
Dr. Fu Manchu is a supervillain who was introduced in a series of novels by the English author Sax Rohmer beginning shortly before World War I and continuing for another forty years. The character featured in cinema, television, radio, comic strips and comic books for over 100 years, and he has also become an archetype of the evil criminal genius and mad scientist, while lending his name to the Fu Manchu moustache.

Sichuan is a province in Southwestern China occupying the Sichuan Basin and Tibetan Plateau between the Jinsha River on the west, the Daba Mountains in the north and the Yungui Plateau to the south. Sichuan's capital city is Chengdu; its population stands at 83 million. Sichuan neighbors Qinghai to the northwest, Gansu to the north, Shaanxi to the northeast, Chongqing to the east, Guizhou to the southeast, Yunnan to the south, and Tibet to the west.

The Three Gorges are three adjacent and sequential gorges along the middle reaches of the Yangtze River path, in the hinterland of the People's Republic of China. With a subtropical monsoon climate, they are known for their scenery.

Chengdu is the capital city of the Chinese province of Sichuan. With a population of 20,937,757 at the 2020 census, it is the fourth most populous city in China, and it is the only city with a population of over 20 million apart from direct-administered municipalities. It is traditionally the hub of Western China.

Chongqing is a municipality in Southwestern China. Chongqing is one of the four direct-administered municipalities under the Central People's Government, along with Beijing, Shanghai, and Tianjin. It is the only directly administrated municipality located deep inland. The municipality covers a large geographical area roughly the size of Austria, which includes several disjunct urban areas in addition to Chongqing proper. Due to its classification, the municipality of Chongqing is the largest city proper in the world by area, though it does not have the largest urban area.

Wanzhou District is Chongqing's second most populated urban core area on the upper reaches of the Three Gorges of the Yangtze River in China. It is currently governed as a district of Chongqing Municipality, bordering Sichuan to the northwest and Hubei to the southeast. It was formerly known as Wanxian or Wan County. Prior to Chongqing's formation as a direct-controlled municipality, Wanzhou was part of Sichuan province. The urban core of Wanzhou is 228 km (142 mi) away from Chongqing's city proper.

Fuling District is a district in central Chongqing, China. As the second largest city in Chongqing, the area is known for zha cai, a hot pickled mustard tuber, as well as serving as the location of former U.S. Peace Corps teacher Peter Hessler's best-selling memoir River Town: Two Years on the Yangtze.
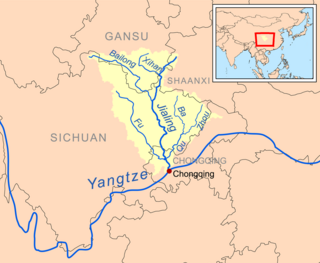
The Jialing River, formerly known by numerous other names, is a major tributary of the Yangtze River in the Sichuan Basin. It is named after the Jialing Valley in Feng County, Shaanxi through which it flows.

Luzhou (simplified Chinese: 泸州; traditional Chinese: 瀘州; pinyin: Lúzhōu; Sichuanese Pinyin: Nu2zou1; Luzhou dialect: ), formerly transliterated as Lu-chou or Luchow, is a prefecture-level city located in the southeast of Sichuan Province, China. It is also known as the "Liquor City" (酒城). It was named Jiangyang (simplified Chinese: 江阳; traditional Chinese: 江陽; pinyin: Jiāngyáng) until the Northern and Southern dynasties. Situated at the confluence of the Tuo River and the Yangtze River, Luzhou has been Sichuan province's largest port in both size and output since Chongqing's separation from Sichuan in 1997. As of the 2020 Chinese census, its population was 4,254,149. Of these, 1,241,273 lived in the built-up (or metro) area made of Jiangyang and Longmatan districts, as Naxi district is not conurbated yet. Luzhou borders Yunnan, Guizhou and Chongqing provinces. As the only geographic junction of the four provinces, it was an important port location in ancient China. After the PRC was founded in 1949, Luzhou became the capital of southern Sichuan province. In 1983, Luzhou was upgraded to prefecture-level city status.

Li Jing, courtesy name Yaoshi, posthumously known as Duke Jingwu of Wei, was a Chinese military general, strategist, and writer who lived in the early Tang dynasty and was most active during the reign of Emperor Taizong. In 630, Li Jing defeated the Göktürks, led by Jieli Khan, with just 3,000 cavalry soldiers in a surprise attack, allowing the Tang Empire to subjugate the Göktürks and reduce them to the status of a vassal under the Tang Empire. Li Jing and Li Shiji are considered the two most prominent early Tang generals.

