Related Research Articles

Agar, or agar-agar, is a jelly-like substance consisting of polysaccharides obtained from the cell walls of some species of red algae, primarily from "ogonori" (Gracilaria) and "tengusa" (Gelidiaceae). As found in nature, agar is a mixture of two components, the linear polysaccharide agarose and a heterogeneous mixture of smaller molecules called agaropectin. It forms the supporting structure in the cell walls of certain species of algae and is released on boiling. These algae are known as agarophytes, belonging to the Rhodophyta phylum. The processing of food-grade agar removes the agaropectin, and the commercial product is essentially pure agarose.

Ammonium ferric citrate (also known as ferric ammonium citrate or ammoniacal ferrous citrate) has the formula (NH4)5[Fe(C6H4O7)2]. A distinguishing feature of this compound is that it is very soluble in water, in contrast to ferric citrate which is not very soluble.

Simmons' citrate agar is used for differentiating gram-negative bacteria on the basis of citrate utilization, especially for distinguishing Gammaproteobacteria of the family Enterobacteriaceae or even between species of the same genus. For example, Salmonella enteritidis would yield a positive (blue) result on Simmons’ agar and thus be distinguished from other Salmonella species like Salmonella typhi, Salmonella pullorum, and Salmonella gallinarum, which would yield a negative (green) result.
Mycolicibacterium alvei is a species of the phylum Actinomycetota, belonging to the genus Mycolicibacterium.
Mycolicibacter arupensis is a slowly growing mycobacterium first isolated from soil and human sputum samples in Spain. Etymology: arupense, pertaining to the ARUP Institute for Clinical and Experimental Pathology, where the type strain was characterized.

Mycobacterium cosmeticum is a rapidly growing mycobacterium that was first isolated from cosmetic patients and sites performing cosmetic procedures.
Mycobacterium elephantis, a bacterium of the family Mycobacteriaceae, was discovered and isolated from a deceased elephant near India and may be linked to respiratory dysfunction. Organisms in the genus Mycobacterium are known to be aerobic and non-motile. Organisms within Mycobacterium belong to either the rapid growing group or the slow growing group. M. elephantis is classified as a rapid grower and relates most closely to Mycobacterium confluentis and Mycobacterium phlei.
Mycobacterium genavense is a slow-growing species of the phylum Actinomycetota, belonging to the genus Mycobacterium.
Mycobacterium gordonae is a species of Mycobacterium named for Ruth E. Gordon. It is a species of the phylum Actinomycetota, belonging to the genus Mycobacterium.
Mycobacterium haemophilum is a species of the phylum Actinomycetota, belonging to the genus Mycobacterium.
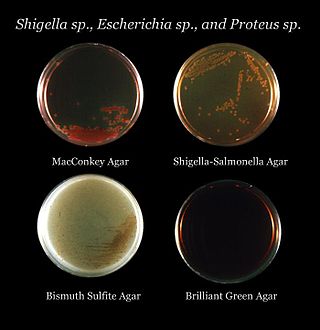
Bismuth sulfite agar is a type of agar media used to isolate Salmonella species. It uses glucose as a primary source of carbon. BLBG and bismuth stop gram-positive growth. Bismuth sulfite agar tests the ability to use ferrous sulfate and convert it to hydrogen sulfide.
In microbiology, the phenotypic testing of mycobacteria uses a number of methods. The most-commonly used phenotypic tests to identify and distinguish Mycobacterium strains and species from each other are described below.
R2A agar is a culture medium developed to study bacteria which normally inhabit potable water. These bacteria tend to be slow-growing species and would quickly be suppressed by faster-growing species on a richer culture medium.

De Man, Rogosa and Sharpe agar, often abbreviated to MRS, is a selective culture medium designed to favour the luxuriant growth of Lactobacilli for lab study. Developed in 1960, this medium was named for its inventors, Johannes Cornelis de Man, Morrison Rogosa, and Margaret Elisabeth Sharpe. It contains sodium acetate, which suppresses the growth of many competing bacteria. This medium has a clear brown colour.

The Triple Sugar Iron (TSI) test is a microbiological test roughly named for its ability to test a microorganism's ability to ferment sugars and to produce hydrogen sulfide. It is often used to differentiate enteric bacteria including Salmonella and Shigella.

Löwenstein–Jensen medium, more commonly known as LJ medium, is a growth medium specially used for culture of Mycobacterium species, notably Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
Mycobacteria Growth Indicator Tube (MGIT) is intended for the detection and recovery of mycobacteria. The MGIT Mycobacteria Growth Indicator Tube contains 7 mL of modified Middlebrook 7H9 Broth base. The complete medium, with OADC enrichment and PANTA antibiotic mixture, is one of the most commonly used liquid media for the cultivation of mycobacteria.
The citrate test detects the ability of an organism to use citrate as the sole source of carbon and energy.
Middlebrook 7H9 broth is a liquid growth medium specially used for culture of Mycobacterium species, notably Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
Middlebrook 7H11 agar is identical to Middlebrook 7H10 agar, with an addition of pancreatic digest of casein to facilitate the growth of fastidious cultures of M. tuberculosis.
References
- ↑ Atlas, Ronald M.; James W. Snyder (2006). Handbook of media for clinical microbiology. CRC Press. p. 307. ISBN 978-0-8493-3795-6.
- ↑ Middlebrook 7H10 Agar Base