pelagia and Pelagiaria, is an order of ray-finned fish within the clade Percomorpha. It contains 287 extant species in 16 families, most of which were previously classified under the suborders Scombroidei and Stromateoidei of the order Perciformes.

Taractes rubescens, the pomfret, keeltail pomfret, knifetail pomfret or black pomfret, is a species of marine ray-finned fish, a pomfret of the family Bramidae. T. rubescens is closely related, and quite similar, to Taractes asper, but adults can most easily be distinguished by the bony keel present on the caudal peduncle. In fact, this bony keel is unique to Taractes rubescens and will distinguish it from all other bramids.

Pterycombus brama is a species of ray-finned fish belonging to the family Bramidae (pomfrets).

Brama orcini is a species of scombriform ray-finned fish in the family Bramidae (pomfrets).

















