The Mousterian is an archaeological industry of stone tools, associated primarily with the Neanderthals in Europe, and to the earliest anatomically modern humans in North Africa and West Asia. The Mousterian largely defines the latter part of the Middle Paleolithic, the middle of the West Eurasian Old Stone Age. It lasted roughly from 160,000 to 40,000 BP. If its predecessor, known as Levallois or Levallois-Mousterian, is included, the range is extended to as early as c. 300,000–200,000 BP. The main following period is the Aurignacian of Homo sapiens.
The Châtelperronian is a proposed industry of the Upper Palaeolithic, the existence of which is debated. It represents both the only Upper Palaeolithic industry made by Neanderthals and the earliest Upper Palaeolithic industry in central and southwestern France, as well as in northern Spain. It derives its name from Châtelperron, the French village closest to the type site, the cave La Grotte des Fées.

The Upper Paleolithic is the third and last subdivision of the Paleolithic or Old Stone Age. Very broadly, it dates to between 50,000 and 12,000 years ago, according to some theories coinciding with the appearance of behavioral modernity in early modern humans. It is followed by the Mesolithic.

Alhama de Granada is a town in the province of Granada, approx. 50 km from the city of Granada. The name is derived from the thermal baths located there, which are called الـحَـمّـة al-hammah in Arabic.

Spy Cave is located in Wallonia near Spy in the municipality of Jemeppe-sur-Sambre, Namur Province, Belgium above the left bank of the Orneau River. Classified as a premier Heritage site of the Walloon Region, the location ranks among the most significant paleolithic sites in Europe. The cave consists of numerous small chambers and corridors.

Teshik-Tash 1 is a Neanderthal skeleton discovered in 1938 in Teshik-Tash Cave, in the Bajsuntau mountain range, Uzbek SSR (Uzbekistan), Central Asia.

Jebel Irhoud or Adrar n Ighoud, is an archaeological site located just north of the town of Tlet Ighoud in Youssoufia Province, approximately 50 km (30 mi) south-east of the city of Safi in Morocco. It is noted for the hominin fossils that have been found there since the discovery of the site in 1961. Originally thought to be Neanderthals, the specimens have since been assigned to Homo sapiens and, as reported in 2017, have been dated to roughly 300,000 years ago.

Alcaucin is a town and municipality in the province of Málaga, part of the autonomous community of Andalusia in southern Spain. It borders with the province of Granada. The municipality is situated approximately 54 kilometers to the city of Málaga. It is 507 km from the capital of Madrid. The name was derived from al-kautín, the Arabic of "the arches." It has a population of approximately 1,600 residents, partly living in the hamlet of Puente Don Manuel. Natives of the town are called Alcaucineños and have the nickname of tiznaos.
Paleolithic Europe, or Old Stone Age Europe, encompasses the Paleolithic or Old Stone Age in Europe from the arrival of the first archaic humans, about 1.4 million years ago until the beginning of the Mesolithic around 10,000 years ago. This period thus covers over 99% of the total human presence on the European continent. The early arrival and disappearance of Homo erectus and Homo heidelbergensis, the appearance, complete evolution and eventual demise of Homo neanderthalensis and the immigration and successful settlement of Homo sapiens all have taken place during the European Paleolithic.

Vindija Cave is an archaeological site associated with Neanderthals and modern humans, located in the municipality of Donja Voća, northern Croatia. Remains of three Neanderthals were selected as the primary sources for the first draft sequence of the Neanderthal genome project in 2010. Additional research was done on the samples and published in 2017.

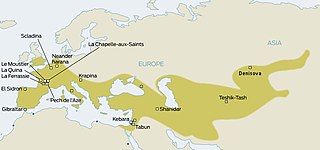
Neanderthals are an extinct group of archaic humans who lived in Eurasia until about 40,000 years ago. The type specimen, Neanderthal 1, was found in 1856 in the Neander Valley in present-day Germany.
Mezmaiskaya Cave is a prehistoric cave site overlooking the right bank of the Sukhoi Kurdzhips in the southern Russian Republic of Adygea, located in the northwestern foothills of the North Caucasus in the Caucasus Mountains system.

Scladina, or Sclayn Cave, is an archaeological site located in Wallonia in the town of Sclayn, in the Andenne hills in Belgium, where excavations since 1978 have provided the material for an exhaustive collection of over thirteen thousand Mousterian stone artifacts and the fossilized remains of an especially ancient Neanderthal, called the Scladina child were discovered in 1993.

The Obi-Rakhmat Grotto is a Middle Paleolithic prehistoric site that yielded Neanderthal fossils. It is a shallow karst cave near the junction of the Chatkal and Pskem Rivers at the southwestern end of the Talassky Alatau Range in the Tien Shan Mountains, 100 km (62 mi) northeast of Tashkent, Uzbekistan.

The Goyet Caves are a series of connected caves located in Belgium in a limestone cliff about 15 m (50 ft) above the river Samson near the village of Mozet in the Gesves municipality of the Namur province. The site is a significant locality of regional Neanderthal and European early modern human occupation, as thousands of fossils and artifacts were discovered that are all attributed to a long and contiguous stratigraphic sequence from 120,000 years ago, the Middle Paleolithic to less than 5,000 years ago, the late Neolithic. A robust sequence of sediments was identified during extensive excavations by geologist Edouard Dupont, who undertook the first probings as early as 1867. The site was added to the Belgian National Heritage register in 1976.

Pešturina is a cave in the municipality of Niška Banja in southeast Serbia. It is located southwest of Jelašnica and 20 km (12 mi) southeast of Niš. Artifacts from the Middle and Upper Paleolithic periods were discovered since the archaeological excavations began in 2006. The remains, identified as the Mousterian culture, were dated from 111,000 BP+ 5,000 to 39,000 BP + 3,000, which makes Pešturina one of the latest surviving Neanderthal habitats. The cave has been nicknamed the "Serbian Atapuerca".

The Uluzzian Culture is a transitional archaeological culture between the Middle Paleolithic and the Upper Paleolithic, found in Italy and Greece.

Fumane Cave is a dolomite cave in the Fumane Valley, which was formed in the Neogene period. The cave contains rich evidence of three prehistoric hominid cultures: Mousterian, Uluzzian and Aurignacian. Additionally, the cave has some of the oldest cave art that has been discovered in Europe.

Balanica is a cave complex and paleoarchaeological site in the City of Niš' municipality of Niška Banja in southeast Serbia. It consists of Velika Balanica and Mala Balanica. The entrances of two caves are 7 m (23 ft) apart, at an elevation of 329 m (1,079 ft), and form one cave system. A third cave, Pešturina, is also nearby. The two Balanica caves extend parallel to each other, likely being connected at the rear.

The Paleolithic in the Iberian peninsula is the longest period of Iberian prehistory, spanning from c. 1.3 million years ago (Ma) to c. 11,500 years ago, ending at roughly the same time as the Pleistocene epoch. The Paleolithic was characterized by climate oscillations between ice ages and small interglacials, producing heavy changes in Iberia's orography. Cultural change within the period is usually described in terms of lithic industry evolution.





















