Models

| Manufacturer | CALT |
|---|---|
| Country of origin | China |
| Used on | Long March rocket family (2C · 2D · 3B · 3C · 5 · 7) |
| Associated stages | |
| Comparable | Fregat |
| Launch history | |
| Status | Active |
| Total launches | 29 |
| Successes (stage only) | 28 |
| Failed | 1 |
| Lower stage failed | 0 |
| First flight | 30 March 2015 BeiDou I1-S |
| Last flight | 21 March 2024 Yunhai-2 Group 02 |
| Launch date | |
| Yuanzheng | |
| Powered by | 1 × YF-50D [1] |
| Maximum thrust | 6.5 kN (1,500 lbf) [2] |
| Specific impulse | 315.5 seconds [2] |
| Propellant | N2O4 / UDMH |
Yuanzheng (Chinese :远征; pinyin :Yuǎn Zhēng; lit.'Expedition') is a restartable upper stage developed by the China Academy of Launch Vehicle Technology (CALT) for the Long March rocket family.
The Yuanzheng stage enables the Chinese launch vehicles to deploy payloads directly to high-energy orbits such as medium Earth orbit (MEO) and geosynchronous orbit (GSO). Since the Long March third stage cannot restart, it cannot circularize a GSO or GEO orbit from a geosyncronous transfer orbit (GTO). With its restart capability, Yuanzheng has enabled the deployment of satellite pairs for the BeiDou Navigation Satellite System in MEO and communications satellites in GSO. This eliminates the need for the spacecraft to include a liquid apogee engine or an apogee kick motor. [3]
Yuanzheng has a thrust of 6.5 kN (1,500 lbf) with a specific impulse of 315.5 seconds. It uses the storable hypergolic propellants unsymmetrical dimethylhydrazine (UDMH) and dinitrogen tetroxide (N2O4), and can perform at least two burns within its rated life of 6.5 hours, sufficient to reach the transfer orbit apogee, and perform the circularization burn from there. [4]
Operational variants are designated YZ-1 for Long March 3B and 3C, YZ-1A for Long March 7, YZ-1S for Long March 2C, YZ-2 for Long March 5, and YZ-3 for Long March 2D.

