
Thiamine, also known as thiamin and vitamin B1, is a vitamin, an essential micronutrient for humans and animals. It is found in food and commercially synthesized to be a dietary supplement or medication. Phosphorylated forms of thiamine are required for some metabolic reactions, including the breakdown of glucose and amino acids.
In organic chemistry, a tetrose is a monosaccharide with 4 carbon atoms. They have either an aldehyde functional group in position 1 (aldotetroses) or a ketone group in position 2 (ketotetroses).

Thiaminase is an enzyme that metabolizes or breaks down thiamine into pyrimidine and thiazole. It is an antinutrient when consumed.
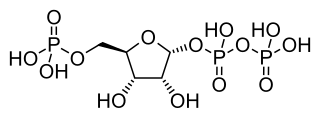
Phosphoribosyl pyrophosphate (PRPP) is a pentose phosphate. It is a biochemical intermediate in the formation of purine nucleotides via inosine-5-monophosphate, as well as in pyrimidine nucleotide formation. Hence it is a building block for DNA and RNA. The vitamins thiamine and cobalamin, and the amino acid tryptophan also contain fragments derived from PRPP. It is formed from ribose 5-phosphate (R5P) by the enzyme ribose-phosphate diphosphokinase:
UTP—glucose-1-phosphate uridylyltransferase also known as glucose-1-phosphate uridylyltransferase is an enzyme involved in carbohydrate metabolism. It synthesizes UDP-glucose from glucose-1-phosphate and UTP; i.e.,

Thiamine monophosphate, also known as ThMP and TMP, is a phosphate ester of thiamine.

Guanosine monophosphate synthetase, also known as GMPS is an enzyme that converts xanthosine monophosphate to guanosine monophosphate.

Diphosphomevalonate decarboxylase (EC 4.1.1.33), most commonly referred to in scientific literature as mevalonate diphosphate decarboxylase, is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a lysine—tRNA ligase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, an adenosine-phosphate deaminase (EC 3.5.4.17) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

In enzymology, a cystathionine gamma-synthase is an enzyme that catalyzes the formation of cystathionine from cysteine and an activated derivative of homoserine, e.g.:

In enzymology, a 2-amino-4-hydroxy-6-hydroxymethyldihydropteridine diphosphokinase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
Choline-phosphate cytidylyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

In enzymology, a glucose-1-phosphate adenylyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a glucose-1-phosphate cytidylyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a glucose-1-phosphate thymidylyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

In enzymology, a hydroxyethylthiazole kinase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a nicotinate-nucleotide adenylyltransferase (EC 2.7.7.18) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
Phosphatidate cytidylyltransferase (CDS) is the enzyme that catalyzes the synthesis of CDP-diacylglycerol from cytidine triphosphate and phosphatidate.
In enzymology, a phosphomethylpyrimidine kinase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction












