The National Severe Storms Laboratory (NSSL) is a National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) weather research laboratory under the Office of Oceanic and Atmospheric Research. It is one of seven NOAA Research Laboratories (RLs).
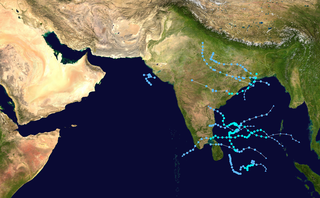
The 2005 North Indian Ocean cyclone season caused much devastation and many deaths in Southern India despite the storms’ weakness. The basin covers the Indian Ocean north of the equator as well as inland areas, sub-divided by the Arabian Sea and the Bay of Bengal. Although the season began early with two systems in January, the bulk of activity was confined from September to December. The official India Meteorological Department tracked 12 depressions in the basin, and the unofficial Joint Typhoon Warning Center (JTWC) monitored two additional storms. Three systems intensified into a cyclonic storm, which have sustained winds of at least 63 km/h (39 mph), at which point the IMD named them.

The Philippine Atmospheric, Geophysical and Astronomical Services Administration is the National Meteorological and Hydrological Services (NMHS) agency of the Philippines mandated to provide protection against natural calamities and to ensure the safety, well-being and economic security of all the people, and for the promotion of national progress by undertaking scientific and technological services in meteorology, hydrology, climatology, astronomy and other geophysical sciences. Created on December 8, 1972, by reorganizing the Weather Bureau, PAGASA now serves as one of the Scientific and Technological Services Institutes of the Department of Science and Technology.

Tropical cyclone observation has been carried out over the past couple of centuries in various ways. The passage of typhoons, hurricanes, as well as other tropical cyclones have been detected by word of mouth from sailors recently coming to port or by radio transmissions from ships at sea, from sediment deposits in near shore estuaries, to the wiping out of cities near the coastline. Since World War II, advances in technology have included using planes to survey the ocean basins, satellites to monitor the world's oceans from outer space using a variety of methods, radars to monitor their progress near the coastline, and recently the introduction of unmanned aerial vehicles to penetrate storms. Recent studies have concentrated on studying hurricane impacts lying within rocks or near shore lake sediments, which are branches of a new field known as paleotempestology. This article details the various methods employed in the creation of the hurricane database, as well as reconstructions necessary for reanalysis of past storms used in projects such as the Atlantic hurricane reanalysis.

The radius of maximum wind (RMW) is the distance between the center of a cyclone and its band of strongest winds. It is a parameter in atmospheric dynamics and tropical cyclone forecasting. The highest rainfall rates occur near the RMW of tropical cyclones. The extent of a cyclone's storm surge and its maximum potential intensity can be determined using the RMW. As maximum sustained winds increase, the RMW decreases. Recently, RMW has been used in descriptions of tornadoes. When designing buildings to prevent against failure from atmospheric pressure change, RMW can be used in the calculations.

The 2008 North Indian cyclone season was one of the most disastrous tropical cyclone seasons in modern history, causing more than 140,000 fatalities and over US$15 billion in damage. At the time, it was the costliest season in the North Indian Ocean, until it was surpassed by 2020. The season has no official bounds but cyclones tend to form between April and December. These dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in the northern Indian Ocean. There are two main seas in the North Indian Ocean—the Bay of Bengal, which is east of India, and the Arabian Sea, which is west of India. The official Regional Specialized Meteorological Centre in this basin is the India Meteorological Department (IMD), however the Joint Typhoon Warning Center releases unofficial advisories for military interests. An average of four to six storms form in the North Indian Ocean every season. Cyclones occurring between the meridians 45°E and 100°E are included in the season by the IMD.

The 2000 North Indian Ocean cyclone season was fairly quiet compared to its predecessor, with all of the activity originating in the Bay of Bengal. The basin comprises the Indian Ocean north of the equator, with warnings issued by the India Meteorological Department (IMD) in New Delhi. There were six depressions throughout the year, of which five intensified into cyclonic storms – tropical cyclones with winds of 65 mph (105 km/h) sustained over 3 minutes. Two of the storms strengthened into a Very Severe Cyclonic Storm, which has winds of at least 120 km/h (75 mph), equivalent to a minimal hurricane. The Joint Typhoon Warning Center (JTWC) also tracked storms in the basin on an unofficial basis, estimating winds sustained over 1 minute.
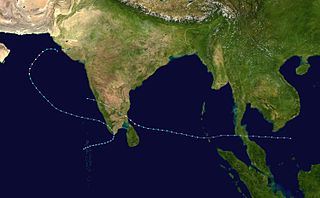
The 1993 North Indian Ocean cyclone season was the least active on record in the basin, with only four tropical disturbances. There are two main seas in the North Indian Ocean – the Bay of Bengal to the east of the Indian subcontinent and the Arabian Sea to the west. The India Meteorological Department (IMD) issued advisories for the systems in its official capacity as the local Regional Specialized Meteorological Center, while the Joint Typhoon Warning Center also issued advisories for two of the storms on an unofficial basis. Of the five disturbances tracked by the IMD, two intensified into cyclonic storms.

