Related Research Articles

Salmonella is a genus of rod-shaped (bacillus) Gram-negative bacteria of the family Enterobacteriaceae. The two species of Salmonella are Salmonella enterica and Salmonella bongori. S. enterica is the type species and is further divided into six subspecies that include over 2,600 serotypes. Salmonella was named after Daniel Elmer Salmon (1850–1914), an American veterinary surgeon.

An agar plate is a Petri dish that contains agar as a solid growth medium plus nutrients, used to culture microorganisms. Sometimes selective compounds are added to influence growth, such as antibiotics.

Salmonella enterica is a rod-shaped, flagellate, facultative aerobic, Gram-negative bacterium and a species of the genus Salmonella. A number of its serovars are serious human pathogens.

A microbiological culture, or microbial culture, is a method of multiplying microbial organisms by letting them reproduce in predetermined culture medium under controlled laboratory conditions. Microbial cultures are foundational and basic diagnostic methods used as a research tool in molecular biology.

Bacteriological water analysis is a method of analysing water to estimate the numbers of bacteria present and, if needed, to find out what sort of bacteria they are. It represents one aspect of water quality. It is a microbiological analytical procedure which uses samples of water and from these samples determines the concentration of bacteria. It is then possible to draw inferences about the suitability of the water for use from these concentrations. This process is used, for example, to routinely confirm that water is safe for human consumption or that bathing and recreational waters are safe to use.

Eosin methylene blue is a selective stain for Gram-negative bacteria. EMB contains dyes that are toxic to Gram-positive bacteria. EMB is the selective and differential medium for coliforms. It is a blend of two stains, eosin and methylene blue in the ratio of 6:1. EMB is a differential microbiological medium, which slightly inhibits the growth of Gram-positive bacteria and provides a color indicator distinguishing between organisms that ferment lactose and those that do not. Organisms that ferment lactose display "nucleated colonies"—colonies with dark centers.

MacConkey agar is an indicator, a selective and differential culture medium for bacteria designed to selectively isolate Gram-negative and enteric bacilli and differentiate them based on lactose fermentation. The crystal violet and bile salts inhibit the growth of Gram-positive organisms which allows for the selection and isolation of gram-negative bacteria. Enteric bacteria that have the ability to ferment lactose can be detected using the carbohydrate lactose, and the pH indicator neutral red.

Chocolate agar (CHOC) or chocolate blood agar (CBA), is a nonselective, enriched growth medium used for isolation of pathogenic bacteria. It is a variant of the blood agar plate, containing red blood cells that have been lysed by slowly heating to 80°C. Chocolate agar is used for growing fastidious respiratory bacteria, such as Haemophilus influenzae and Neisseria meningitidis. In addition, some of these bacteria, most notably H. influenzae, need growth factors such as nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide and hemin, which are inside red blood cells; thus, a prerequisite to growth for these bacteria is the presence of red blood cell lysates. The heat also inactivates enzymes which could otherwise degrade NAD. The agar is named for its color and contains no chocolate products.
Bacillary dysentery is a type of dysentery, and is a severe form of shigellosis.

DCA agar is a solid bacteriological growth medium used for isolation of enteric pathogens.

Xylose Lysine Deoxycholate agar is a selective growth medium used in the isolation of Salmonella and Shigella species from clinical samples and from food. It has a pH of approximately 7.4, leaving it with a bright pink or red appearance due to the indicator phenol red. Sugar fermentation lowers the pH and the phenol red indicator registers this by changing to yellow. Most gut bacteria, including Salmonella, can ferment the sugar xylose to produce acid; Shigella colonies cannot do this and therefore remain red. After exhausting the xylose supply Salmonella colonies will decarboxylate lysine, increasing the pH once again to alkaline and mimicking the red Shigella colonies. Salmonellae metabolise thiosulfate to produce hydrogen sulfide, which leads to the formation of colonies with black centers and allows them to be differentiated from the similarly coloured Shigella colonies.
Rappaport-Vassiliadis soya peptone broth is used as an enrichment growth medium for the isolation of Salmonella species. It is not recommended for the enrichment of Salmonella Typhi, which is inhibited in RVS broth. It is an alternative to selenite broth. It is not associated with potential teratogenicity problems seen with the use of selenite broth. It enriches salmonellae because they are better able to survive the high osmotic pressure in the medium and because they can multiply at relatively lower pH and higher temperatures compared with other gut bacteria. RVS broth has a pH around 5.2.

Mannitol salt agar or MSA is a commonly used selective and differential growth medium in microbiology. It encourages the growth of a group of certain bacteria while inhibiting the growth of others. This medium is important in medical laboratories as one method of distinguishing pathogenic microbes in a short period of time. It contains a high concentration of salt (NaCl), making it selective for most Gram-negative and some Gram-positive bacteria since this level of salt is inhibitory to most other bacteria. It is also a differential medium for mannitol-fermenting staphylococci, containing carbohydrate mannitol and the indicator phenol red, a pH indicator for detecting acid produced by mannitol-fermenting staphylococci. Staphylococcus aureus produces yellow colonies with yellow zones, whereas other coagulase-negative staphylococci produce small pink or red colonies with no colour change to the medium. If an organism can ferment mannitol, an acidic byproduct is formed that causes the phenol red in the agar to turn yellow. It is used for the selective isolation of presumptive pathogenic (pp) Staphylococcus species.
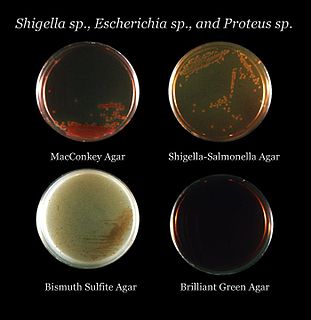
Bismuth sulfite agar is a type of agar media used to isolate Salmonella species. It uses glucose as a primary source of carbon. BLBG and bismuth stop gram-positive growth. Bismuth sulfite agar tests the ability to use ferrous sulfate and convert it to hydrogen sulfide.

Hektoen enteric agar is a selective and differential agar primarily used to recover Salmonella and Shigella from patient specimens. HEA contains indicators of lactose fermentation and hydrogen sulfide production; as well as inhibitors to prevent the growth of Gram-positive bacteria. It is named after the Hektoen Institute in Chicago, where researchers developed the agar.
XLT may refer to:

Müller-Hinton agar is a microbiological growth medium that is commonly used for antibiotic susceptibility testing. It is also used to isolate and maintain Neisseria and Moraxella species.

Endo agar is a microbiological growth medium with a faint pink colour. Originally developed for the isolation of Salmonella typhi, it is now used mostly as a coliform medium. Most gram-negative organisms grow well in this medium, while growth of gram-positive organisms is inhibited. Coliform organisms ferment the lactose in this medium, producing a green metallic sheen, whereas non-lactose-fermenting organisms produce clear, colourless colonies, i.e. Salmonella sp..
Apocholate Citrate Agar or ACA is a selective environment used to isolate Shigella and Salmonella bacteria. The name comes for apocholate and citrate in agar.
XLD may refer to: