
Osmundaceae is a family of ferns containing four to six extant genera and 18–25 known species. It is the only living family of the order Osmundales in the class Polypodiopsida (ferns) or in some classifications the only order in the class Osmundopsida. This is an ancient and fairly isolated group that is often known as the "flowering ferns" because of the striking aspect of the ripe sporangia in Claytosmunda, Osmunda, Osmundastrum, and Plensium. In these genera the sporangia are borne naked on non-laminar pinnules, while Todea and Leptopteris bear sporangia naked on laminar pinnules. Ferns in this family are larger than most other ferns.

Osmundastrum is genus of leptosporangiate ferns in the family Osmundaceae with one living species, Osmundastrum cinnamomeum, the cinnamon fern. It is native to the Americas and eastern Asia, growing in swamps, bogs and moist woodlands.

Corylus johnsonii is an extinct species of hazel known from fossil fruits found in the Klondike Mountain Formation deposits of northern Washington state, dated to the early Eocene Ypresian stage. Based on described features, C. johnsonii is the oldest definite species in the genus Corylus.
Neviusia dunthornei is an extinct species of flowering plants in the family Rosaceae. The species is solely known from the early Eocene, Ypresian stage, Allenby Formation Lacustrine deposits near the town of Princeton, British Columbia.
Carya washingtonensis is an extinct species of hickory nut in the walnut family Juglandaceae. The species is solely known from the Miocene sediments exposed in Kittitas County near Ellensburg, Washington.
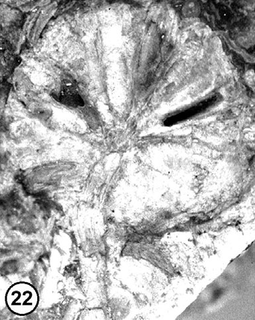
Osmunda wehrii is an extinct species of fern in the modern genus Osmunda of the family Osmundaceae. Osmunda wehrii is known from Langhian age Miocene fossils found in Central Washington.
Acer washingtonense is an extinct maple species in the family Sapindaceae described from one fossil leaf and four fossil samaras. The species is solely known from the Early Eocene sediments exposed in northeast Washington state, United States. It is one of three species belonging to the extinct section Torada.
Acer stewarti is an extinct maple species in the family Sapindaceae described from a series of fossil leaves and samaras. The species is solely known from the Early Eocene sediments exposed in south central British Columbia, Canada adjacent to northeast Washington state, United States. It is one of only two species belonging to the extinct section Stewarta.

Fothergilla malloryi is an extinct species of flowering plant in the family Hamamelidaceae known from fossil leaves found in the early Eocene Klondike Mountain Formation deposits of northern Washington state. The F. malloryi leaves are the earliest appearance in the fossil record of a member of the witchalder genus Fothergilla, which includes the living species F. gardenii, and F. major, both of which are native to the southeastern United States. The genus also includes three or four other fossil species with two Asian Miocene species, F. viburnifolia from China, F. ryozenensis from Japan along with one Miocene North American species, F. praeolata of Oregon. Fothergilla durhamensis described from Eocene sediments in King County, Washington is considered dubious in placement, and it was transferred to the genus Platimeliphyllum by Huegele et al. (2021).

Anchistea is a genus of leptosporangiate ferns in the family Blechnaceae. It has only one species, Anchistea virginica the Virginia chain fern, which has long creeping, scaly, underground stems or rhizomes giving rise to tall widely separated, deciduous, single leaves. In contrast, the leaves of Osmundastrum cinnamomeum, which can be mistaken for A. virginica, grow in a group from a crown. Also in contrast to O. cinnamomeum the leaves are monomorphic without distinct fertile fronds. The lower petiole or stipe is dark purple to black, shiny and swollen, the upper rachis is dull green. The leaf blade is green and lanceolate, composed of 12 to 23 paired, alternate pinnatifid pinnae. The pinnae are subdivided into 15 to 20 paired segments that are ovate to oblong. The lower rachis is naked for about half its length. The sori or spore-producing bodies are found on the underside of the pinnae and are long and form a double row which outlines the major veins of the pinnae. In common with all ferns, A. virginica exhibits a gametophyte stage in its life cycle and develops a haploid reproductive prothallus as an independent plant. The spores are produced in red-brown sori which line the spaces (areolae) between the costa and costules. Further photographs can be found at the Connecticut Botanical Society and Ontario Ferns websites.

The Allenby formation is a sedimentary rock formation in British Columbia which was deposited during the Ypresian stage of the Early Eocene. It consists of conglomerates, sandstones with interbedded shales and coal. The shales contain an abundance of insect, fish and plant fossils known from 1877 and onward, while the Princeton Chert was first indented in the 1950's and is known from anatomically preserved plants.
Stonebergia is an extinct genus in the rose family, Rosaceae, which contains the single species Stonebergia columbiana. The genus was described from a series of isolated fossil leaves in shale from an early Eocene location in southern British Columbia.
Coryloides is an extinct genus of flowering plants in the hazelnut family, Betulaceae, containing the single species Coryloides hancockii. The species is solely known from the middle Eocene sediments exposed in north central Oregon and was first described from a series of isolated fossil nuts in cherts.
Liquidambar changii is an extinct species of sweetgum in the Altingiaceae genus Liquidambar. Liquidambar changii is known from Middle Miocene fossils found in Central Washington.

Quercus hiholensis is an extinct species of oak in the Fagaceae genus Quercus. The species is known from Middle Miocene fossils found in Central Washington.

Shirleya is an extinct genus in the crape myrtle family, Lythraceae, which contains a single species, Shirleya grahamae. The genus and species are known from Middle Miocene fossils found in Central Washington.

Nuphar carlquistii is an extinct species of flowering plant in the family Nymphaeaceae related to the modern spatterdock, Nuphar advena. The species is known from fossil seeds and fruits found in the early Eocene deposits of northern Washington state, United States, and a similar aged formation in British Columbia, Canada.
Acer beckianum is an extinct maple species in the family Sapindaceae described from a single fossil wood section. The species is solely known from the Middle Miocene sediments exposed in central Washington in the United States. It is one of three Washington state Acer species described in 1961 from petrified wood.

Tetracentron hopkinsii is an extinct species of flowering plant in the family Trochodendraceae. The species is known from fossil leaves found in the early Eocene deposits of northern Washington state, United States and south Central British Columbia. The species was first described from fossil leaves found in the Allenby Formation. T. hopkinsii are possibly the leaves belonging to the extinct trochodendraceous fruits Pentacentron sternhartae.