Theatre of China has a long and complex history. Traditional Chinese theatre, generally in the form of Chinese opera, is musical in nature. Chinese theatre can trace its origin back a few millennia to ancient China, but the Chinese opera started to develop in the 12th century. Western forms like the spoken drama, western-style opera, and ballet did not arrive in China until the 20th century.
Elizabeth Foreman Lewis was an American children's writer. She received the Newbery Award and the Lewis Carroll Shelf Award.

Sichuan opera is a type of Chinese opera originating in China's Sichuan province around 1700. Today's Sichuan opera is a relatively recent synthesis of five historic melodic styles. Regionally Chengdu remains to be the main home of Sichuan opera, while other influential locales include Chongqing, Guizhou, Yunnan, Hubei and Taiwan. Sichuan opera was listed in the first batch of 518 national intangible cultural heritage list announced on May 20, 2006.

Fah Lo Suee is a character who was introduced in the series of novels Dr. Fu Manchu by the English author Sax Rohmer (1883-1959). She is the daughter of Dr. Fu Manchu and an unnamed Russian woman, sometimes shown as an ally, sometimes shown as a rival. The character featured in cinema and comic strips and comic books alongside her father, sometimes using another names, and she has also become an archetype of the Dragon Lady.
The Chinese city of Chongqing has a history dating back at least 3,000 years.

Kui Prefecture, Kuizhou Circuit, or Kuizhou was initially established in 619 CE, as a renaming of the existing Xin Prefecture. Kuizhou was an important area from the beginning and through the end of the Tang dynasty of China, when it was alternatively part of several of the Circuits which made up typical large scale political structural organizations of the Tang era. Kuizhou continued as a political entity through the end of the Song dynasty, during which it was of Provincial level, a typical large scale political organization of Song era. Kui Prefecture was located in what is now eastern Chongqing. During the Song dynasty, Kuizhou's capital was located in what is now Fengjie County, Chongqing, and the extent of the province was to what today includes Chongqing, eastern Sichuan, and Guizhou. Part of the importance of Kuizhou was related to its prominent location along the Yangzi River. Kui was also known for its spectacular scenerary, and being a location in which exiled poets wrote their laments.

The economy of Chongqing, China, has developed rapidly since it was separated from the Sichuan and became a centrally-administered municipality in 1997. In 2019, it was the sixth-largest Chinese city economy and ranked as China's third-largest municipal economy. In China's overall layout, Chongqing is also important for connecting China's underdeveloped western region with its more advanced eastern region, as well as promoting the economy of the mid-lower reaches of Yangtze river and the central western region.

Samuel Cornell Plant was a British sailor who is best known as the first to command a merchant steamer plying on the Upper Yangtze River in 1900. The Upper Yangtze is the section of river stretching through gorges from Yichang to Chongqing. Plant later collaborated with Chinese merchants and the government to create Sichuan Steam Navigation Company, serving as Captain of SS Shutung and SS Shuhun, providing the first regular merchant steam service on the Upper Yangtze. He is further recognized for his contributions as Chinese Maritime Customs’ First Senior River Inspector on the Upper Yangtze. Plant installed the river's navigational marks, established signaling systems, wrote a manual for shipmasters, and trained hundreds of foreign and Chinese pilots.
Twelve Views of Bayu are popular scenic views in and around the city of Chongqing, China. Ba and Yu are old names of Chongqing in Imperial times. Influenced by Eight Views of Xiaoxiang in Hunan Province, people in Chongqing listed their own most beloved views during the reign of the Tianshun Emperor of the Ming dynasty. Scenic views in the list changed throughout the history. Some scenic views appeared in earlier lists no longer exist in modern days due to the change of physical geography, landscapes and land-uses.

St John's Cathedral, today known as Gospel Church, is a Protestant church situated on Yangtianjing Street in the county-level city of Langzhong, Nanchong, Sichuan Province. Founded in 1908, the church had been the Anglican cathedral, originally designated as a pro-cathedral, of the Szechwan Diocese of the Church in China, and the largest Anglican church in Southwest China. It has been subjected to the control of the state-sanctioned Three-Self Patriotic Church since 1954.
















