
The Andes, Andes Mountains or Andean Mountain Range are the longest continental mountain range in the world, forming a continuous highland along the western edge of South America. The range is 8,900 km (5,530 mi) long and 200 to 700 km wide and has an average height of about 4,000 m (13,123 ft). The Andes extend from South to North through seven South American countries: Argentina, Chile, Bolivia, Peru, Ecuador, Colombia, and Venezuela.

Hordeum is a genus of annual and perennial plants in the grass family. The species are native throughout the temperate regions of Africa, Eurasia, and the Americas.

Araucaria araucana, commonly called the monkey puzzle tree, monkey tail tree, piñonero, pewen or pehuen pine, is an evergreen tree growing to a trunk diameter of 1–1.5 m (3.3–4.9 ft) and a height of 30–40 m (98–131 ft). It is native to central and southern Chile and western Argentina. It is the hardiest species in the conifer genus Araucaria. Because of the prevalence of similar species in ancient prehistory, it is sometimes called an animate fossil. It is also the official tree of Chile and of the neighboring Argentine province of Neuquén. The IUCN changed its conservation status to Endangered in 2013 as logging, forest fires, and grazing caused its population to dwindle.

Nothofagus, also known as the southern beeches, is a genus of 43 species of trees and shrubs native to the Southern Hemisphere in southern South America and east and southeast Australia, New Zealand, New Guinea, and New Caledonia. The species are ecological dominants in many temperate forests in these regions. Some species are reportedly naturalised in Germany and Great Britain. The genus has a rich fossil record of leaves, cupules, and pollen, with fossils extending into the late Cretaceous period and occurring in Australia, New Zealand, Antarctica, and South America.

Fitzroya is a monotypic genus in the cypress family. The single living species, Fitzroya cupressoides, is a tall, long-lived conifer native to the Andes mountains and coastal regions of southern Chile, and only to the Argentine Andes, where it is an important member of the Valdivian temperate forests. Common names include alerce, lahuén, and Patagonian cypress. The genus was named in honour of Robert FitzRoy.

Alstroemeriaceae is a family of flowering plants, with 254 known species in four genera, almost entirely native to the Americas, from Central America to southern South America. One species of Luzuriaga occurs in New Zealand, and the genus Drymophila is endemic to south-eastern Australia.

The kodkod, also called güiña, is the smallest felid species native to the Americas. It lives primarily in central and southern Chile, as well as marginally in adjoining areas of Argentina. Since 2002, it has been listed as Vulnerable on the IUCN Red List as the total population may be less than 10,000 mature individuals; it is threatened by persecution, and habitat loss and prey base.

Geoffroy's cat is a small wild cat native to the southern and central regions of South America. It is around the size of a domestic cat. It is listed as Least Concern on the IUCN Red List due to it being widespread and abundant over its range.

Hippocamelus is a genus of Cervidae, the deer family. It comprises two extant Andean and two fossil species. The living members are commonly known as the huemul, and the taruca, also known as northern huemul.

The South American gray fox, also known as the Patagonian fox, the chilla or zorro gris, is a South American species of Lycalopex in the Canidae family, which includes dogs, wolves, jackals, coyotes and foxes, among other canids. It is endemic to the southern parts of Argentina and Chile, primarily Patagonia and Tierra Del Fuego.

Calyceraceae is a plant family in the order Asterales. The natural distribution of the about sixty species belonging to this family is restricted to the southern half of South America. The species of the family resemble both the family Asteraceae and the Dipsacaceae.
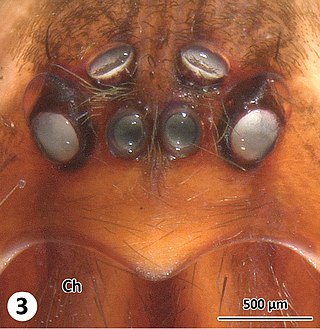
Austrochilidae is a small spider family with nine species in two genera. Austrochilus and Thaida are endemic to the Andean forest of central and southern Chile and adjacent Argentina.

The Pampas cat is a small wild cat native to South America. It is listed as Near Threatened on the IUCN Red List as habitat conversion and destruction may cause the population to decline in the future.

The south Andean deer, also known as the southern guemal, south Andean huemul, southern huemul, or Chilean huemul or güemul, is an endangered species of deer native to the mountains of Argentina and Chile. Along with the northern guemal or taruca, it is one of the two mid-sized deer in the Hippocamelus genus and ranges across the high mountainsides and cold valleys of the Andes. The distribution and habitat, behaviour, and diet of the deer have all been the subject of study. The viability of the small remaining population is an outstanding concern to researchers.

Acrisione is a genus of the tribe Senecioneae of the family Asteraceae, native to Chile and southern Argentina. It was first described as a genus in 1985.

Octodontidae is a family of rodents, restricted to southwestern South America. Fourteen species of octodontid are recognised, arranged in seven genera. The best known species is the common degu, Octodon degus.
Aphyllocladus is a genus of flowering plants in the family Asteraceae.
Oriastrum is a genus of plants in the family Asteraceae, found in western South America. It is placed in the tribe Mutisieae.

Gamocarpha is a genus of flowering plants in the family Calyceraceae, native to the Andes of Chile and Argentina. It includes the former genus Nastanthus.
Belloa chilensis is a species of perennial herb belonging to the family Asteraceae that is endemic to parts of South America.
