Yuanzheng was presented in a 2013 paper [3] and performed its first mission on 30 May 2015. The debut flight of the Long March 7 in 2016 included an improved version called Yuanzheng-1A that can flexibly deploy multiple payloads into various target orbits. [5] Further variants were later deployed for Long March 5 (YZ-2) in 2016, Long March 2C (YZ-1S) and Long March 2D (YZ-3) in 2018.
| Flight No. | Date (UTC) | Carrier Rocket | Stage Model | Serial Number | Launch site | Mission | Result |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2015-03-30 13:52 | Long March 3C | YZ-1 | Y1 | Xichang | BDS I1-S | Success |
| 2 | 2015-07-25 12:29 | Long March 3B | YZ-1 | Y2 | Xichang | BDS M1-S / BDS M2-S | Success |
| 3 | 2016-02-01 07:29 | Long March 3C | YZ-1 | Y3 | Xichang | BDS M3-S | Success |
| 4 | 2016-06-25 12:00 | Long March 7 | YZ-1A | Y1 | Wenchang | Inaugural Mission | Success |
| 5 | 2016-11-3 12:43 | Long March 5 | YZ-2 | Y1 | Wenchang | Inaugural Mission | Success |
| 6 | 2017-11-5 11:45 | Long March 3B | YZ-1 | Y4 | Xichang | BDS-3 M1 BDS-3 M2 | Success |
| 7 | 2018-01-11 23:18 | Long March 3B | YZ-1 | Y5 | Xichang | BDS-3 M7 BDS-3 M8 | Success |
| 8 | 2018-02-12 05:03 | Long March 3B | YZ-1 | Y6 | Xichang | BDS-3 M3 BDS-3 M4 | Success |
| 9 | 2018-03-29 17:56 | Long March 3B | YZ-1 | Y7 | Xichang | BDS-3 M9 BDS-3 M10 | Success |
| 10 | 2018-07-29 01:48 | Long March 3B | YZ-1 | Y8 | Xichang | BDS-3 M5 BDS-3 M6 | Success |
| 11 | 2018-08-24 23:52 | Long March 3B | YZ-1 | Y9 | Xichang | BDS-3 M11 BDS-3 M12 | Success |
| 12 | 2018-09-19 14:07 | Long March 3B | YZ-1 | Y10 | Xichang | BDS-3 M13 BDS-3 M14 | Success |
| 13 | 2018-10-09 02:43 | Long March 2C | YZ-1S | Y1 | Jiuquan | Yaogan 32A, 32B | Success |
| 14 | 2018-10-15 04:23 | Long March 3B | YZ-1 | Y11 | Xichang | BDS-3 M15 BDS-3 M16 | Success |
| 15 | 2018-11-18 18:00 | Long March 3B | YZ-1 | Y12 | Xichang | BDS-3 M17 BDS-3 M18 | Success |
| 16 | 2018-12-29 08:00 | Long March 2D | YZ-3 | Y1 | Jiuquan | Yunhai-2 01, 02, 03, 04, 05, 06 Hongyan-1 | Success |
| 17 | 2019-09-22 21:10 | Long March 3B/E | YZ-1 | Y13 | Xichang | BDS-3 M23 BDS-3 M24 | Success |
| 18 | 2019-11-23 00:55 | Long March 3B/E | YZ-1 | Y14 | Xichang | BeiDou-3 M21 BeiDou-3 M22 | Success |
| 19 | 2019-12-16 07:22 | Long March 3B/E | YZ-1 | Y15 | Xichang | BeiDou-3 M19 BeiDou-3 M20 | Success |
| 20 | 2021-08-24 11:15 | Long March 2C | YZ-1S | Y2 | Jiuquan | RSW-01 RSW-02 unknown payload | Success |
| 21 | 2021-11-03 07:43 | Long March 2C | YZ-1S | Y4 | Jiuquan | Yaogan 32-02A, 32-02B | Success |
| 22 | 2022-05-20 10:30 | Long March 2C | YZ-1S | Y5 | Jiuquan | LEO Test Sat 1/2 Digui Tongxin Weixing | Success |
| 23 | 2023-07-09 11:00 | Long March 2C | YZ-1S | Y3 | Jiuquan | Hulianwang Jishu Shiyan 1A Hulianwang Jishu Shiyan 1B | Success |
| 24 | 2023-11-16 03:55 | Long March 2C | YZ-1S | Y9 | Jiuquan | Haiyang-3A | Success |
| 25 | 2023-11-23 10:00 | Long March 2D | YZ-3 | Y2 | Xichang | Hulianwang Jishu Shiyan 2A Hulianwang Jishu Shiyan 2B Hulianwang Jishu Shiyan 2C | Success |
| 26 | 2023-12-26 03:26 | Long March 3B/E | YZ-1 | Y16 | Xichang | BeiDou-3 M25 BeiDou-3 M26 | Success |
| 27 | 2023-12-30 00:13 | Long March 2C | YZ-1S | Y17 | Jiuquan | Hulianwang Jishu Shiyan 4A Hulianwang Jishu Shiyan 4B Hulianwang Jishu Shiyan 4C | Success |
| 28 | 2024-03-13 12:51 | Long March 2C | YZ-1S | Y18 | Xichang | DRO-A DRO-B | Failure |
| 29 | 2024-03-21 05:27 | Long March 2D | YZ-3 | Y3 | Jiuquan | Yunhai-2 Group 02 | Success |
Currently, there is known to be five versions:
The Kaituozhe or KT rocket family is a series of launch vehicles built by the China Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation (CASC).

This comparison of orbital launch systems lists the attributes of all current and future individual rocket configurations designed to reach orbit. A first list contains rockets that are operational or have attempted an orbital flight attempt as of 2024; a second list includes all upcoming rockets. For the simple list of all conventional launcher families, see: Comparison of orbital launchers families. For the list of predominantly solid-fueled orbital launch systems, see: Comparison of solid-fueled orbital launch systems.

The Long March 3C, also known as the Changzheng 3C, CZ-3C and LM-3C, is a Chinese orbital launch vehicle. It is launched from Launch Complex 2 and 3 at the Xichang Satellite Launch Center (XSLC). A three-stage rocket with two strapon liquid rocket boosters, it is a member of the Long March 3 rocket family, and was derived from the Long March 3B. It was designed to fill a gap in payload capacities between the Long March 3A and 3B.
The Goldfish class remotely operated underwater vehicle (ROUV) is a class of light ROUV developed by the Shenyang Institute of Automation of the Chinese Academy of Science. It is in service with both the People's Liberation Army Navy (PLAN) and other civilian agencies of the People's Republic of China.