Cyclonic Storm Nisha was a fairly weak but catastrophic tropical cyclone that struck Sri Lanka, and India which killed over 200. It was the ninth tropical cyclone of the 2008 North Indian Ocean cyclone season, and the seventh tropical cyclone in the Bay of Bengal that year.

Severe Tropical Cyclone Olivia was a powerful cyclone, the 13th named storm of the 1995–96 Australian region cyclone season, which formed on 3 April 1996 to the north of Australia's Northern Territory. The storm moved generally to the southwest, gradually intensifying off Western Australia. On 8 April, Olivia intensified into a severe tropical cyclone and subsequently turned more to the south, steered by a passing trough. On the morning of 10 April, passing over Barrow Island off the Western Australian northwest coast, Olivia produced the strongest non-tornadic winds ever recorded, with peak gusts of 408 kilometres per hour (254 mph). On the same day the cyclone made landfall on the Pilbara coast, about 75 kilometres (47 mi) north-northwest of Pannawonica. The storm quickly weakened over land, dissipating over the Great Australian Bight on 12 April.

India is a country in the north of Indian Ocean that is the most vulnerable to getting hit by tropical cyclones in the basin, from the east or from the west. On average, 2–3 tropical cyclones make landfall in India each year, with about one being a severe tropical cyclone or greater.

Regional Meteorological Centre, Chennai is one of the six regional meteorological centres (RMCs) of the India Meteorological Department (IMD) and is responsible for the weather-related activities of the southern Indian peninsula comprising the states of Andhra Pradesh, Telangana, Karnataka, Kerala, Tamil Nadu and the union territories of Andaman and Nicobar, Lakshadweep Islands and Puducherry. The other regional centres are located at Kolkata, Guwahati, Mumbai, Nagpur and New Delhi.

The 2002 West Bengal cyclone was a deadly tropical cyclone that affected India and Bangladesh in November 2002. The sixth tropical cyclone and fourth cyclonic storm of the 2002 North Indian Ocean cyclone season, it developed in the Bay of Bengal northeast of Sri Lanka on November 10, as a tropical depression. After tracking northeast, the system strengthened into a cyclonic storm on November 11, as maximum sustained winds exceeded 65 km/h (40 mph). On November 12, it further intensified into a severe cyclonic storm. Later that day, the storm made landfall on Sagar Island in West Bengal with winds of 100 km/h (60 mph). After moving inland, it rapidly weakened and dissipated over Bangladesh on November 12.

The 2013 North Indian Ocean cyclone season was an event in the annual cycle of tropical cyclone formation, in which tropical cyclones formed in the North Indian Ocean and Arabian Sea. The season had no official bounds, but cyclones typically formed between May and December, with the peak from October to November. These dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in the northern Indian Ocean.

The Climate of Tamil Nadu, India is generally tropical and features fairly hot temperatures over the year except during the monsoon seasons. The city of Chennai lies on the thermal equator, which means Chennai and Tamil Nadu does not have that much temperature variation.

Cyclonic Storm Nilam was the deadliest tropical cyclone to directly affect South India since Cyclone Jal in 2010. Originating from an area of low pressure over the Bay of Bengal on October 28, 2012, the system began as a weak depression 550 km (340 mi) northeast of Trincomalee, Sri Lanka. Over the following few days, the depression gradually intensified into a deep depression, and subsequently a cyclonic storm by October 30. It made landfall near Mahabalipuram on October 31 as a strong cyclonic storm with peak winds of 85 km/h (55 mph). In Chennai's Marina Beach, strong winds pushed piles of sand ashore and seawater reached nearly a 100 m (330 ft) inland. Schools and colleges in the city remained closed for more than three days.

The 2016 North Indian Ocean cyclone season was an event in the annual cycle of tropical cyclone formation. It was the deadliest season since 2010, killing more than 400 people. The season was an average one, seeing four named storms, with one further intensifying into a very severe cyclonic storm. The first named storm, Roanu, developed on 19 May while the season's last named storm, Vardah, dissipated on 18 December. The North Indian Ocean cyclone season has no official bounds, but cyclones tend to form between April and December, with the two peaks in May and November. These dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in the northern Indian Ocean.

The 2017 North Indian Ocean cyclone season was a below average yet deadly season in the annual cycle of tropical cyclone formation. This season produced only three named storms, of which one only intensified into a very severe cyclonic storm. The North Indian Ocean cyclone season has no official bounds but cyclones tend to form between April and December with the two peaks in May and November. These dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in the northern Indian Ocean. The season began with the formation Cyclone Maarutha on April 15 and ended with the dissipation of a deep depression on December 9.

Very Severe Cyclonic Storm Vardah was the fourth cyclonic storm, as well as the most intense tropical cyclone of the 2016 North Indian Ocean cyclone season. The remnants of the system later regenerated into Depression ARB 02 in the Arabian Sea. The system struck the Andaman and Nicobar Islands, as well as South India, before later affecting Somalia.
The 2021 South India floods are a series of floods associated with Depression BOB 05 and a low pressure system that caused widespread disruption across the Indian states of Tamil Nadu, Andhra Pradesh, and the nearby Sri Lanka. The rainfall started on 1 November in Tamil Nadu. The flooding was caused by extremely heavy downpours from BOB 05, killing at least 41 people across India and Sri Lanka.



