The Long March 7, or Chang Zheng 7 in pinyin, abbreviated LM-7 for export or CZ-7 within China, originally Long March 2F/H or Chang Zheng 2F/H, nicknamed Bingjian, is a Chinese liquid-fuelled launch vehicle of the Long March family, developed by the China Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation (CAST). It made its inaugural flight on 25 June 2016.
Kuaizhou is a family of Chinese "quick-reaction" orbital launch vehicles. Flying since 2013, Kuaizhou 1 and 1A consist of three solid-fueled rocket stages, with a liquid-fueled fourth stage as part of the satellite system. Kuaizhou 11, which flew an unsuccessful maiden flight in July 2020, is a larger model able to launch a 1,500 kg (3,300 lb) payload into low Earth orbit. Heavy-lift models KZ-21 and KZ-31 are in development. The Kuaizhou series of rockets is manufactured by ExPace, a subsidiary of China Aerospace Science and Industry Corporation (CASIC), as their commercial launch vehicles.

Tianlongsi station, is a station of Line 1 of the Nanjing Metro. It began operations on 28 May 2010, as part of the southern extension of line 1 from Andemen to CPU.

Zhushanlu station, is a station of Line 1 of the Nanjing Metro. It began operations on 28 May 2010, as part of the southern extension of line 1 from Andemen to CPU.

Tianyindadao station, is a station of Line 1 of the Nanjing Metro. It began operations on 28 May 2010, as part of the southern extension of line 1 from Andemen to CPU.

Yunjinlu station, is a station of Line 2 of the Nanjing Metro. It started operations on 28 May 2010 along with the rest of Line 2.

Xianlinzhongxin station, is a station of Line 2 of the Nanjing Metro. It started operations on 28 May 2010 along with the rest of Line 2.

Yangshangongyuan station, is a station of Line 2 of the Nanjing Metro. It started operations on 28 May 2010 along with the rest of Line 2.
The CTS is an upper stage developed by the China Academy of Launch Vehicle Technology (CALT) to improve the performance of the Long March 2C to high LEO missions like SSO. The two stage LM-2 delivers the payload and stage to an elliptical orbit with the desired apogee and the CTS points the stack in the direction of the correct vector and activates the solid rocket motor (SRM) main engine to circularize it. It then dispenses the spacecraft and does a passivisation procedure.

i-Space is a Chinese private space technology development and space launch company based in Beijing, founded in October 2016.

Galactic Energy is a Chinese private space launch enterprise flying the Ceres-1 and developing the Pallas-1 orbital rockets. The company's long-term objective is to mine asteroids for rare metals and minerals.
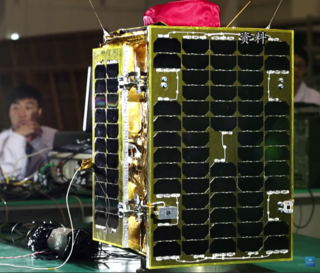
Jilin-1 is China's first self-developed commercial remote sensing satellite system. The satellites are operated by Chang Guang Satellite Technology Corporation and named after Jilin Province where the company is headquartered. The first set of satellites were launched by Long March 2D in Jiuquan Satellite Launch Center on 7 October 2015, at 04:13 UTC. All launched Jilin-1 satellites are in Sun-synchronous orbit (SSO).

Kinetica 1 is a Chinese small-lift orbital launch vehicle developed by CAS Space.
Ceres-1, is a four-stage rocket manufactured and operated by Galactic Energy, the first three stages use solid-propellant rocket motors and the final stage uses a hydrazine propulsion system. It is about 20 m (62 ft) tall and 1.4 m in diameter. It can deliver 400 kg (880 lb) to low Earth orbit or 300 kg (660 lb) to 500 km Sun-synchronous orbit.
Tianyan, often translated into English as SkyEye or Eye in the Sky, is a reconnaissance satellite program of the People's Republic of China. To date, the Tianyan satellite program has launched one satellite from the Yizheng class (Yizheng-1) and two satellites from the Xingshidai class.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: DOI inactive as of November 2024 (link)